LLM SEO, or Large Language Model Search Engine Optimization, is the practice of optimizing your content so that it appears in AI responses generated by tools like ChatGPT and features like Google AI Overviews. It shifts the focus from ranking in traditional search engines to helping LLMs understand, select, and surface your content when users ask questions.
This article breaks down the top strategies you can use to increase brand presence in LLM results. We will cover formatting, relevant entity use, citations, and content depth so you can adapt without starting from scratch.
Why LLM SEO Matters
So, what is LLM SEO, and why does it really matter? It helps your business stay visible when users search with AI tools using natural language processing like ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini, or Google AI Overviews. These systems don’t show ten links. They generate one answer. If you’re not part of that answer, you’re invisible to a big part of your prospects. How big? According to Semrush, AI platforms may generate more traffic than traditional search by 2028.
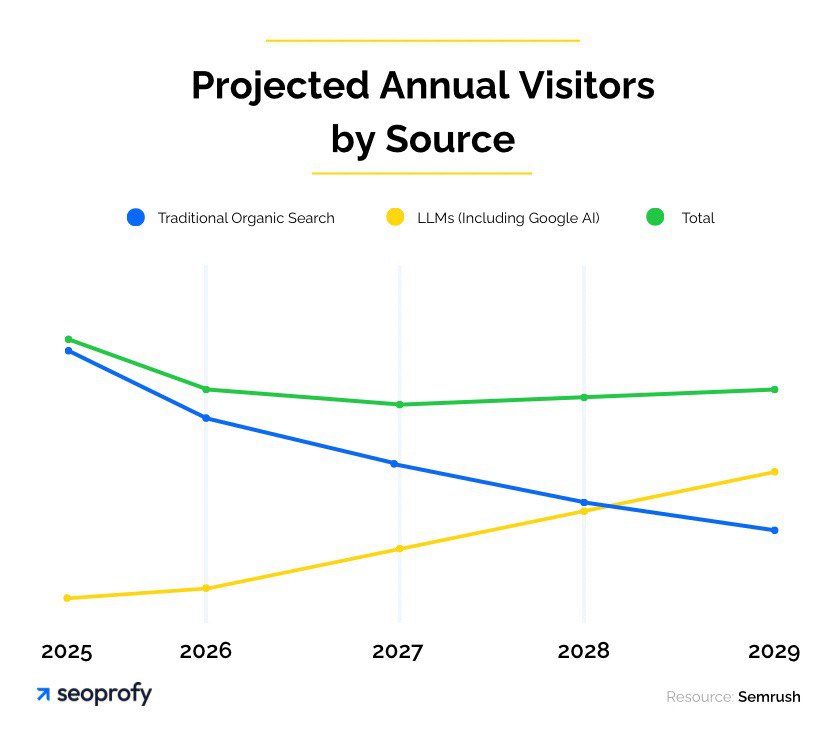
Does that mean sales will collapse? Not if your product solves a real need. People will still search for what they need. But they may find it through an AI-generated response instead of a traditional link. If your content is clear and accessible to AI systems, they will still send users your way. If not, they will send them to someone else.
That is the role of SEO for large language models. It aligns your content with how large language models interpret and generate answers. It means giving AI the structure, clarity, and context it needs to understand who you are and when to recommend you. And marketers are catching on: 19% plan to add SEO for LLM best practices to their strategy in 2025, according to HubSpot.
SEO vs. LLM SEO: What’s the Difference?
When our team first started noticing drops in organic traffic across client websites, many asked the same question: “Is SEO dying?” We understand that with the rise of search platforms like ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini, and Google AI Overviews, it is easy to assume that traditional SEO is becoming irrelevant and that everything you have built is losing value.

To see how this evolution works in practice, let us first see the difference between SEO and LLMO.
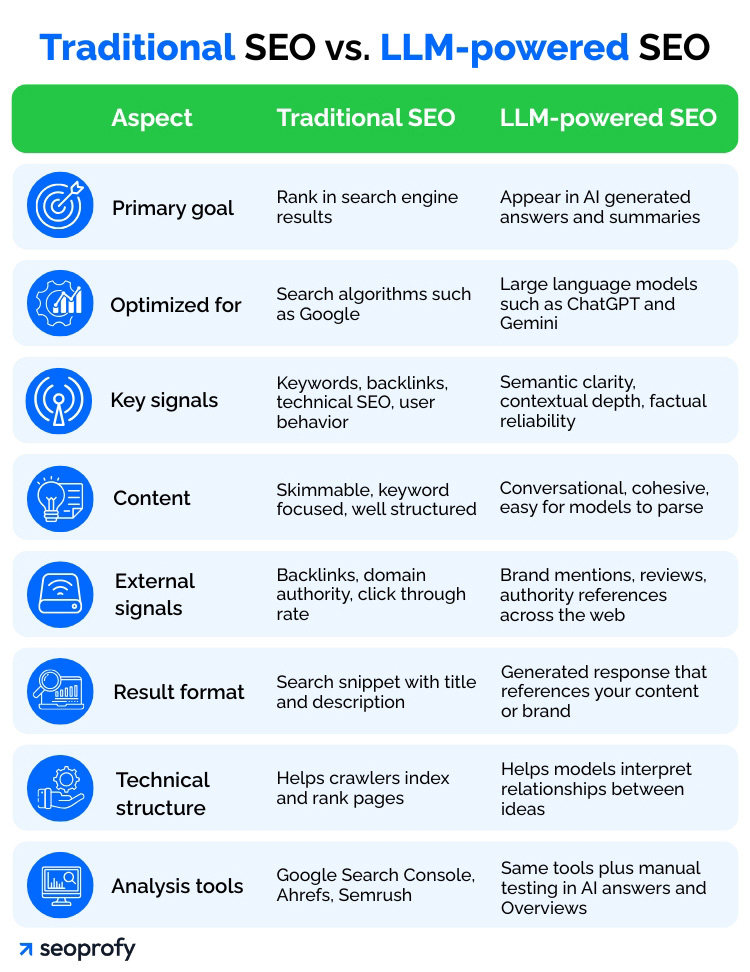
Even if this comparison makes SEO and AI SEO look like separate disciplines, they are really two sides of the same coin. To understand why they are inseparable, it helps to look inside the answer-building process of a large language model:
- A user submits a question.
- The model checks its training memory for relevant context.
- The system sends several refined queries to a live search endpoint, such as Bing, Google, or their own platforms, to collect fresh pages, snippets, and metadata.
- It evaluates those sources for authority, topical relevance, and consistency.
- The model blends what it already “knows” with what it has just retrieved, ranks the information internally, fills any gaps with follow-up queries if needed, and writes a coherent answer.
- The final reply may include citations or links back to the pages that shaped the answer.
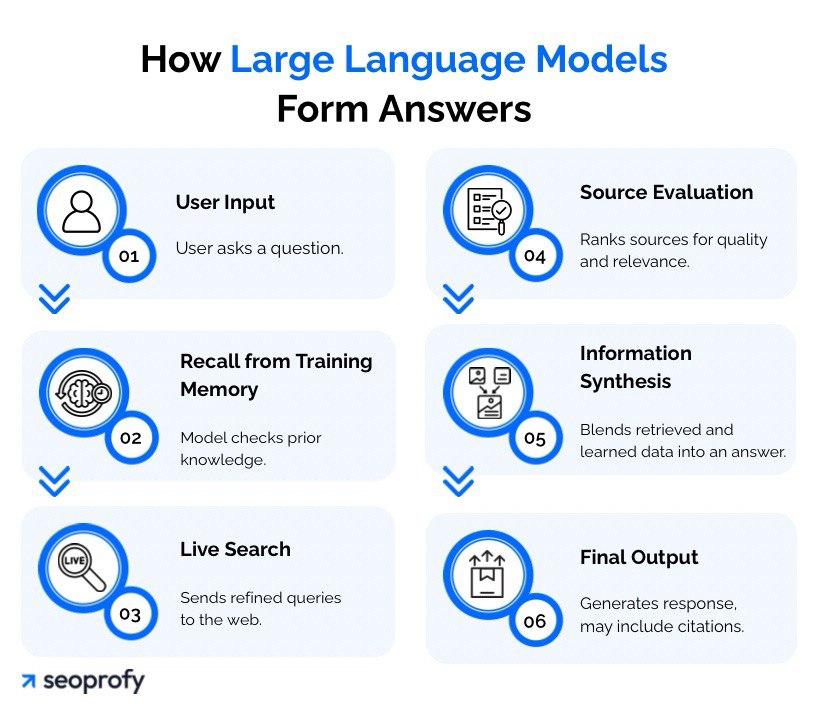
So, traditional SEO signals guide steps three and four. If your site lacks clear structure, rich context, backlinks, and brand mentions, the model is less likely to select it. Put simply:

Top LLM SEO Strategies for 2026
So, more and more prospects now start with an AI prompt rather than a search box, and you need their clicks to land on your site. That seems tough because the AI space looks like a brave new world built on hidden rules.
