Typing your website into Google and seeing… nothing? If you’ve been wondering why is my website not showing up on Google, it’s time for answers.
It’s easy to panic when your site doesn’t show up. Maybe it’s brand new, maybe it’s been live for months — but if Google’s ignoring it, so is your audience. The truth? Search engines follow a checklist of technical, content, and trust signals. Miss one, and you’re off the radar. This guide unpacks 16 common (and often missed) reasons — and offers clear, non-techie fixes to get your site seen.
- Websites may not appear on Google due to technical errors, weak SEO, or strong competition.
- Indexing issues like blocked crawling or missing sitemaps can prevent visibility.
- Low-quality or unoptimized content limits keyword relevance and ranking potential.
- Google penalties or algorithm updates may suppress your site without clear warnings.
- Building authority, trust (E-E-A-T), and quality backlinks is critical for visibility.
16 Common Reasons Why Website May Not Appear in Google Search Results
If you’ve just launched your website, it may simply take some time for Google to notice it. The search engine doesn’t index new sites instantly — it can take a few weeks for your website, or even recent changes to existing pages, to appear in search results. This delay is completely normal.
But what if your site has existed for a while and still isn’t showing up? This is the time to conduct a more thorough investigation. The reasons generally fall into three main groups:
- Technical errors: Sometimes, your site might have technical problems that stop Google from crawling and indexing it. For instance, Google can’t read your pages properly.
- Weak SEO: Your site should have clear titles and helpful content, optimized with targeting keywords, as Google wants to know what your site offers and if it’s worth being recommended to others.
- Competition: Other times, your website might be technically fine and optimized. But if you try to rank in a very competitive niche, it’s more challenging.
Technical Errors
Think of technical SEO as the foundation of your entire search presence. If that foundation’s shaky, even great content can go unseen. Before diving into fixes, make sure Google can actually find your pages. Sometimes, a simple technical hiccup is all it takes to keep your site off the map.
Just because your site exists doesn’t mean it’s visible to search engines. Pages might be blocked, missing, or simply overlooked — and without fixing that, no amount of content will help.
That’s where troubleshooting matters. Instead of guessing what’s wrong, take time to review how your site is set up behind the scenes. Even small oversights — like a blocked page or missing setting — can explain why your website isn’t showing up on Google.
One quick way to see what Google has indexed is by running a site search — just type site:yourdomain.com into Google and review the results. This shows you which of your pages (if any) are indexed. For example, to check ours, we’d type: site:seoprofy.com
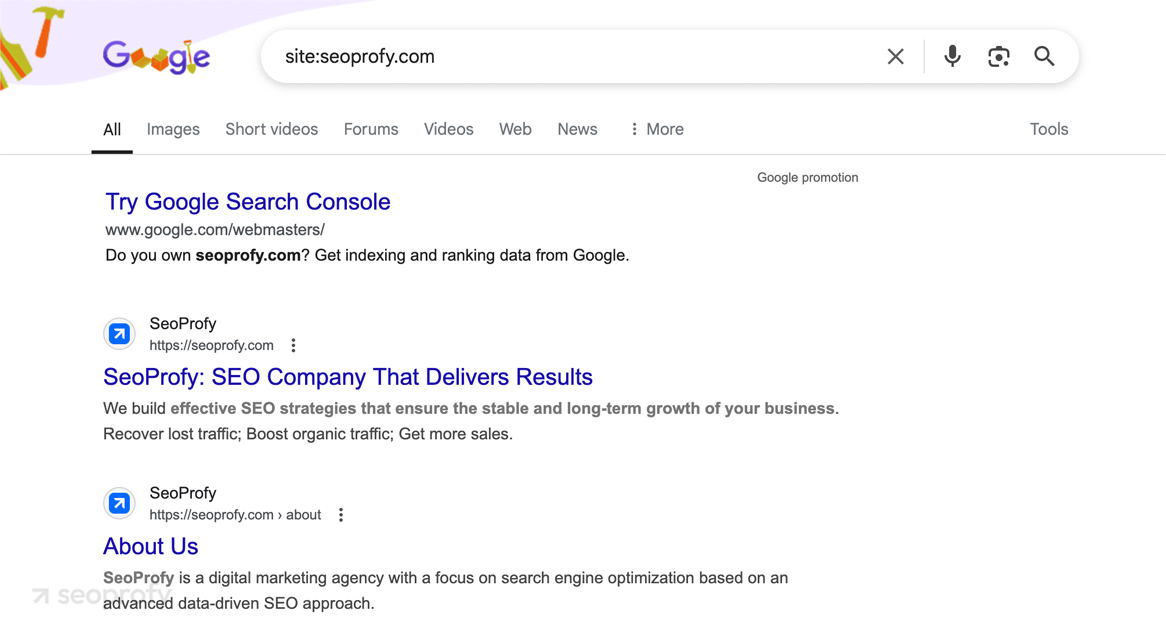
You can also take a closer look by inspecting specific URLs in the Google Search Console account. Just paste your page’s link into the top search bar, and Google will tell you whether it’s indexed, if there are any crawl issues, and what might be stopping it from showing up. It’s like getting a direct answer from Google about what’s going on with your page.
