It’s a method businesses use to create thousands of web pages automatically and get them to rank on Google. The best advantage of this strategy is that you don’t need to write each page manually, which saves both time and money.
Ever searched for the best places to stay in a certain city? Sites like TripAdvisor, NerdWallet, and Airbnb always show up in these searches. But they don’t make these pages from scratch. They use programmatic SEO to publish large numbers of pages and show up on search engine results pages without spending months on content.
Although programmatic SEO examples are quite common, this tactic is not for everyone, and it comes with certain risks if done incorrectly. In this guide, you’ll learn who this strategy is for and get a step-by-step walkthrough on how to get started.
- Programmatic SEO helps businesses generate thousands of pages and rank for specific search queries.
- Indexing hundreds of pages can be tricky. Dynamic sitemaps and internal linking can help Google find and index your site faster.
- CMSs like WordPress or Webflow work best for pSEO because they have plugins and features that simplify managing lots of pages.
- Duplicate content and indexing problems can pop up with automated content, so businesses need to check Google Search Console regularly to spot issues before they affect their rankings.
What Is Programmatic SEO?
Programmatic SEO, or pSEO, is a search engine optimization tactic used for scalability that involves creating a large number of landing pages to rank on Google. This strategy is most commonly used in ecommerce SEO and directory-style websites. Basically, any site that needs to target lots of different keywords, locations, or product categories can benefit from it.
So, how exactly does it work? You need these key components: a dataset, a list of target keywords, page templates, and automation tools. First, you find the terms you want to target, then build a template that each page should follow. From there, automation tools take the information from your pre-build dataset and fill it in automatically for each of your keywords.
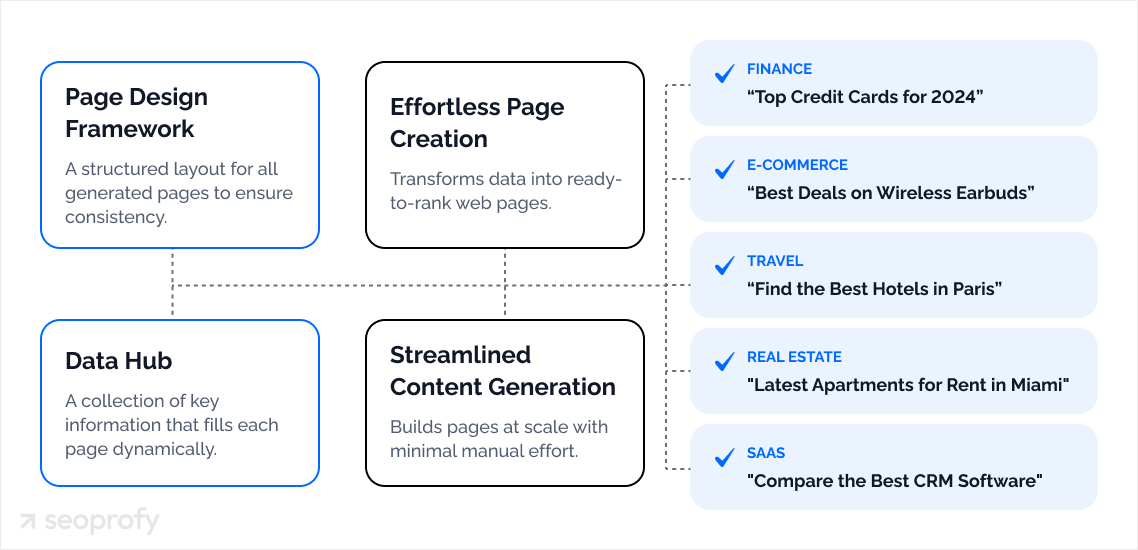
Job listing sites are some of the best programmatic SEO examples. If we search for “marketing jobs in NYC”, we’ll see that Indeed ranks first in the search engine results.
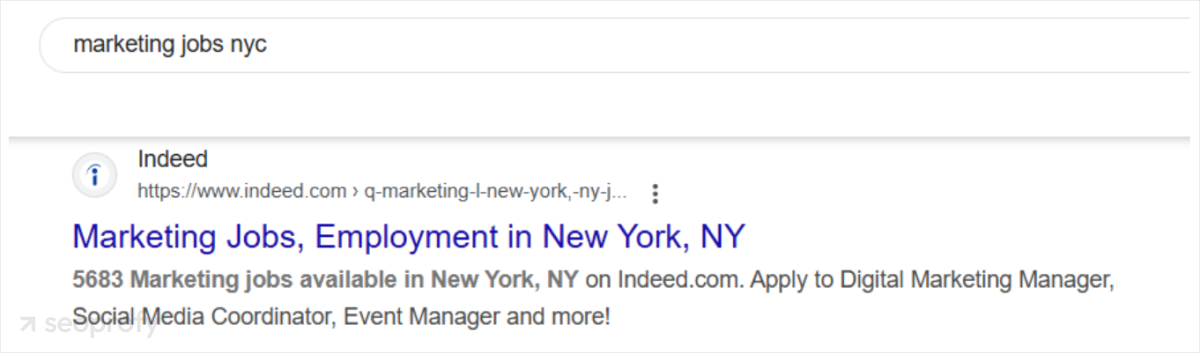
Now, if we switch the location to LA, we’ll see the same website. That’s because it has a dynamic template for these pages, which extracts the data from job listings and swaps cities automatically.