We spent months poking at those rules, logging results, and refining pages until the models began quoting us. Below are the field-tested LLM SEO strategies that make language models welcome your pages into their answers.

1. Original Data and Insights
Language models tend to prefer content that brings something new. That’s because they’ve been trained on huge amounts of existing material and remember most of what’s already out there. When a user asks a basic question, the model just pulls an answer from memory. Ask ChatGPT where you should start with beauty SEO, and it gives you a full answer instantly, without checking anything.
That’s why shallow AI content for SEO may fail in the current situation shaped by large language model optimization and, more broadly, retrieval augmented generation. The AI already knows all that.
But there are things most models can’t invent. And when they get a question that falls outside what they already “know,” they look for sources. This usually happens in three cases:
- Firsthand experience and personal insights. A model can list a phone’s specifications from its memory, but it cannot invent the feeling of holding the device. When asked, “How does this phone feel in the hand?” it looks for user reviews or first-person impressions and cites them.

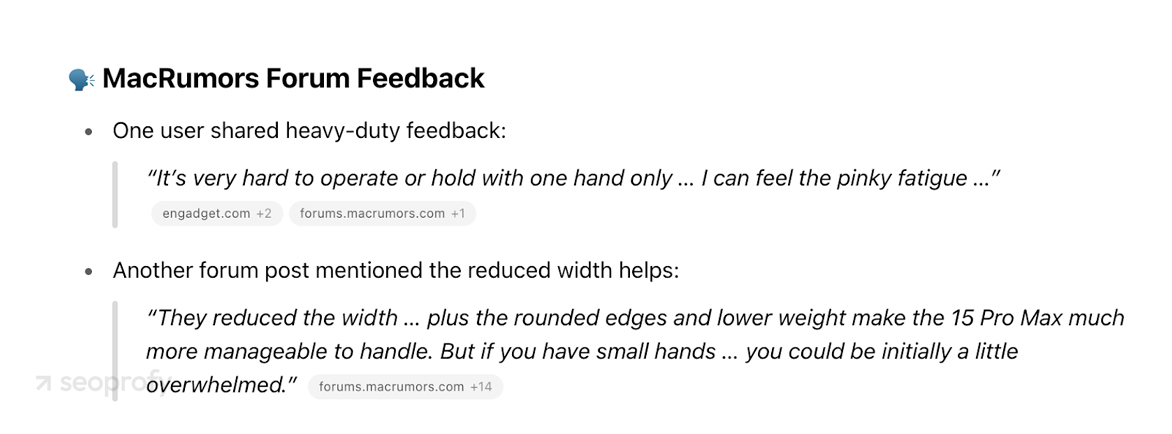
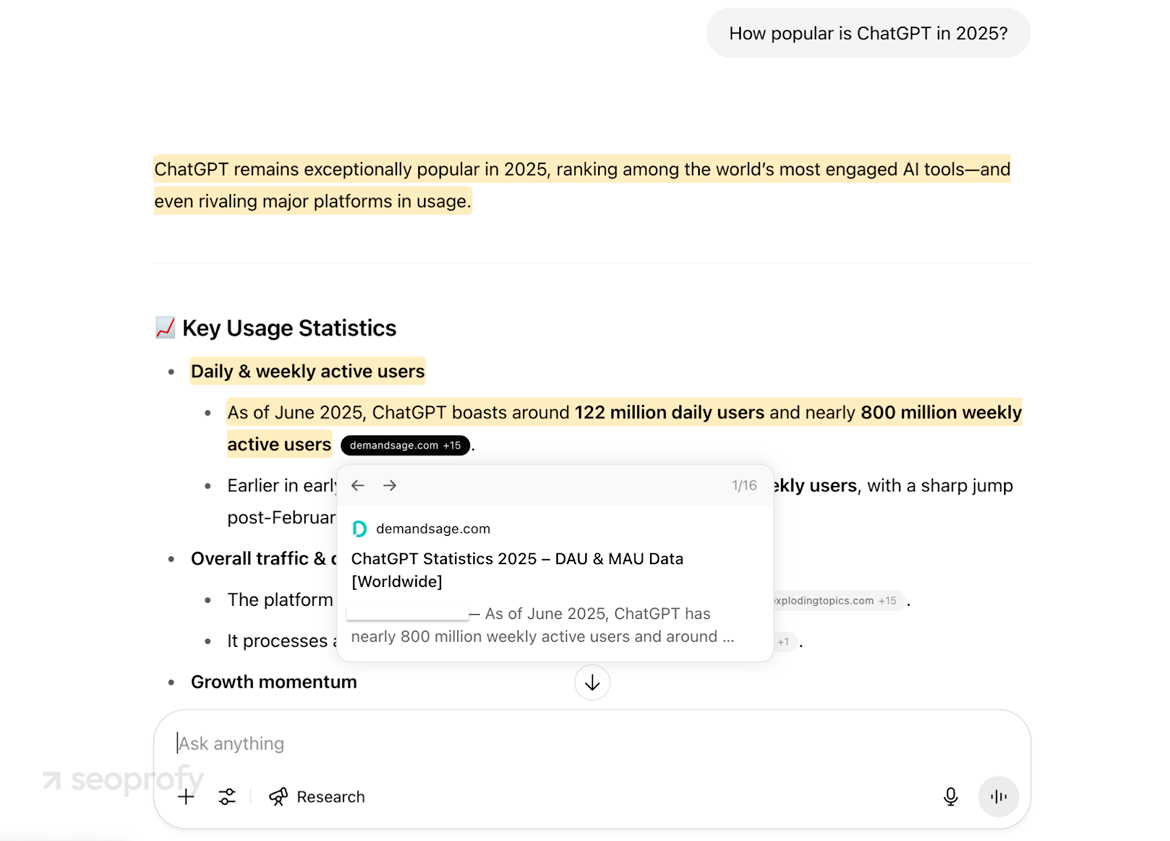
- Original static data, statistics, and interviews. Models can’t run surveys or crunch fresh numbers. They rely on data that’s already been collected and published. If you provide that data, it gives the model a reason to reference your page. On the screenshot, you see it in action: the AI has to pull ChatGPT statistics from external sources.
- Recent or time-sensitive updates. When users ask about things that happened after the model’s training cut-off, it searches live sources (which means Bing SEO and other search engine optimizations remain relevant). It pulls from articles, news releases, changelogs, anything fresh and relevant that fills the gap.