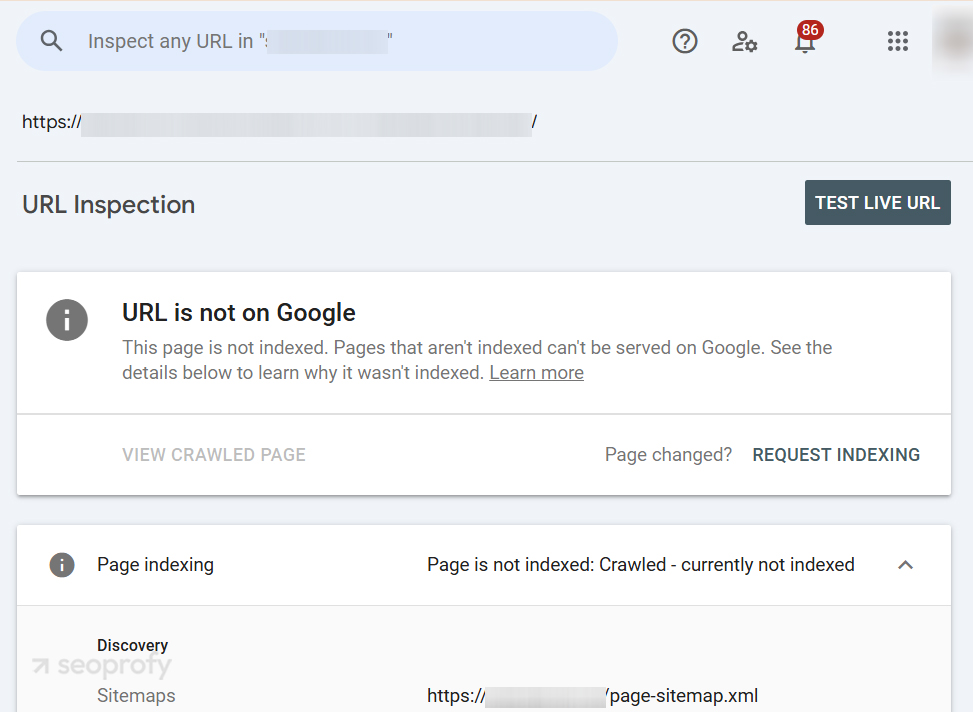
If you see zero results, don’t panic — but it’s a clear sign something’s blocking Google.