How Programmatic SEO Differs from Traditional SEO
Both strategies help businesses rank on Google and attract organic traffic, but they serve different purposes. Let’s look at the comparison between the two:

Manual Work vs. Automation
Programmatic SEO uses automation to create web pages. It pulls information from structured data sources, inserts it into pre-made templates, and then publishes pages.
In contrast, traditional SEO needs more hands-on effort. It requires a specialist who would research, write, and then optimize each page individually.
Scalability
Programmatic SEO is beneficial for businesses that need to grow the number of pages fast. A site like Zillow, with millions of properties, can’t afford to write every page manually. It needs automation to generate listings quickly.
Traditional SEO, conversely, takes more time to scale. A company that provides specialized services, like a law firm, will need to create expert content, build high-quality backlinks, and optimize site structure. Each of these takes time and won’t show results immediately.
Content Approach
Programmatic SEO follows a structured format. It puts information into templates, which makes the writing process faster but increases the risk of thin or repetitive content. It works best for pages that don’t require much writing, like price comparisons or job postings.
In traditional SEO, every article is written with E-E-A-T in mind, so the information and structure of such pages will differ. They need to be well-researched, demonstrate expertise, and provide value for the target audience.
Internal Linking
Just like with content, programmatic SEO automates this process. It links pages based on categories, locations, or other structured data points.
On the other hand, traditional SEO needs a well-planned strategy for internal linking. SEO teams choose which pages are relevant to each topic and also write the anchor texts manually.
Speed of Implementation
Traditional SEO takes time as there are multiple processes involved. Writing a single page can take hours or even days. You’ll need to research specific keywords, the target audience, and competitors, and then write, edit, and optimize your text.
Programmatic SEO works differently. In the beginning, you’ll need to conduct detailed research, analyze the search intent, gather all the data, and build templates for pages. But once that’s done, you’ll be able to create hundreds of pages much faster.
Potential Risks
The biggest issue with programmatic SEO is that you can end up with pages that look almost identical, which can result in duplicate or thin content. Since such pages don’t deliver value for the users, Google might not rank them well as they are against their spam policies.
With traditional SEO, the situation is somewhat different. The main downside is that you need to dedicate a lot of time and resources to each page, but the results could be more precise.
Is Programmatic SEO Right for Your Business?
Programmatic SEO has many benefits but it doesn’t work for every type of business. Before implementing this strategy, consider whether your business meets these key criteria:
- Your target audience searches for similar information with different variables (locations, products, services).
- Your business needs to rank for hundreds or thousands of similar keywords that would be impractical to target manually.
- You have access to substantial, structured data that can be used in templates for multiple pages.
- You have the technical capability to implement, monitor, and maintain these pages over time.
- Each generated page will provide distinct value to users, not just slight variations of the same content.
If your business lacks these elements, traditional SEO might be more appropriate for your needs.
Industries That Benefit the Most from Programmatic SEO
Businesses in these sectors can get exceptional results from programmatic SEO due to their inherent data structures and user search patterns:
- Travel: Travelers are always searching for destination info, places to stay, itineraries, and local tips. Sites like Booking.com and TripAdvisor dominate search results by creating landing pages tailored to specific search intents, thanks to structured data and dynamic content. They tap into user-generated content through reviews and ratings to power their programmatic pages, automatically organizing this information into city guides, hotel listings, and suggested routes.
- Real estate: Real estate searches are local and specific. Programmatic SEO helps websites in this niche produce tons of pages. Platforms like Zillow and Redfin use this method to scale up content and drive major traffic through thousands of hyper-specific property pages like listings by neighborhood or town, rent vs. buy comparisons, and local market trends.
- Ecommerce: Online stores with lots of products can also benefit from programmatic SEO. Giants like Amazon and Best Buy rely on pSEO to create optimized pages, which help them catch customers with very specific needs. The strategy is perfect for scaling online shop product pages, category pages, and detailed product filters.
- Local business directories: Local directories like Yelp, Angi, and Thumbtack are great programmatic SEO examples. They use it to build landing page templates for each business, service, or location.
- SaaS & B2B marketplaces: For software companies and business-to-business marketplaces, programmatic SEO helps target industry-specific searches. Platforms like G2 and Capterra use this approach to attract organic search traffic from buyers doing detailed comparisons or looking for reviews.
- Finance: Companies could create pages for different financial products, loan calculators, currency prices, and investment comparisons. Think of sites like NerdWallet that create comparison pages for credit cards, loans, and banking products across different regions.
Examples of Programmatic SEO in Action
One of the programmatic SEO examples is NerdWallet’s Cost of Living Calculator. They’ve created city-specific pages that show how much it costs to live in different places across the U.S. If someone wants to know how much it costs to live in Miami, Denver, or New York, they can find a page that lays it all out — rent, groceries, transportation, utilities, and more.
As you might’ve guessed, they didn’t write all these pages from scratch. They created a template and used a database to fill in the details for each city. The structure stays the same, but the numbers, comparisons, and local specifics change.
In the screenshot below, you can see their cost of living page for Chicago. The tool shows the average salary and a breakdown of costs in each category.