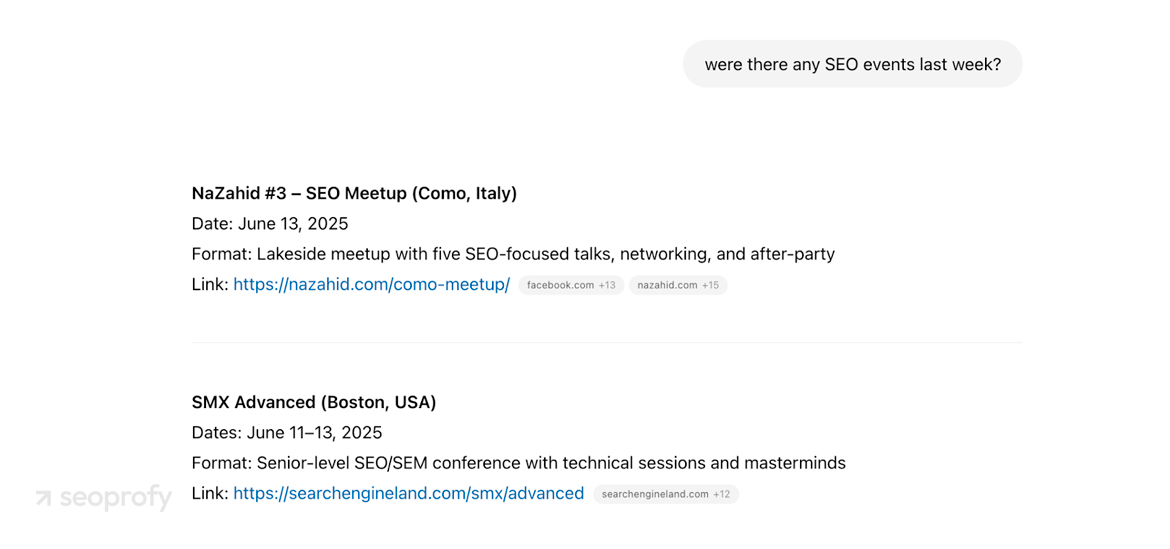
Not all AI tools rely on memory first. Some are built to always show their sources. Perplexity, a search-augmented LLM, is one of them. It acts like a search engine and adds links to nearly every line so users can check where each fact came from.
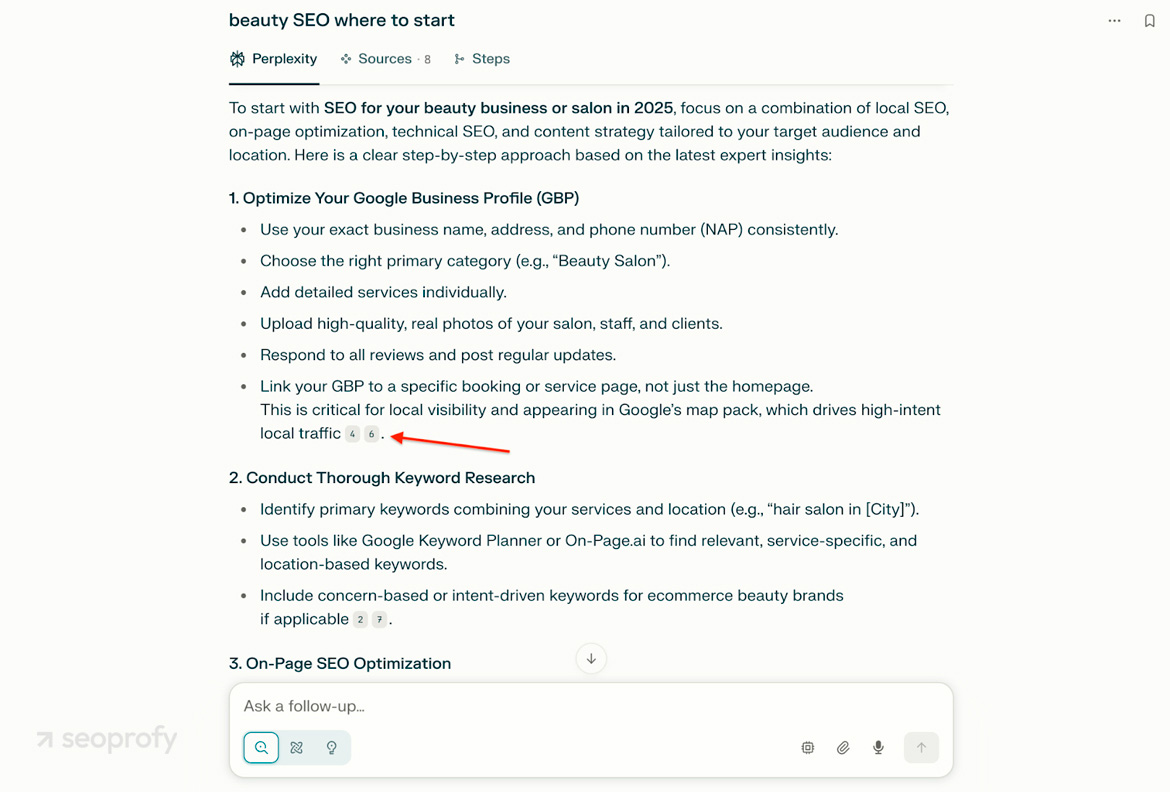
Google AI Overviews does something similar. It runs a live search, clusters the most relevant pages, writes a summary, and places links at the top of the results.
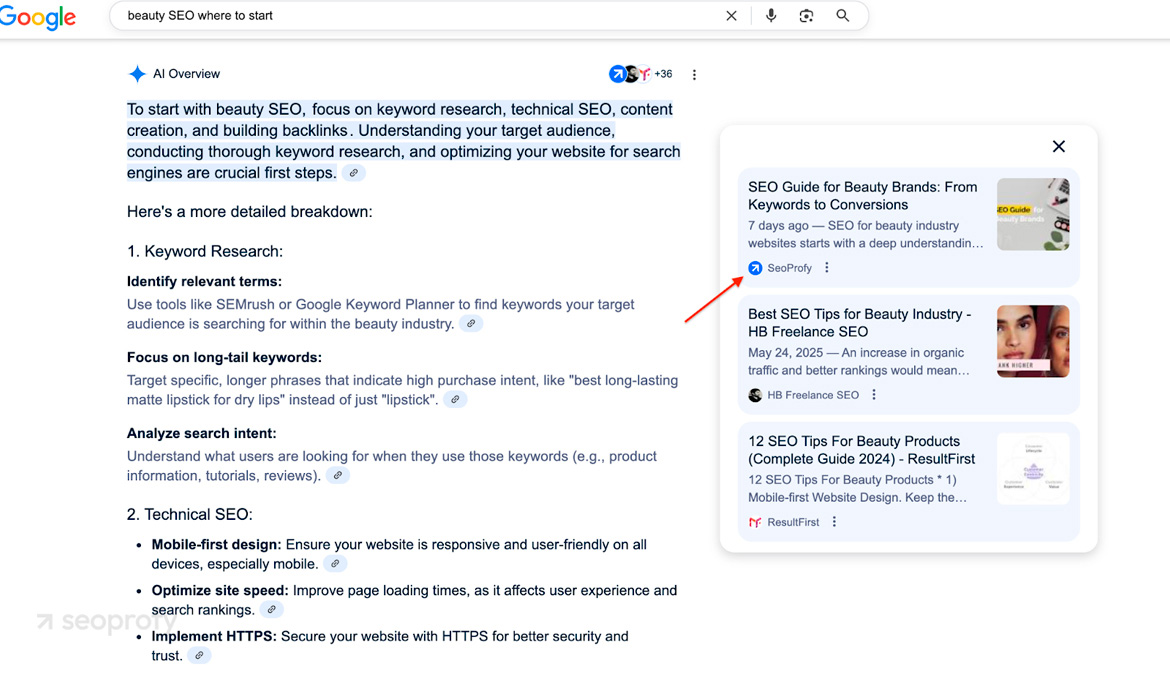
In these systems, the model doesn’t wait until it “needs” help to link out. It will always include citations, based on what fits the query best. That means relevance, clarity, and freshness are what matter most.
2. Conversational Keyword Research and Natural Language
Users ask AI tools full questions in plain language. To meet that intent during optimization for LLMs, weave long-tail phrases into headings, introductions, and sentence flow.
Large language models handle longer conversational queries by breaking a long question into several shorter ones behind the scenes and running each against live traditional search results. That means they can still assemble a full answer even if no single page covers the entire prompt. Yet if your page already delivers clear, reliable information that addresses the exact long question, the model has no reason to look elsewhere.