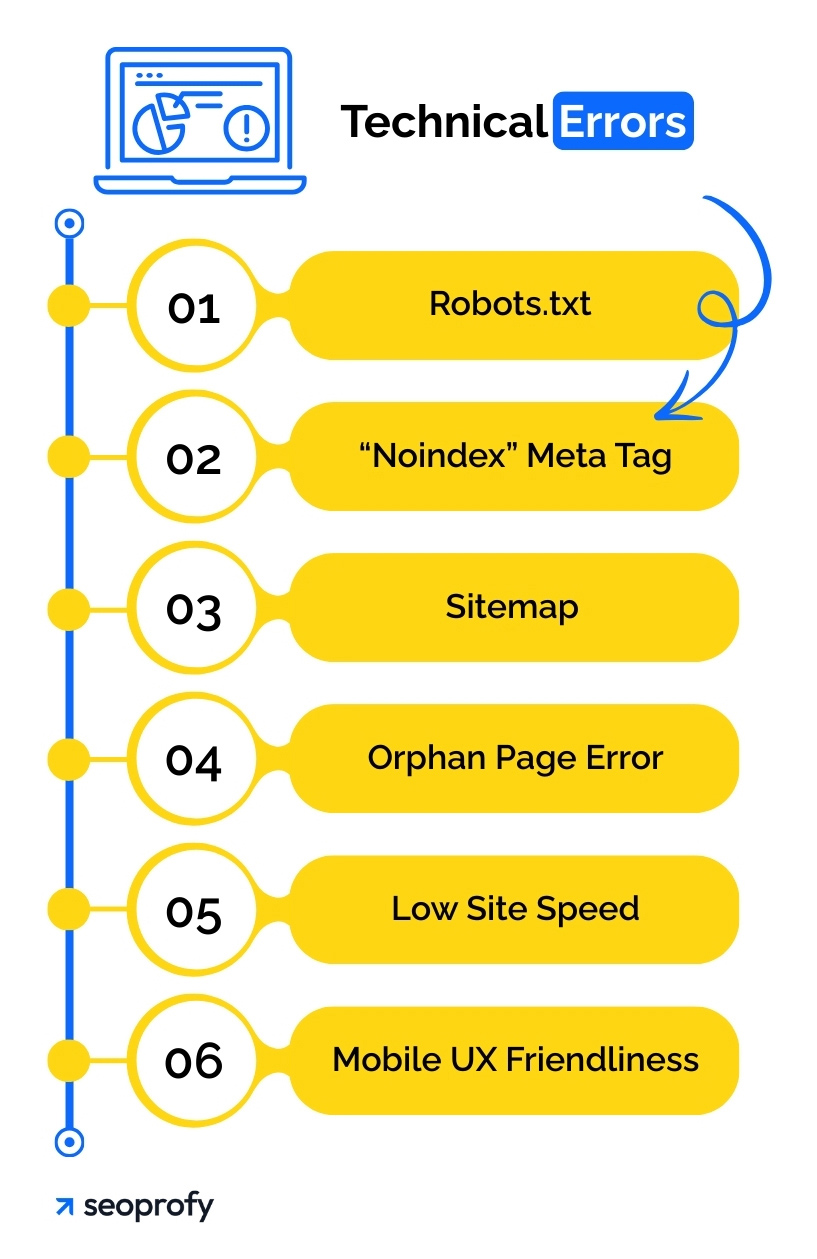
1. Robots.txt
Robots.txt is a simple text file that gives instructions to search engine crawlers about the parts of your site they can crawl (visit and explore). If it’s set up incorrectly, it might block important pages from being crawled and, thus, indexed (stored in Google’s database and shown in search results).
To check:
- Open the URL Inspection tool in Search Console
- Enter the URL you want to review
- If the URL Inspection tool shows “Blocked by robots.txt,” Google can’t crawl the page — and in most cases, it won’t index the content either. This could be why your website isn’t showing in Google search. If the page is linked elsewhere, it might still appear as a bare URL without content. To fix this, update your robots.txt to allow crawling.
To fix:
- Determine which rule in your robots.txt file causes the block with the help of a robots.txt validator
- If you can edit your robots.txt directly, remove or change the rule that results in the page not showing up on Google
If your website uses a popular and best CMS for SEO, check its help center (such as Squarespace or Wix) for specific instructions on how to edit the robots.txt file.
2. “Noindex” Meta Tag
Unlike robots.txt, which only controls crawling, the “noindex” meta tag tells search engines to exclude a specific page from search results, even if it’s crawled. This tag is typically added intentionally to login/account pages or shopping cart and checkout pages. But sometimes, the “noindex” meta tag ends up on pages by mistake.
To check: View the source code of your page and look for <meta name=”robots” content=”noindex”> or similar tags in the <head> section. You can also use the above-mentioned Google Search Console’s URL Inspection tool to see if this one page is blocked by noindex directives.