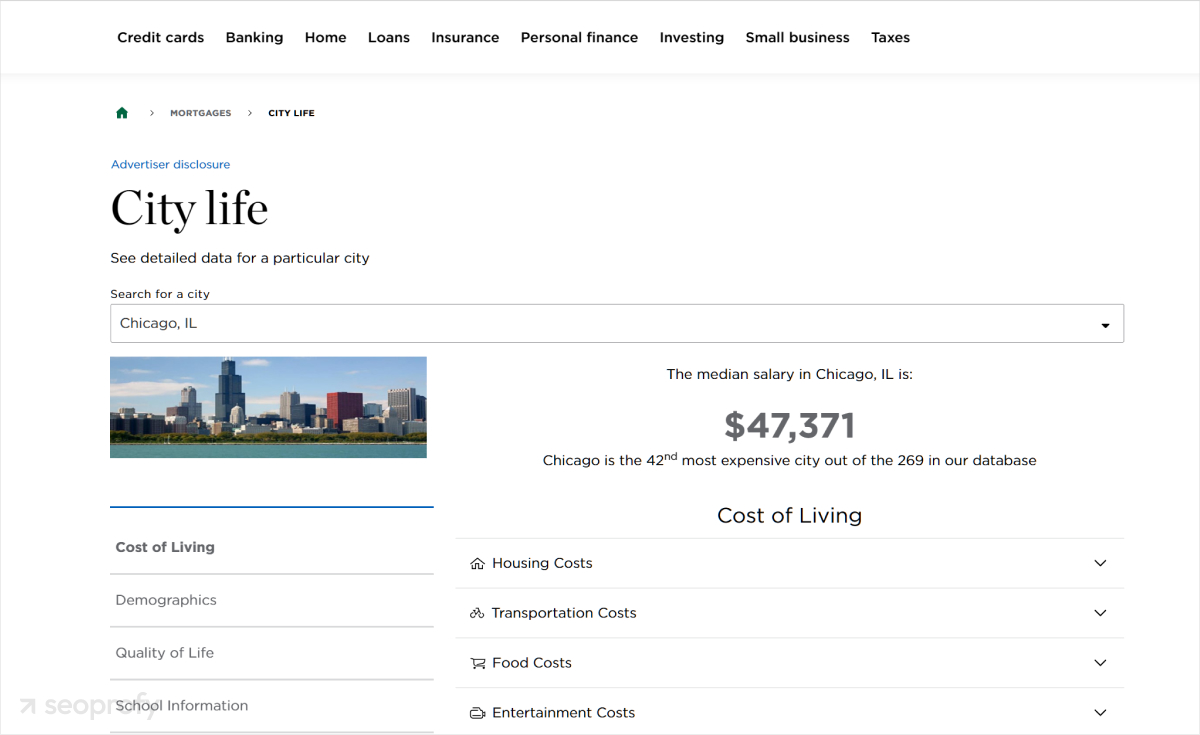
If we choose a different city, like San Diego, we can notice that the structure of the page stays the same. But all the other details are different and extracted from the dataset for that specific location.
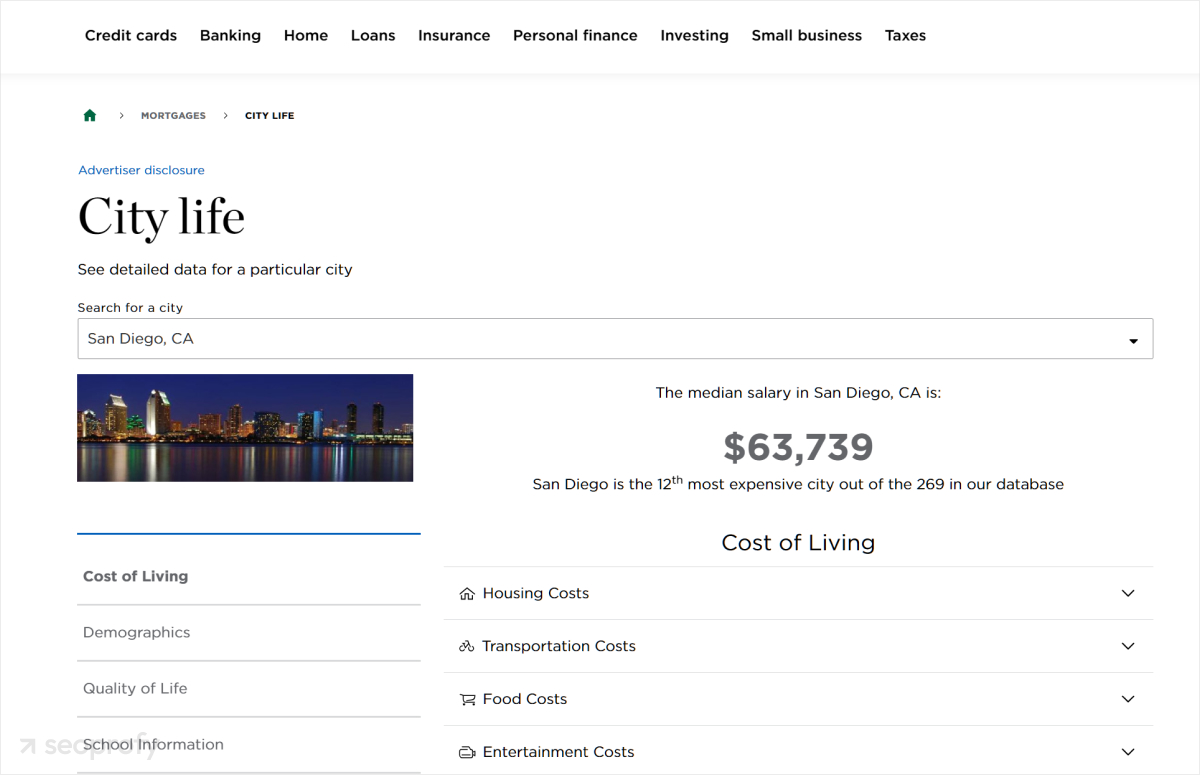
The titles, headings, and subheadings on these programmatic landing pages are all optimized for local keywords. This helps NerdWallet rank for thousands of different searches and since the content is tailored to each city, it also offers something of value for the searchers.