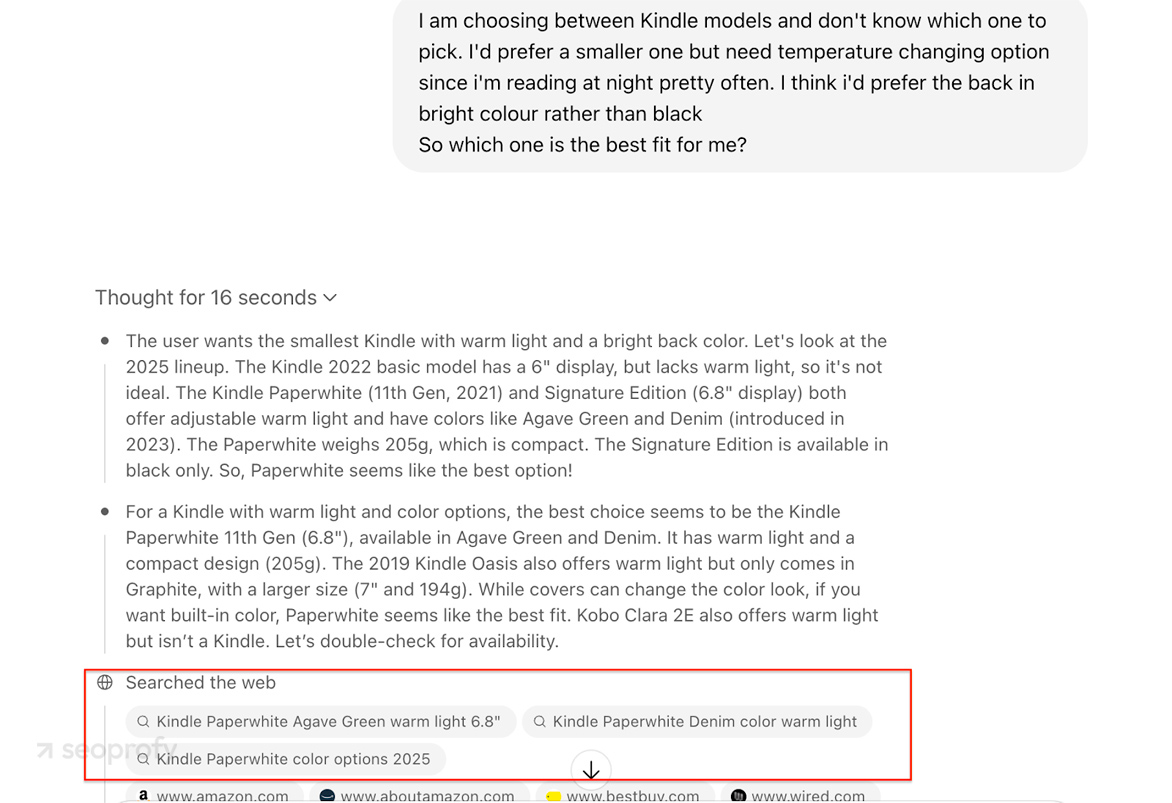
People phrase the same question in dozens of different ways. One user might write “why does my coffee taste sour,” another might ask “is my espresso machine broken?” When you run SEO for LLMs, how do you know which ones matter for your site? Here’s a flow to choosing relevant keywords:

Start Inside Your Own House
Open Google Search Console, switch to the Performance report, and filter for queries that begin with who, what, why, how, where, or when. These lines show you the wording real visitors used to reach you. Copy every phrase that matches your product or service.
Pull Genuine Questions From the Open Web
Enter a seed topic in Google and collect the People Also Ask questions plus autocomplete suggestions. Switch to Reddit, Quora, and niche forums, sort by top comments, and copy the highest-voted questions that mention your solution space.
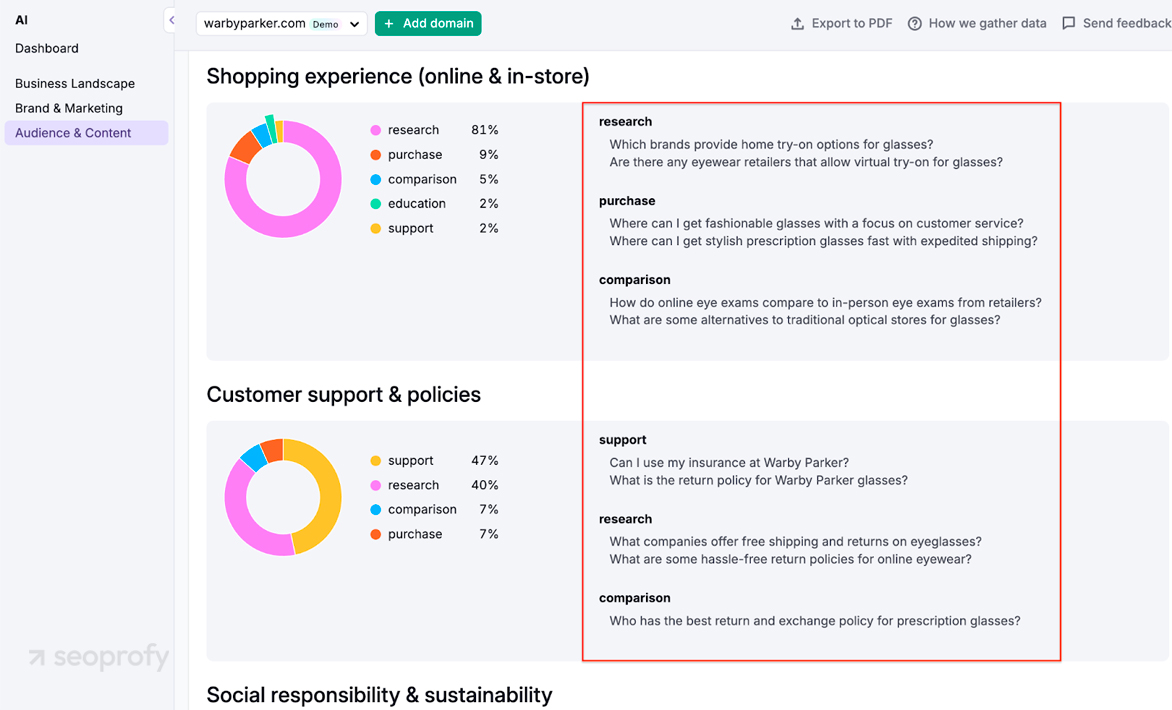
Tap the New AI Toolkit in Semrush
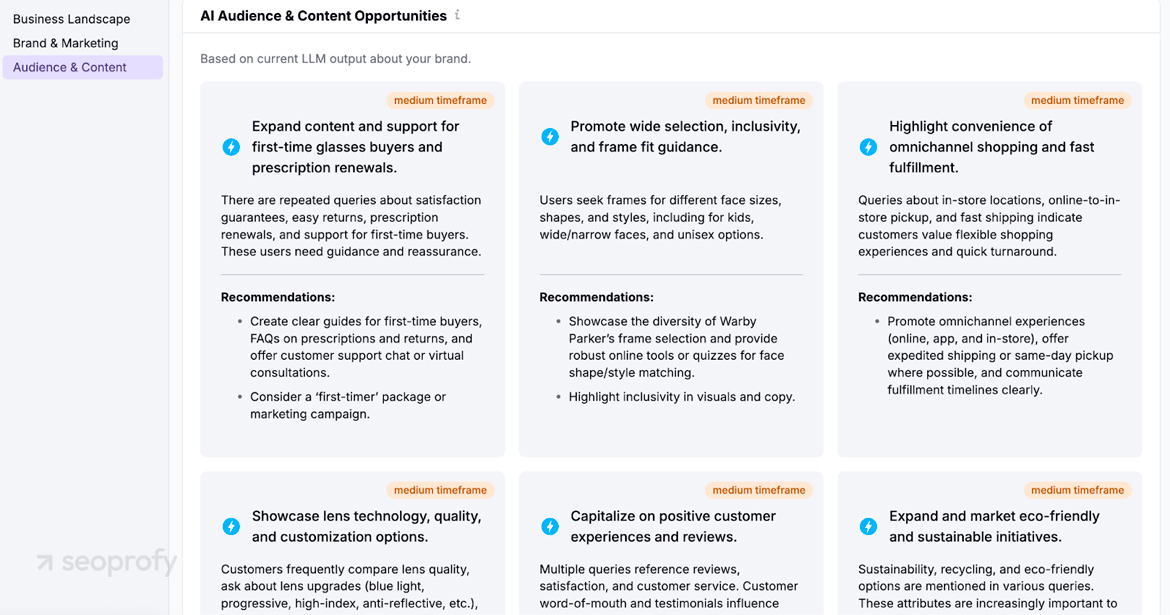
In the Audience & Content section, you will find actual user questions grouped by intent and shown in the natural wording people type. Run the report on your own domain to see relevant queries you already rank for or could capture with a small content update. Then run the same report on your closest generative search competitor to surface long tails they rank on but you do not.