To fix: If you find “noindex” tags on pages that should appear in search results, simply remove them from the HTML code and request indexing.
3. Sitemap
Without a sitemap, important pages might never make it into Google’s index, which means they won’t appear in search results at all.
To check: Type your website address, followed by /sitemap.xml, into your browser. If you see a page with links and code, then you’ve got a sitemap. If nothing appears, you’ll need to create and submit one.
Here’s what a part of a sitemap of the Microsoft website looks like:
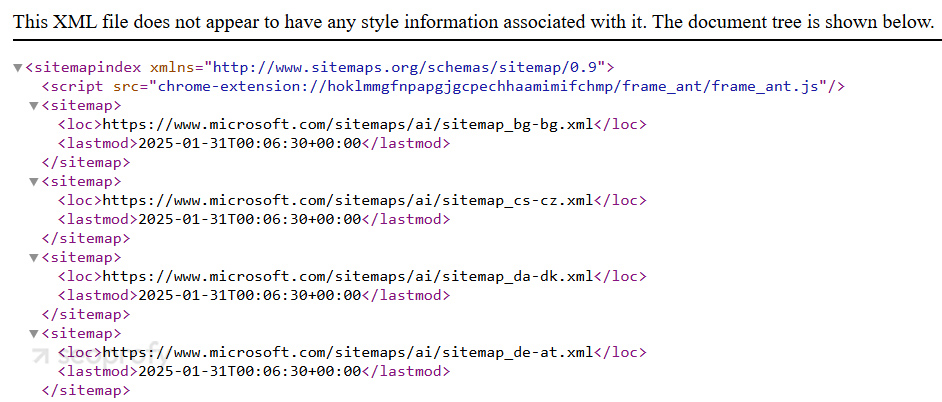
To fix: Create a sitemap using a free online tool like XML-Sitemaps.com. After creating it, you can submit it directly through Google Search Console to start ranking.
4. Orphan Page Error
Orphan pages are pages on your website that no other pages link to. Since search engines find content mainly by following links, they might never come across these orphan pages. And even if you have a sitemap, Google could still miss them.
To check: Review the Search Console’s Page Indexing report to find orphan pages.
To fix:
- Generate your sitemap using your CMS or an SEO plugin.
- Submit it in Search Console.
- Ensure it’s updated and doesn’t contain broken or redirected links.
5. Low Site Speed
Google considers site speed as one of the ranking factors because it directly affects user experience. It measures your site’s performance using Core Web Vitals — three specific speed metrics (INP, LCP, and CLS) that assess loading time, interactivity, and visual stability. If your scores are low, your indexed pages might not rank as well.
To check: Use Google’s PageSpeed Insights tool. Enter your URL, and you’ll get a detailed report with your Core Web Vitals scores along with specific suggestions on what to fix.
To fix: Compress images, remove unused plugins, and consider a faster hosting provider, like GoDaddy. Most websites benefit from a combination of caching, code optimization, and quality hosting — even small improvements here can significantly boost performance scores.
6. Mobile UX Friendliness
Google favors sites that are fast, easy to use, and mobile-friendly. Bad layouts, slow loading, or intrusive popups reduce user satisfaction and rankings.
In the last quarter of 2024, smartphones (not including tablets) accounted for 62.54% of all website traffic worldwide. So, the majority of people search via their phones. Therefore, if your site doesn’t work well on mobile devices, you lose both search rankings and visitors.
To check:
- Use Google Lighthouse, which is integrated into Chrome DevTools, to evaluate mobile usability and performance metrics.
- Check Core Web Vitals in Search Console.
- Run PageSpeed Insights for mobile UX scores.
To fix: Use a responsive design that automatically adjusts to different screen sizes. Most modern website builders are already mobile-friendly, so you might just need to update your current design to streamline your mobile experience.
Don’t let technical issues hold your business back. SeoProfy will optimize your site to achieve:
- More organic traffic
- Enhanced user experience
- Increased sales opportunities

Weak SEO
While we’ve discussed the technical side of SEO, there’s a lot more to it. You’ll also need to focus on creating valuable content and optimizing it with the right keywords. That includes both technical and on-page SEO — things like meta titles, internal links, and content structure all play a role in how search engines understand and rank your site.