How Programmatic SEO Works: Step-by-Step Guide
In earlier sections, we explained what programmatic SEO is and showed you an example of it in action. So now, let’s look at how you can get started.
Step 1. Research & Collect Data
An effective programmatic SEO strategy starts with organized data. Here’s what you can use to gather it:
- APIs and databases: The most convenient way to extract data is from APIs (Application Programming Interfaces). In the case of a travel website, it can fetch hotel prices from a booking platform. Similarly, an automotive site could use an API to list car specs:
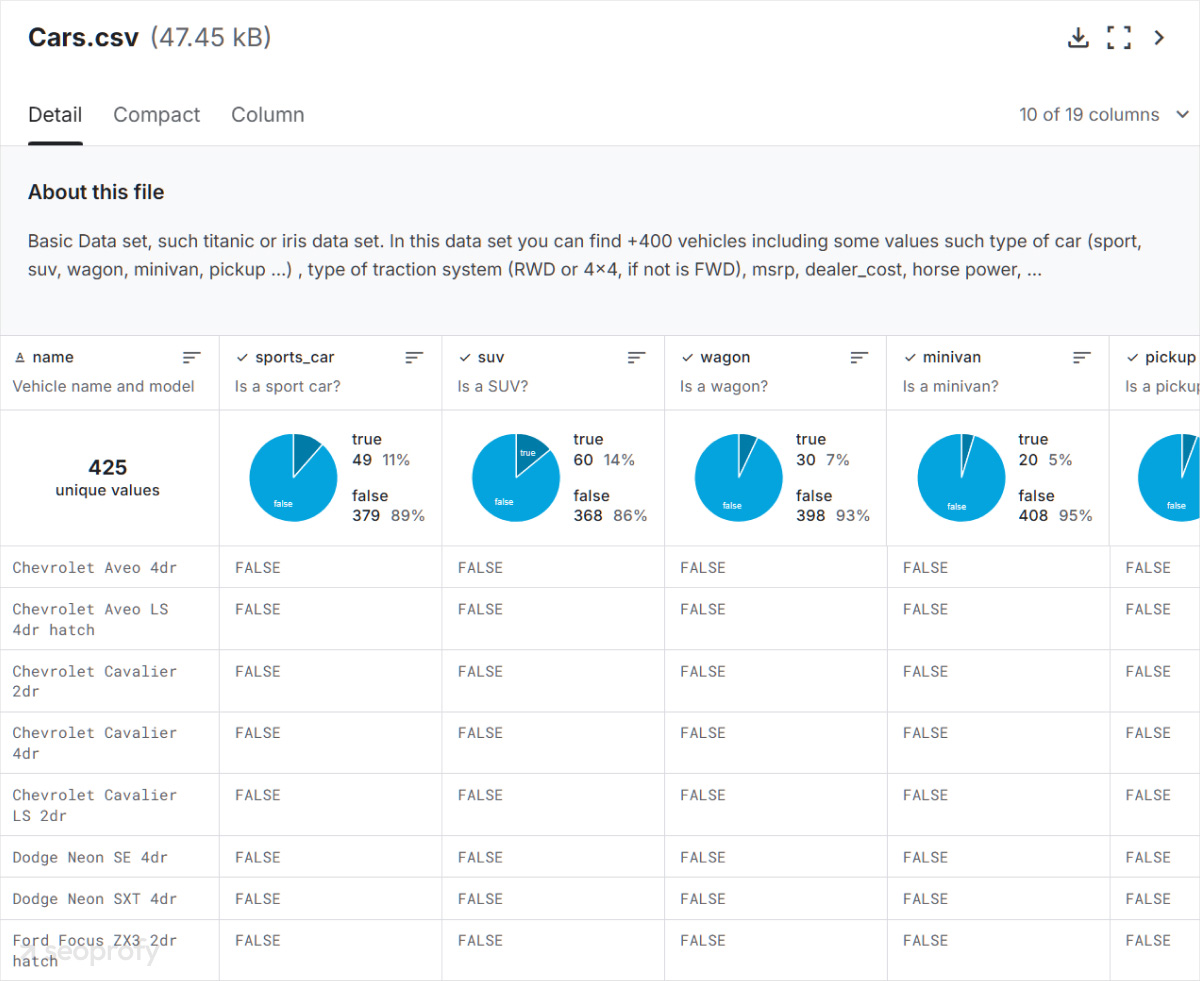
- Internal spreadsheets and lists: If you already have any product inventories, service directories, or location-specific records, you can store them in a spreadsheet or a database and use them to populate your pages.