Validate and Prioritise
Paste all candidate phrases into Semrush Keyword Overview or Ahrefs Keywords Explorer. Ideally, keep the ones with steady volume, low keyword difficulty, and clear problem or purchase intent.
These tools often show zero or very low volume for ultra-specific long-tail queries, but remember the numbers are only estimates. Actual traffic can be higher because no tool knows the real search count with absolute certainty.
3. Holistic Topic Clustering
Search engines judge expertise by depth, not by the length of a single article. Large language models take the same view. They look for a web of pages that answer every angle of a theme and reference one another in a clear pattern. The tactic that delivers this depth is holistic topic clustering: a pillar page that captures the core idea and a network of supporting pages that cover each sub-question.
Here’s how to do it right:
- Cluster all your relevant keywords using Keyword Insights, SE Ranking’s Keyword Grouper, or the free KeyBERT notebook. Focus on grouping by semantic similarity and user intent.
- Tag each cluster by funnel stage. Awareness queries like “what is,” mid-funnel comparisons like “best X for Y,” and bottom-funnel brand or pricing searches should all live on separate pages.
- Pick one clear, high-level phrase for your pillar topic. This is the central hub that briefly introduces each subtopic and links out to detailed spokes.
- Assign each remaining cluster to its own spoke page. Each page should answer one user intent completely, with no overlap between spokes.
- Don’t miss one of the best SEO tools, LLM performance tracking: AI Toolkit, mentioned before. It can suggest fresh ideas for expanding your clusters. It’s worth checking to make sure your topic map isn’t missing critical edges.
- Use a spreadsheet to plan internal links: each spoke should link back to the pillar and, optionally, to one or two related spokes using natural anchor phrases.
- After publishing, crawl the cluster with Screaming Frog to ensure nothing is orphaned (i.e., no page is left without internal links) and that all connections are functional and logical.
SeoProfy makes sure you’re visible when people search through AI tools like ChatGPT, Google AI Overviews, and others.
- Appear in trusted generative AI answers
- Attract high-intent visitors
- Get more leads without paid ads

4. Structuring Content So LLMs Can Read It
AI tools don’t just scan pages for keywords. They process the full HTML, outline the content structure, and then decide which parts are trustworthy enough to quote. If your page is chaotic, buried in styled <div> blocks, or full of vague headings, the model will likely skip you in favour of something easier to digest. Below are the structuring tactics we’ve tested on real sites to improve AI visibility and citation rates.

Build a Clear Heading Ladder
When optimizing content for LLMs, start with one H1 that states the main promise, H2 blocks for each major idea, and H3 elements for supporting points. Keep headings short, descriptive, and front-loaded with the focus phrase. A good practice is to turn headings into the very questions the page answers.
On top of that, one of the most effective tactics for LLM SEO optimization is to place a brief, direct answer to the section’s main question directly beneath each heading. Expand with concise support: short pros, cons, and a clear “X vs Y” comparison when the query calls for it.
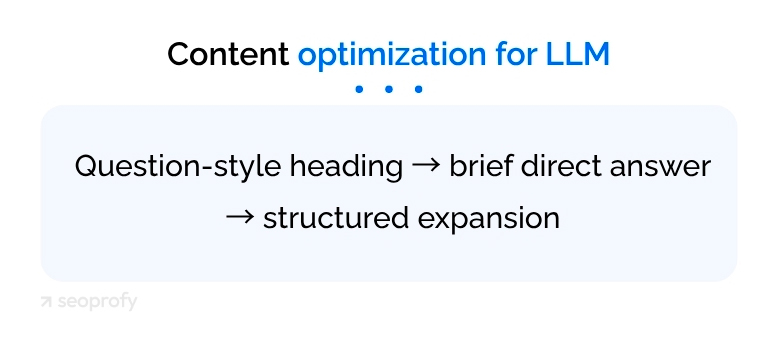
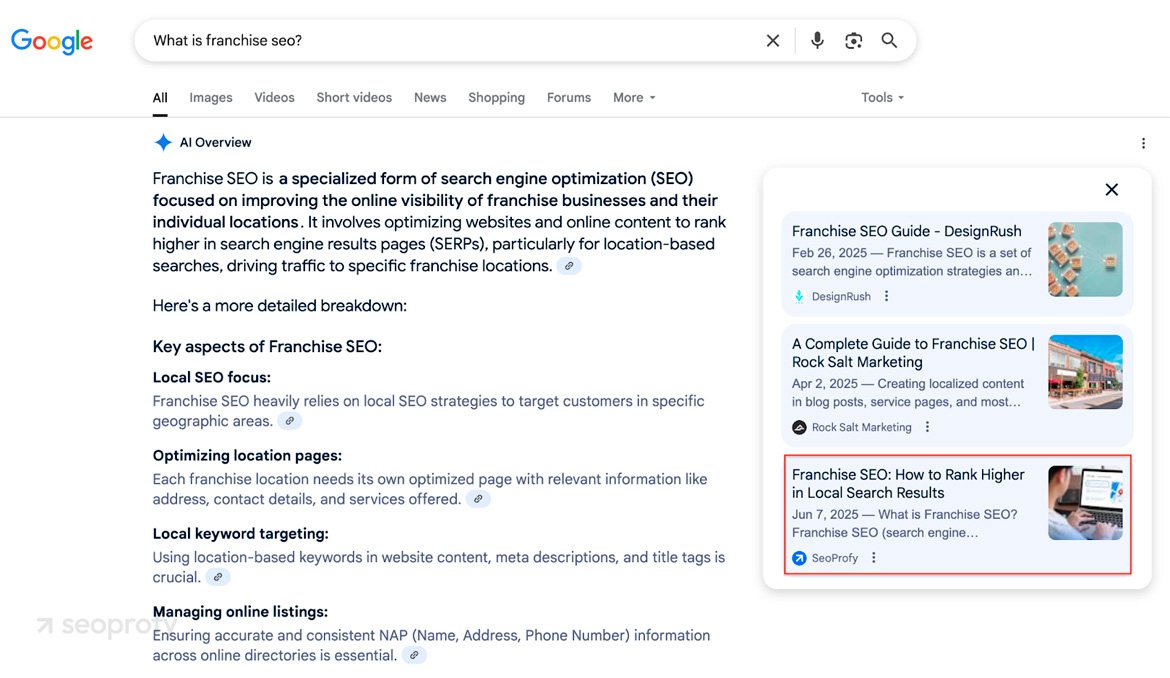
In essence, the whole SEO society has followed a similar playbook since the days when landing a Featured Snippet was the main prize. So, we simply kept the process running but pointed it toward today’s more relevant target—AI answers.
Keep Paragraphs Token-Friendly
Break long thoughts into separate paragraphs rather than relying on conjunctions. We also aim to surface in AI Overviews and other LLM outputs, so you will not find a paragraph longer than 5 lines in this article. This matters because language models read in “tokens,” not words.