7. Poor Keyword Optimization and Relevance
If your website isn’t showing up on Google, one common reason is poor keyword targeting. You might be using terms that don’t align with what people actually search for or not including enough relevant keywords in the right places. Even if the words seem related to your topic, they might not match search intent, which is what Google uses to decide whether your content is genuinely useful to a user’s query.
This often comes down to weak on-page SEO — things like headings, meta titles, and page structure that fail to clearly signal relevance.
You can use Google Search Console to see which queries are already driving traffic to your site. For more detailed insights, tools like Ahrefs or SEMrush can help you with choosing keywords with strong search volume and manageable competition, which are essential for improving visibility through effective on-page optimization.
SEO takes 3-6 months to show results, so give your optimizations some time to be reflected in rankings.
8. Lack of Content
Your website needs enough content to perform well in search engines. Plus, each page on your site serves as a canvas for keywords. More pages give you additional chances to target a wider range of search terms and phrases your potential customers are using.
To see if you have enough content, compare your site to the top-ranking pages. And remember to update your site regularly with more content, as this maintains your site’s SEO value over time.
9. Low-Quality Content
Having content on your website is important, but what’s equally crucial is the quality of this content. If your pages are poorly written or you copy material from other sites, they won’t rank well.
In times of AI progress, you may also wonder, “Is AI content good for SEO?” Currently, Google doesn’t give it any special advantages or disadvantages in search rankings.
The main idea here is that if your site doesn’t answer questions or help visitors solve problems, search engines see that as a sign that it isn’t very useful. The result? Your site isn’t offered to searchers looking for solutions you don’t have. This also reduces your chances of appearing in Google Discover, which favors helpful, engaging, and well-structured content.
So, if your website is absent on Google search, we recommend reviewing your existing pages for issues such as spelling mistakes and insufficient coverage of topics. You can also cooperate with an SEO agency that, along with its core SEO services, offers expert content writing.