- Web scraping: In cases where no direct API exists, you can use scraping tools to collect publicly available data, such as pricing, product specs, or user reviews. But remember that you need to handle it responsibly and follow the legal guidelines.
- Third-party datasets: Government reports, industry research, and public databases can also be useful. A site that compares the cost of living in different cities, like NerdWallet, might gather data from official economic reports.
The other thing to keep in mind is that raw data is rarely usable in its original form. Before feeding it into a system, it’s a good idea to clean, standardize, and validate it for accuracy. If the data is unreliable, the generated pages won’t perform well.
Keywords Research
Thorough keyword research is a critical part of any programmatic strategy. You’ll need to use an SEO tool like Ahrefs for this.
Once you open the tool, go to the Keyword Explorer and enter a broad term that’s relevant to your business. Then, use the “Matching terms” feature to see more variations that people are searching for — long-tail keywords are key for more specific locations and services. You can also apply filters to find queries with low competition.
Repeat the process for the rest of the broad keywords that are relevant to your niche. Also, remember about the search intent when doing your research. In simple words, it’s the reason why someone searches online. There are four main types of search intent:
- Navigational: The user wants to find a specific page.
- Informational: The user wants to read more on the topic.
- Commercial: The user researches their options and is closer to making a purchase.
- Transactional: The user wants to buy a product or service.
Keywords that show transactional or commercial search intent usually work best for programmatic SEO. For example, Airbnb goes for location terms like “pet-friendly apartment in Paris.” This is a category of commercial investigation because people are searching for a location and are interested in booking it.
Step 2. Come Up with SEO-Friendly Templates
The next step is to build dynamic templates for on-page SEO. These will help you generate titles, descriptions, headings, and URLs automatically.
Meta Tags
For programmatic SEO pages, you’ll need to create a template for meta titles and descriptions with your main keyword and placeholders. If we go back to the example of NerdWallet’s pricing calculator, they use the following title:

The placeholder in this case is the name of the city. It changes automatically depending on the location where the user is searching.
The meta description goes right below the title tag and gives people more information about the page. That’s where you can add more details so users would want to click on your site. NerdWallet uses a template, where the city names change depending on the comparison, so the search result always shows what the user is looking for.

Headings (H1-H6)
Headings help organize your text and make it easier for visitors to skim through. They also give more context to search engines about your page.
In the case of NerdWallet, their H1 title introduces the page and the H2s split off sections such as city comparisons, sources of data, and cost of living information.
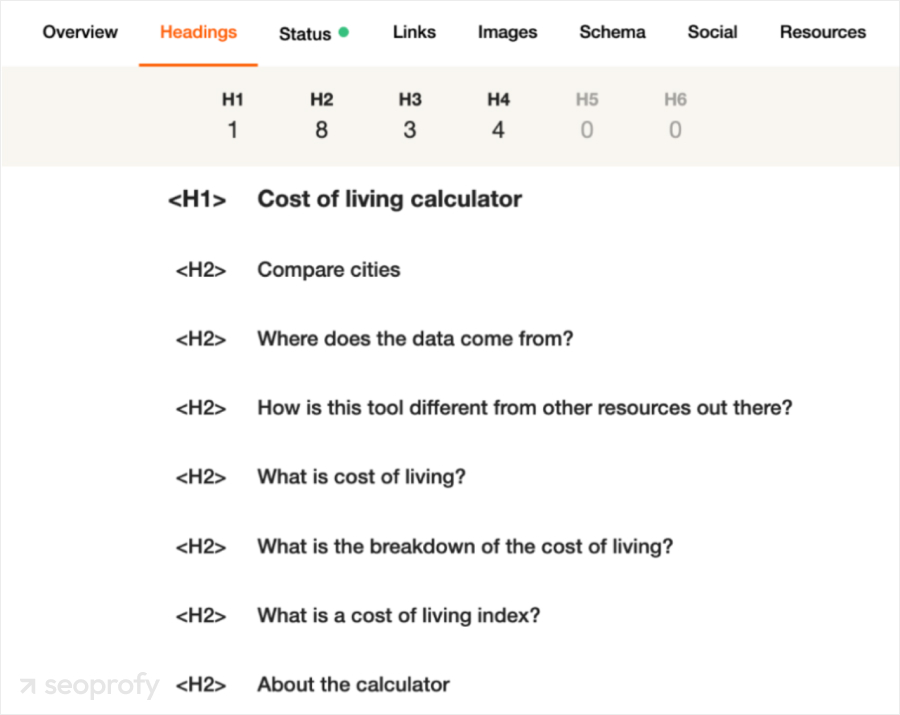
Structured URL Paths
A structured URL is another important element of programmatic SEO. Take CoinGecko as an example. Their URLs follow the format /coins/bitcoin/ to keep everything organized and make it simple for both search engines and users to understand the context.