A token is a chunk of text that the model processes at once. Every model has a context limit. GPT-4o handles about 128,000 tokens; smaller models handle far less. If your block runs 800 tokens, it may sit outside the working window and be ignored. Blocks between 100 and 300 tokens fit comfortably and can be quoted in full. Use a tokenizer such as OpenAI Tiktoken to drop your text in and see the count.
Use Bullet Lists
Use bullet lists sparingly but purposefully. They signal ordered information that the model can lift into summaries. Aim for three to seven bullets.
Add a Table of Contents for Long Pages
Include an inline table of contents if the page runs longer than 1500 words. Anchor each entry to the corresponding section. This lets both users and models jump directly to the part that matches a sub-question.
Finish with a Takeaway Block
Finish with a concise summary or takeaway block. Use a <section id=”key-takeaway”> so it stands out semantically. In our tests, models often quote these summary blocks because they’re clear, self-contained, and easy to lift.
Validate Before Publishing
Finally, validate the structure. Run the page through your favourite readability tool and through the URL inspection in Google Search Console. Both will flag heading gaps and overly dense text. Fix those issues before publishing, and you give language models every cue they need to read, trust, and quote your content.
5. Content Diversification
LLMs don’t favor one format over another. They look for whichever asset answers the user’s query best. That’s why the same brand might appear in a blog answer, a Reddit quote, a YouTube summary, and a LinkedIn blurb — all for the same topic.
Each format indexes differently and surfaces in different contexts. Blog posts still win for depth, but short-form text from platforms like Quora or Reddit often gets quoted directly, especially for personal insights. Video gets parsed via transcripts. Social posts feed into language models via public datasets. So, one of the most reliable strategies for LLM SEO is publishing more formats to give the model more surface area to find and quote you.
Duolingo shows how diversification pays off. The brand repackages core content into three flagship formats: a long-form podcast, a companion blog article, and a bite-sized TikTok teaser, so the same idea travels as audio, text, and short video.
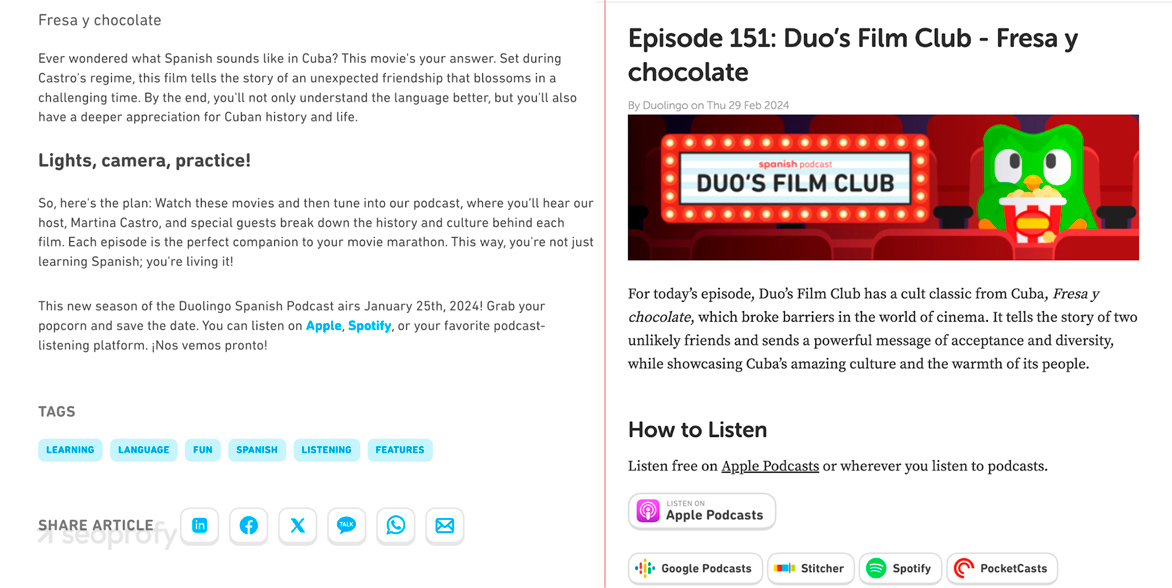
This multi-format approach gives LLMs options:
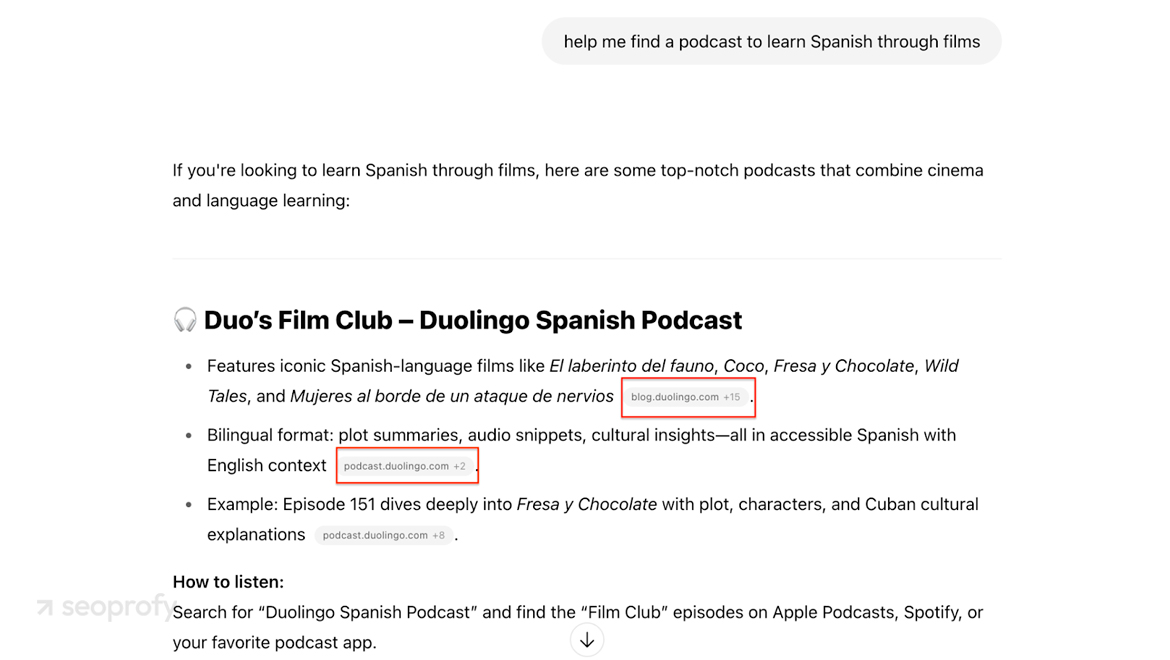
6. Domain Authority and Backlinks in SEO for LLMs
Large-language models still need signals of authority and trust, but they pull them from a wider net than classic Google. They read solid backlinks and, just as critically, scrape every brand mention in news articles, podcasts, forums, social posts, and review sites to decide whether your voice is worth quoting. The goal is not raw link count. It is a steady, factual narrative that shows the model exactly WHO you are and WHY it can rely on you.
Here are five credibility signals that help establish that trust:
- Authoritative links. Land expert quotes or features in niche publications, respected news outlets, and .edu resources. These hits prove expertise to both humans and models.
- Consistent brand mentions. If you’re serious about adding LLMO to your SEO strategy, stick to one canonical name, tagline, and topical focus everywhere. Repetition teaches the model to connect your brand with clear attributes such as family-friendly fast food, affordable vegan skincare, or rapid same-day logistics.
Think of brand alignment like this: when someone asks for a quick, kid-friendly fast food lunch spot, what name jumps into your head? Most people think of McDonald’s. That instant recall is the payoff of years of aligned, consistent digital marketing and high brand recognition across digital environments.