10. Absence of Local SEO Optimization
Your business not showing up on Google Maps could be due to an unverified Google Business Profile and other local SEO issues. This is critical, as nearly all consumers — about 96% — discover local businesses through online searches.
Suppose you’re a personal injury attorney in Atlanta. To check if your target audience can find you in search results, search for “personal injury law firm Atlanta.” Ideally, you should appear in the first three results of the local pack (the map listings):
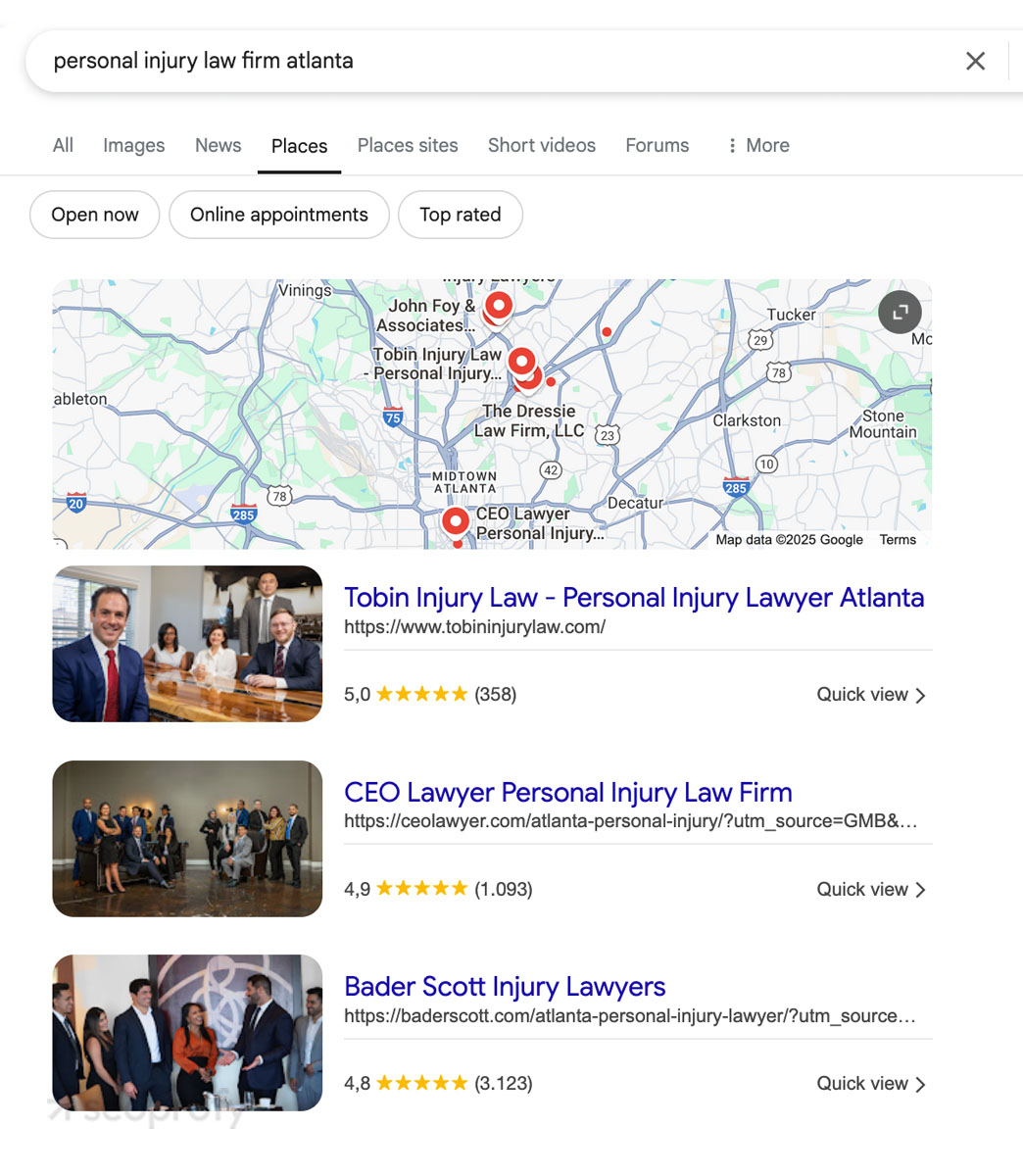
To improve your local SEO presence, you should:
- Optimize your Google Business Profile
- Get listed in local directories and citations
- Create location-specific content optimized with local keywords
- Do local link building
- Collect reviews from local clients
11. Duplicate Content
If your site shows the same or very similar content on multiple pages, this can confuse search engines about which one to show to users. Usually, Google picks just one version to display, which means the others don’t get the attention they might deserve. As a result, your website isn’t showing up on Google. Common examples of duplicate content are:
- Product descriptions copied from manufacturers
- Printer-friendly versions of pages
- Category pages with filtering options that create similar URLs (size/color/price variants)
You can find issues related to duplicate content using tools like Screaming Frog or Siteliner. To fix this issue or prevent it, create unique content for each page and use technical signals like canonical tags to let Google know which page to prioritize.
12. Possible Google Penalty
A sudden drop in your rankings might be caused by a Google penalty — either manual or algorithmic. Manual penalties occur when a human reviewer flags your site for violating guidelines (e.g., keyword stuffing or link schemes).
To detect the reason for your website not showing up on Google search, you can check for these in Google Search Console under “Security & Manual Actions.”
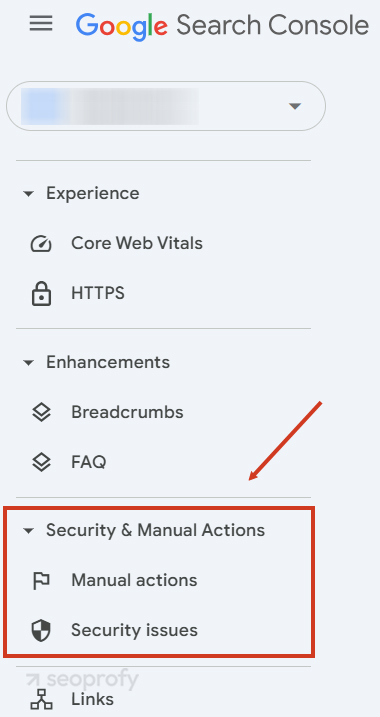
However, if no manual penalty action is listed, your website may still be affected by an algorithmic filter, triggered automatically by core updates or spam detection. These don’t show up in Search Console but can still cause your site to disappear from search.