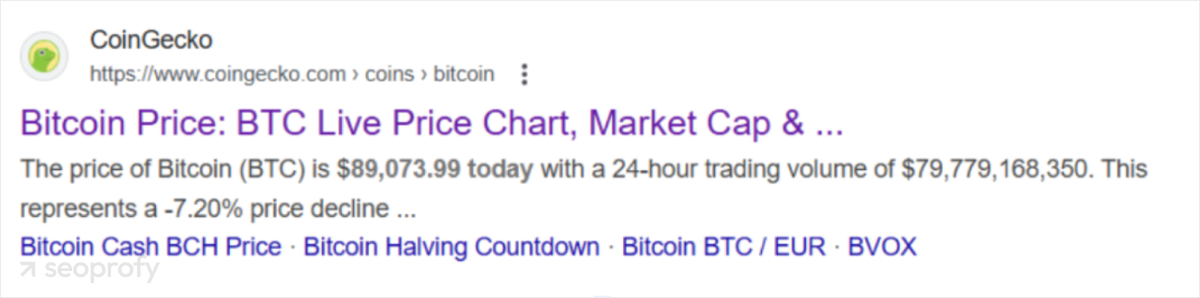
When dealing with thousands of pages, generating URLs automatically can spare you hours of manual work. But, you also need to remember to add relevant keywords to your URLs to improve search rankings.
Step 3. Automate Page Generation
In this section, we’ll review content management systems (CMS), data sources, and AI tools you can use to speed up page generation. A combination of these will help you make this process more efficient.
Choose a Content Management System (CMS)
WordPress and Webflow are two of the popular options. They both have plugins and features that can easily handle a lot of content.
WordPress works with plugins like WP All Import and Advanced Custom Fields (ACF). You can use them to import data from spreadsheets or databases directly into your templates, which is ideal when you have hundreds of pages.
If you need a CMS that makes design a priority, Webflow is a great option. It leans more toward creative flexibility and also lets you store structured data, which you can later use to fill the generated pages.
Some businesses that have bigger projects opt for a custom CMS. They integrate it directly with their databases or APIs, which gives them more control over the automation process.
Use Google Sheets
For your programmatic SEO strategy, you will require a setup that bridges your data source (database or spreadsheet) to your CMS. Google Sheets is a great place to start. You can use it to organize columns with company names, addresses, reviews, categories, images, and other associated information.
Work with Python
Python is a helpful programming tool for automating repetitive tasks. It can handle the following tasks for you:
- Extract data from Google Sheets or databases with the help of APIs.
- Clean and format the data with libraries like pandas.
- Generate HTML or Markdown files dynamically if you’re using static site generators similar to Jekyll or Hugo.
- Upload your content directly to your CMS via API integrations.
Python can automatically populate templates with city-specific data like hotel names, ratings, and prices.
Generate Content with AI Tools
As for the content creation, AI tools like ChatGPT and Claude can help you generate product or meta descriptions or come up with a structure for headings that’s specific to each page topic. Even though AI can accelerate the creation of content, remember to review the text for quality and accuracy.
Step 4. Optimize Internal Linking
An internal link is simply a hyperlink that connects one page on your website to another. Your site’s overall structure is shaped by these connections.
From a technical SEO perspective, these links are crucial. They help Google grasp how your web pages are linked and related. On top of that, they improve the user experience by making site navigation easier.
A good practice is to keep all your pages accessible within three or four clicks. This keeps things user-friendly and makes it easier for Google’s bots to crawl your site.
Zapier, a well-known automation platform, does a great job at this. Their app directory branches out into more specific app pages, such as their Gmail page.
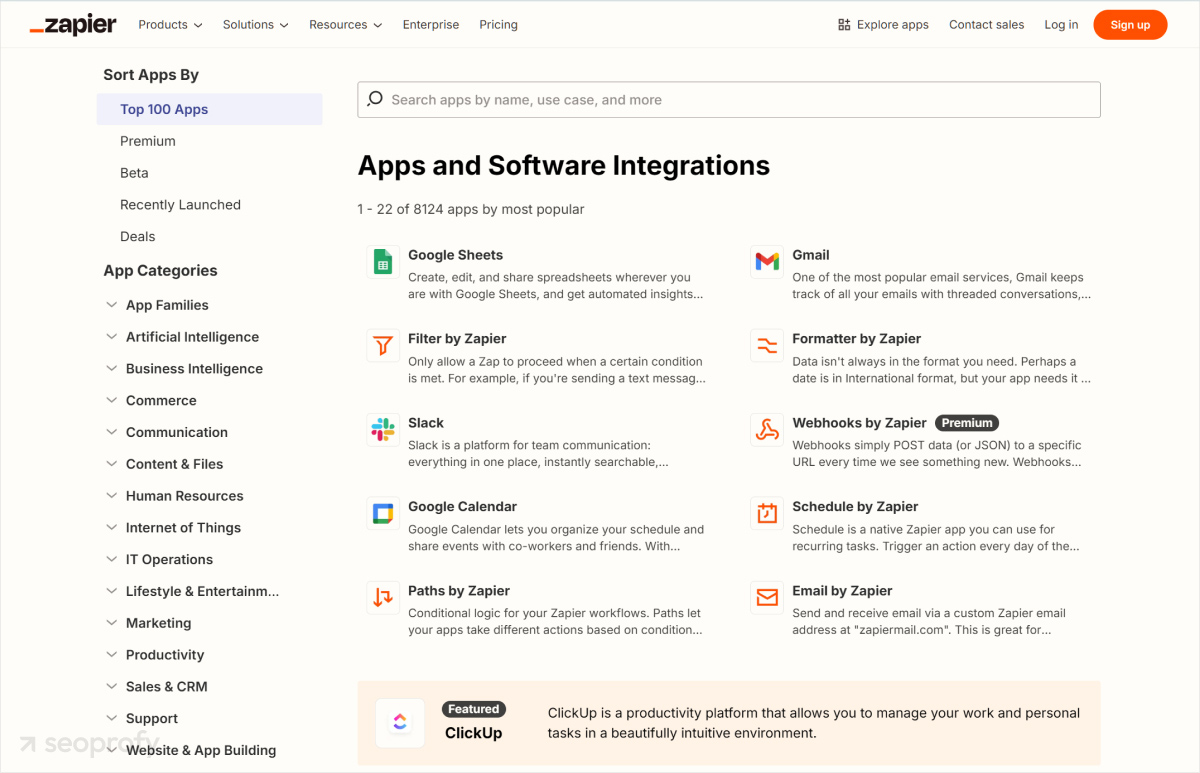
From the Gmail collections page, Zapier includes internal links to even more app integrations. In the screenshot below, you can see that it links to apps like Google Sheets and other related tools.