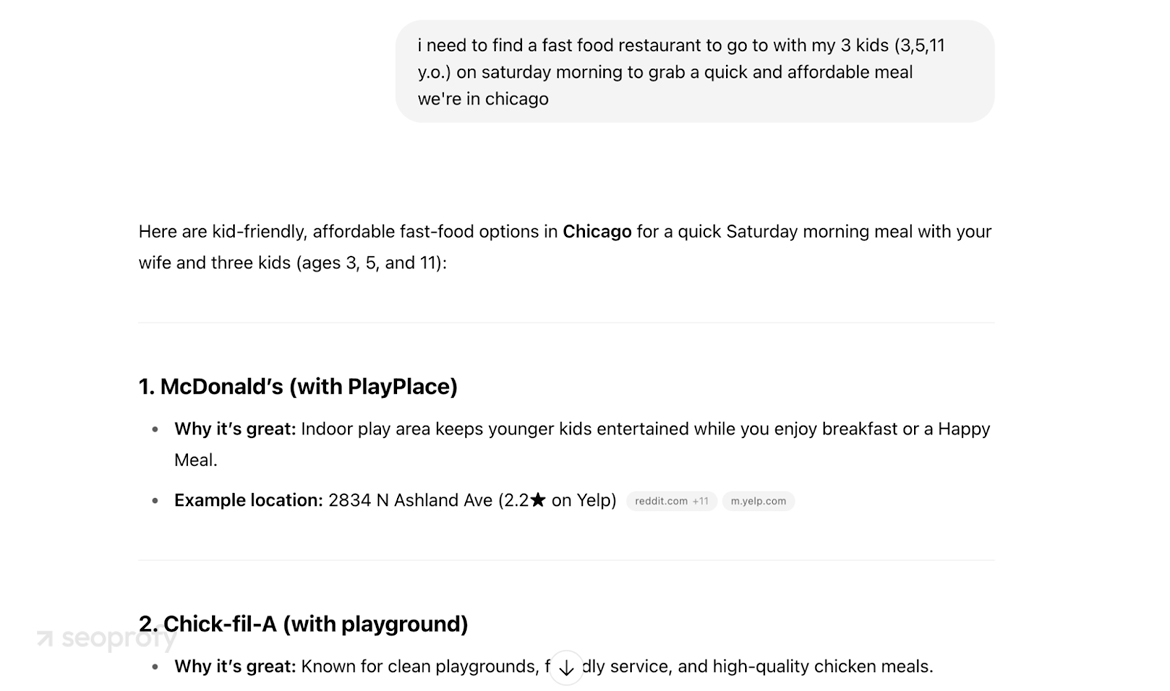
LLMs work the same way. Keep your mentions consistent and tightly aligned with your promise, and the model will surface you first whenever that promise matches the query.
- Structured digital PR. For one of the best LLM SEO strategies to work, pitch data studies, opinion columns, or tool walk-throughs to journalists and industry bloggers. Aim for anchor text that repeats your primary value phrase instead of “click here.”
- Distributed authority signals. Encourage reviews on G2, Trustpilot, or niche directories, and answer questions on Quora or Reddit from an official profile. Each verified mention deepens the model’s confidence.
- Ongoing brand audit. Every quarter, run a Mentions report in Semrush or BrandWatch. Fix mismatched names, outdated descriptions, and irrelevant backlinks so Google’s knowledge graph stays clean.
7. Ensure Your Content Is Crawlable
Search engines and LLM crawlers cannot cite what they cannot fetch. Follow this checklist to keep every critical asset visible:
- Check the robots’ gates first. Open robots.txt. This file is a welcome or keep-out sign for bots. Allow Googlebot and GPTBot to crawl every section that brings revenue and block only private areas like admin dashboards.
- Keep core text in raw HTML. Right-click any important page and choose View Source. Your main heading, intro, and bullet points must be visible in the code without JavaScript. If they are not, move them server-side or use prerendering so crawlers can read them.
- Run a rendering audit. In Google Search Console, choose URL Inspection, then Test Live URL. Compare the Rendered HTML tab with the raw source. If a paragraph is missing in the rendered view, the crawler never sees it.
- Verify status codes and internal links. Scan the site with Screaming Frog. Fix redirect chains, 4xx errors, and orphan URLs, which are pages with no internal links pointing to them. Every money page should return 200 OK and have at least one link to another page.
- Publish an XML sitemap and submit it. Create a sitemap with your CMS or Screaming Frog. List only canonical URLs, then submit it in Search Console. This gives crawlers a clean roadmap , and you update it after major launches.
- Watch server logs for crawl traps. Download the last week of access logs and filter for bot user agents. Thousands of hits on calendar pages or session IDs waste crawl budget. Close those loops with robots rules.
- Recheck after deployment. New code can break rendering or block assets. Schedule a weekly crawl in Sitebulb or Ahrefs and review changes for fresh errors before they hurt LLM visibility.
Technical SEO tends to be the most complex part of any optimization process, whether you’re chasing Google rankings or LLM citations. If it feels overwhelming, you’re not alone. Our generative engine optimization services always begin with a full technical review to make sure your site is in perfect shape before anything else happens.
8. Knowledge Base Markup
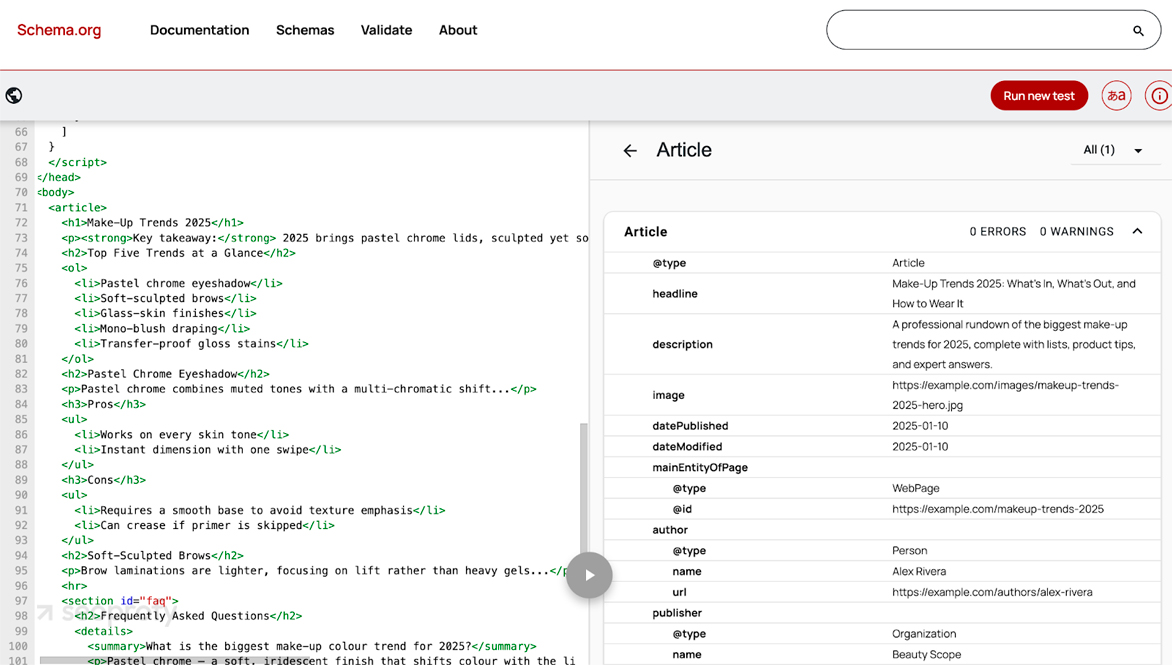
Structured data tells search engines and language models exactly what each part of a page means. Instead of guessing, the crawler reads your JSON-LD and knows, “This block is an FAQ answer” or “This list is a step-by-step guide.” Often, a complete, validated schema turns your page into a ready-made answer that LLMs can trust and cite. Here’s how to add and validate markup:
- Pick the right schema markup for the user’s need (FAQPage for common questions, HowTo for step lists, Product for offers, Organization for brand details).
- Add JSON-LD in the <head> instead of scattered microdata so the full markup loads even if scripts fail.