A few reasons that can lead to penalties include:
- Overloading pages with keywords in unnatural ways (keyword stuffing)
- Getting third-party links from link farms (websites that exist solely to collect links)
- Using text that’s invisible to users but readable by search engines
To recover from a penalty, you must find all the problematic practices, fix them fully, and then ask Google to review your site again. This process can be tricky and may take some time, especially if the penalty is complex. That’s why website owners often opt for Google penalty recovery services from experienced SEO agencies.
13. Essential Search Results Changes After Google Updates
If your website is not appearing in Google search without any clear issues, a recent algorithm update might be the cause. Check what the update prioritizes — such as page speed or content quality. The Search Central Blog is a reliable source for tracking major changes.
Once you understand what the update focused on, try to align your site with these new priorities. For example, if the update places more emphasis on your page loading speed, start by improving your Core Web Vitals.
Competitiveness
Since you compete for ranking positions, you essentially don’t operate in a vacuum. Thus, you should take into account what your competitors do. This is an integral part of any effective SEO strategy.
If you see your competitors’ pages in search results but not yours, take time to compare your SEO efforts against theirs. This analysis often reveals exactly where you might be falling short.
14. Established Competitors
You may compete with websites that have a well-established SEO presence. These sites might not even be your direct business competitors, yet they’re still your direct rivals for a competitive keyword.
One of the solutions is to focus on more specific long-tail keywords that big sites might overlook. These niche search terms tend to have less competition and attract more targeted visitors. In fact, keywords with 10-15 words get almost twice as many clicks as single-word searches.
15. Lack of Backlinks and Authority
If your home page and other pages have only a few or low-quality backlinks, Google might not rank your website highly, especially if you’re in a competitive industry. This is because search engines like Google use external backlinks when evaluating your website’s authority. Therefore, even if your content is perfectly optimized, without solid backlinks, it can still be hard to get noticed.
Start by checking your backlink profile with tools like Ahrefs or Semrush and compare it to competitors who rank well for your keywords. Building relationships with other website owners in your niche can help you earn natural backlinks and streamline your off-page SEO. In addition, backlinks aren’t created equal, so make sure they only come from credible sources.
16. Trustworthiness
Google aims to recommend trustworthy sites. If your website isn’t showing up in Google search, it may be due to weak signals of Experience, Expertise, Authority, and Trustworthiness — collectively known as E-E-A-T. While not a direct ranking factor, E-E-A-T guides how quality raters assess content, and their feedback helps shape the algorithm’s direction over time.
These factors help Google decide which sites should rank for important topics, because Google relies on signals of expertise and trust to surface reliable information. To improve your site’s EEAT signals, you can:
- Create high-quality content written by qualified professionals
- Add author bios with clear credentials
- Display certifications, awards, and testimonials
- Get mentions or backlinks from well-known sites in your industry
Here’s an example of credentials you might include in your author bio:
If Your Website Isn’t Showing Up on Google, We Can Help
Google considers numerous factors when deciding on the most relevant search results. Sometimes, a small thing like a robots.txt can hide all the pages.
Figuring out exactly why your site isn’t visible can take much time if you’re not an SEO expert. If you’re ready to delegate this task to professionals, SeoProfy knows how to detect and fix what’s keeping your website hidden. We’ve already helped hundreds of businesses increase rankings, search traffic, and convert visitors into paying customers. Our SEO case studies prove it.
Our experts reveal technical issues, content problems, and Google penalties that affect your rankings. We also provide recovery services if the Google Search Console’s Manual Actions report points out some problems.
Contact us if your website isn’t showing up on Google! We’ll discuss your online presence goals, and we’ll create an effective strategy so your site appears in search results.