You can automate the process of internal linking through tools and plugins. For example, you can use Link Whisper to get suggestions for suitable links as you publish new content.
Likewise, you can design templates that automatically create internal links by categories, tags, or even keywords. As you publish new programmatic pages, the templates will dynamically update links.
Use HTML Sitemap and Dynamic Navigation
In addition, you’ll need an HTML sitemap. Briefly put, it’s a document with all your site pages in one location. It helps Google know the content of your site and crawl it faster. You can create a sitemap with the help of plugins like Simple Sitemap, which works with WordPress, or do it manually. Here’s what Airbnb’s sitemap looks like.
There is also dynamic navigation that comes in handy. It is your menus and sitemap adjusting automatically whenever you add new pages. You can do it in WordPress with the help of Max Mega Menu or UberMenu plugins.
Step 5. Monitor Indexing and Performance
Programmatic sites generate a large number of pages, which often leads to an index bloat. This happens when unwanted or low-value pages are being indexed.
It can make Google spend time crawling site sections that are not important, raise duplicate content issues, and degrade your site’s overall SEO performance. So, you will have to check your programmatic pages quite often to tackle such issues.
One of the tools that can help you with this is Screaming Frog. It helps you identify duplicate content and thin pages. It will also show you any URL parameters that are potentially causing duplicate pages.
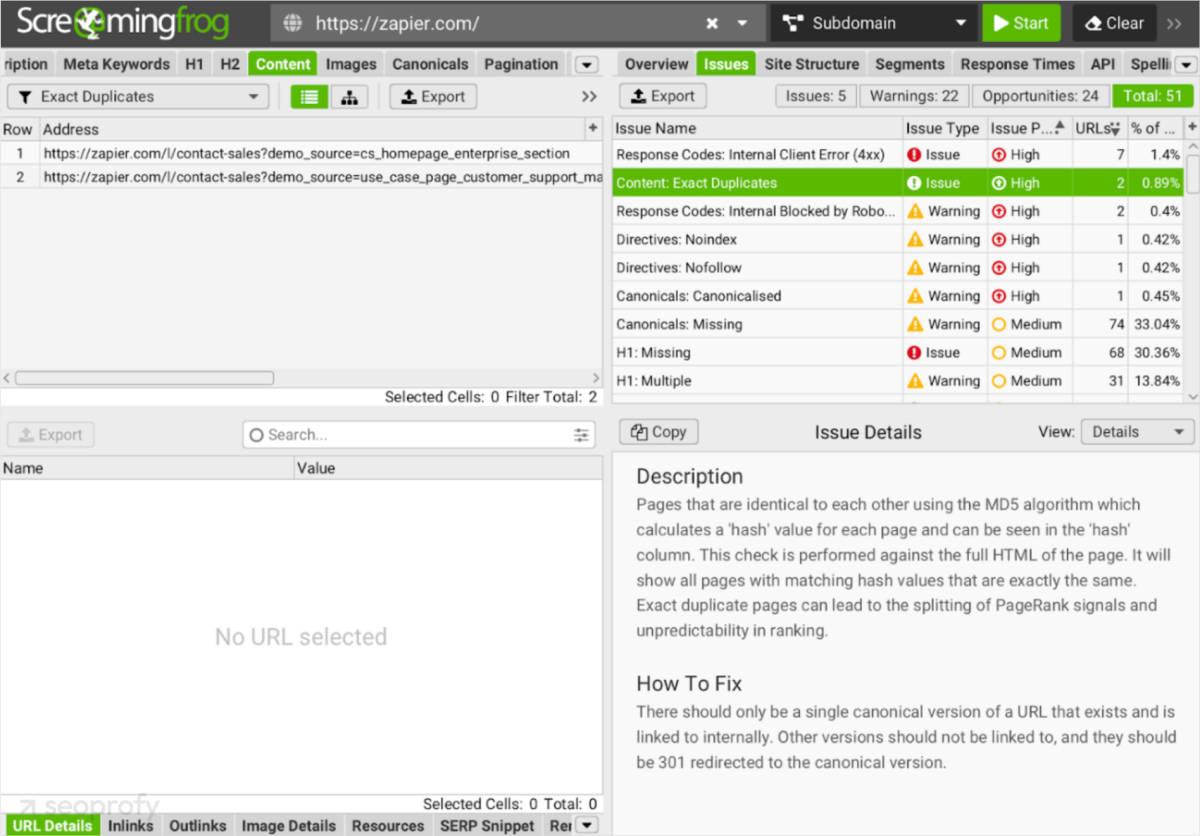
You can then noindex the pages that don’t need indexing by Google or add canonical tags to the pages to tell search engines which page is the primary one.