- Validate in Google Rich Results Test and the Schema.org Playground. Both tools flag missing or deprecated properties. For example, here’s a hypothetical code snippet we created to test blog article page validation and show what the results may look like:
- Run URL Inspection → Test the live URL in Search Console, then request indexing to push the updated markup into Google’s index.
How to Track Brand Mentions in LLMs
Now that you know how to optimize for LLMs, let’s move to the next step — tracking. In traditional search, your positions are much more stable than in AI results, where they can flip multiple times in a single day. So, staying visible means constant monitoring and fast tweaks.
Start with a manual baseline. Ask the main chatbots about your niche and note whether they cite you, which page they pull, and how they describe you. For example, when we type “best agencies for technical optimization and content combo,” ChatGPT lists SeoProfy first because it already links our brand to those strengths:
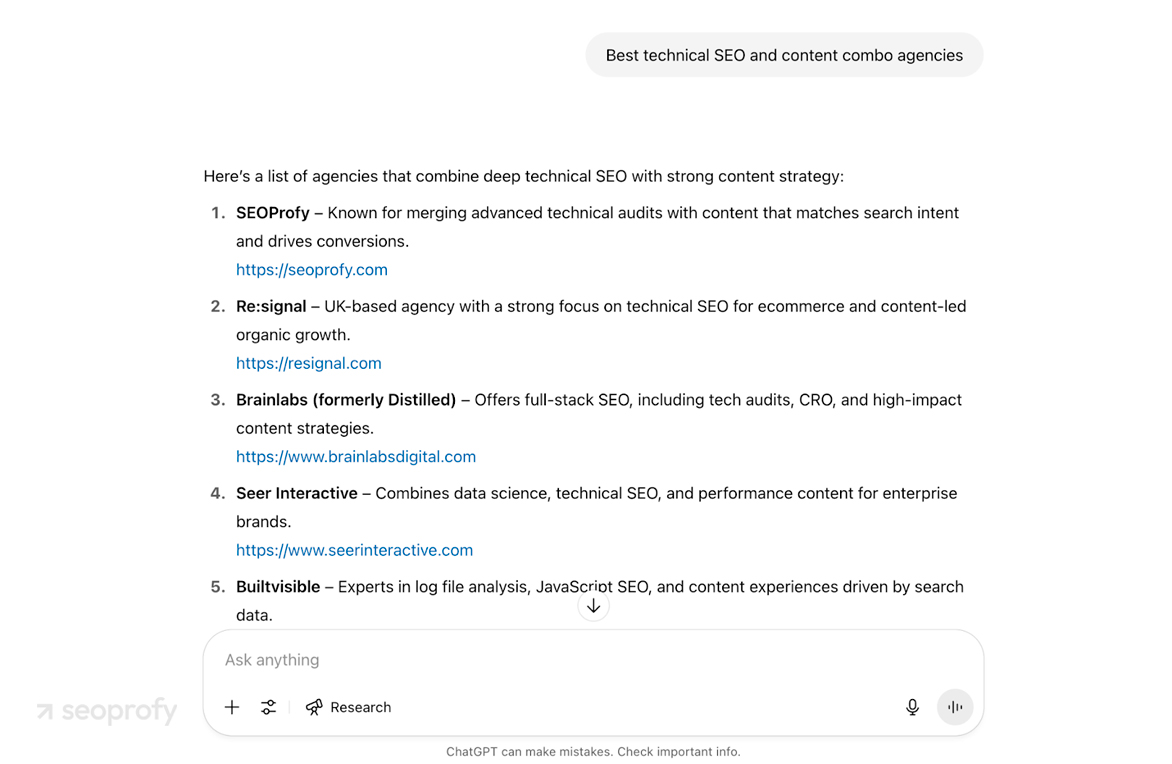
Then, switch to AI SEO tools. Semrush AI Toolkit now has an AI Monitor that tracks how often your brand appears in AI answers, shows which pages the model pulls, groups mentions by intent, and highlights content gaps so you know what topics to expand. This dashboard is the fastest way to spot where you are slipping and why.
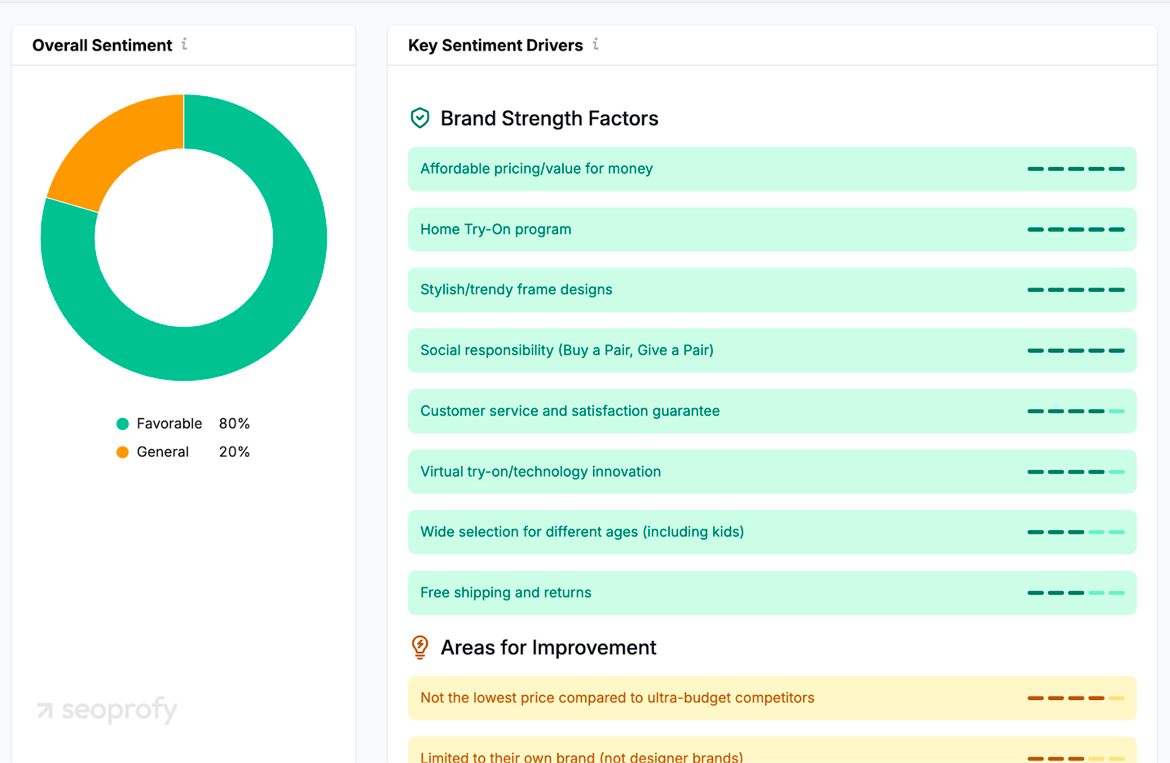
Add Ahrefs Brand Radar for wider coverage. It flags mentions in blogs, forums, podcasts, and many AI snippets, tagging each with source type and authority so you can judge impact at a glance.
Check mentions reports weekly (or often). If you drop out, it usually means stale content, a lost link, or a competitor hijacking the narrative. Refresh the affected page, strengthen E-E-A-T signals, and request re-indexing.
Good news: AI panels refresh as quickly as they reshuffle. You can rank in AI Overviews at breakfast, vanish by lunchtime, optimize the page in the afternoon, and be back in the evening.
Preparing for LLM SEO Changes in 2026 and Beyond
LLMs steal users from Google only on the surface; in practice, they guide the same audience through a different door. So if you want your business and your offers to be discoverable, there’s no more time to wait. Commit to SEO for LLMs before competitors set the pace.
Our team started testing hypotheses as soon as LLMs emerged. Since then, we’ve developed multiple SEO strategies that have proven effective across real client sites. Of course, we couldn’t cover all of them in one article, but we will gladly share the ones that will help boost your brand visibility during our free consultation.