Also, check the Crawl Stats report in Google Search Console to see what pages are and aren’t indexed. GSC will show crawl errors, so you know what to fix.
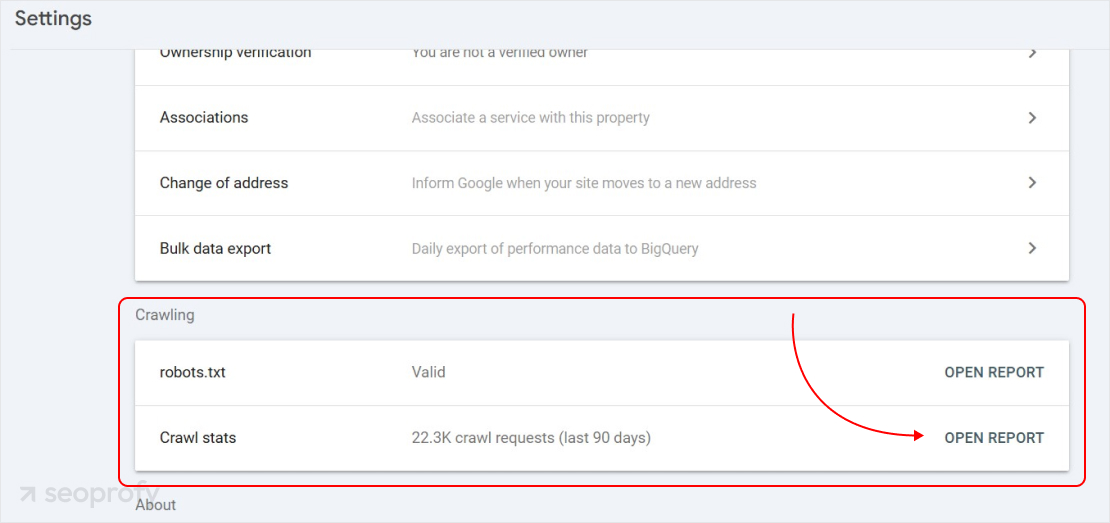
Another convenient method is looking at your log files to see how search engines are crawling your programmatic pages. This will indicate which pages are being searched for and how frequently.
Finally, use SEO crawlers that simulate the perspective of search engines for your site. They will help you determine technical problems that could arise from your SEO setup.
Tools and Resources to Get Started with Programmatic SEO
To be able to execute programmatic SEO effectively, you’ll need to have the right tools and resources at your disposal. We’ve already mentioned CMS tools and data organization platforms like Google Sheets. Now, let’s look at other tools that will help you automate content creation, optimize pages for search, and handle large sets of data.
Keyword Research Tools
For keyword research and competitor analysis, tools like Semrush, Ahrefs, or SE Ranking work best. They let you find low-competition keywords, so you can prioritize the best opportunities for your content. You’ll also be able to analyze search volume, keyword difficulty, and user intent for each term.
Data Organization and Management
In addition to Google Sheets and databases, Airtable is another useful tool you can use to organize and manage your data. It combines the functionalities of a spreadsheet and a database, so you can keep track of your keywords and content ideas. You can also create custom views and collaborate with your team inside the tool.
AI Copywriting Tools
Plenty of AI tools can speed up your SEO writing process. Scalenut, Frase.io, and others can quickly generate optimized content for you following best SEO practices. But again, always double-check the quality and accuracy so your readers get high-quality content.
Challenges and Common Pitfalls of Programmatic SEO
Programmatic SEO can hugely scale up your content creation, but it does come with its own set of problems. Being aware of these issues can keep your strategy effective and safe from Google’s penalties.
Duplicate & Low-Quality Content (Doorway Pages)
One of the main pitfalls of programmatic SEO is ending up with duplicate content. If you keep reusing almost the same text across many pages, it can get difficult for Google to figure out what makes each one different. This can hurt your rankings since Google values unique and valuable content.
Another issue to watch for is thin content. Many people assume thin content means just writing too little, but it’s also about content that doesn’t offer valuable information to the reader or doesn’t match the search intent.
Pages with duplicate or thin content are often called “doorway pages”. Google frowns upon creating pages that don’t offer anything useful to the visitor and are designed simply to direct the user to other parts of your site.

To steer clear of these problems, make sure that your programmatically generated pages offer something valuable. Additionally, align them with the search intent so that your content gives people exactly what they are searching for.
Risks of AI Content
AI-generated content isn’t necessarily bad unless it is generic, unhelpful, or churned out in massive amounts. Google itself has said that using AI-generated content is fine as long as it’s not designed to manipulate search results.
But as good as AI sounds for writing, relying too much on it without human review often results in content that lacks originality, depth, or even accuracy. It’s important to remember that even though generated texts are a good starting point, they are not the finished product. All AI content should pass through a regular editing process to ensure it meets quality standards and genuinely helps your readers.
Wrapping Up
Many industries can win big with programmatic SEO. However, you need to balance automation with great content, match the search intent, and back up your strategy with keyword research, internal linking, and structured data.
If you need expert help with your strategy, contact us at SeoProfy. We’ve worked with multiple niches for the past 12 years and have the technical expertise to set up and organize your data. Our team will handle everything for you so you can launch pages faster and start driving traffic and sales to your business.