Ever wondered how to make your website connect with global audiences? Localization SEO is the secret weapon. It’s not just about translating words — it’s about adapting your content to feel like it’s meant specifically for each region, creating an authentic and personalized experience for users no matter where they are.
Localization SEO involves understanding the unique search behaviors, cultural references, and preferences of your target markets. This means adjusting keywords, content, website structure, and technical elements. With this SEO localization guide, you’ll boost search rankings, enhance user experience, and drive higher conversions, building trust and fostering strong connections with local audiences worldwide.
- SEO localization adapts your site to how users search and behave in each specific market.
- Local keyword research must reflect real phrasing, not textbook translations.
- Cultural mismatches in tone, visuals, or formatting reduce engagement and trust.
- Technical setup, like hreflang and consistent URL structure, is critical for visibility.
What is SEO Localization?
SEO localization is the practice of optimizing website content and SEO tactics to suit specific languages, cultures, and geographic areas. It extends beyond simple translation by adjusting keywords, meta tags, URLs, and content to fit the search behavior and preferences of a targeted audience. Unlike basic SEO translation, which often swaps words without changing structure or tone, localization adjusts the entire experience to feel native.
Major global brands use SEO localization to stay visible and competitive in different markets. For example, H&M runs separate sites for dozens of countries, each with localized content, product naming, and language tone tailored to local search habits.
For their European audience, the homepage may feature bright summer collections and beachwear.
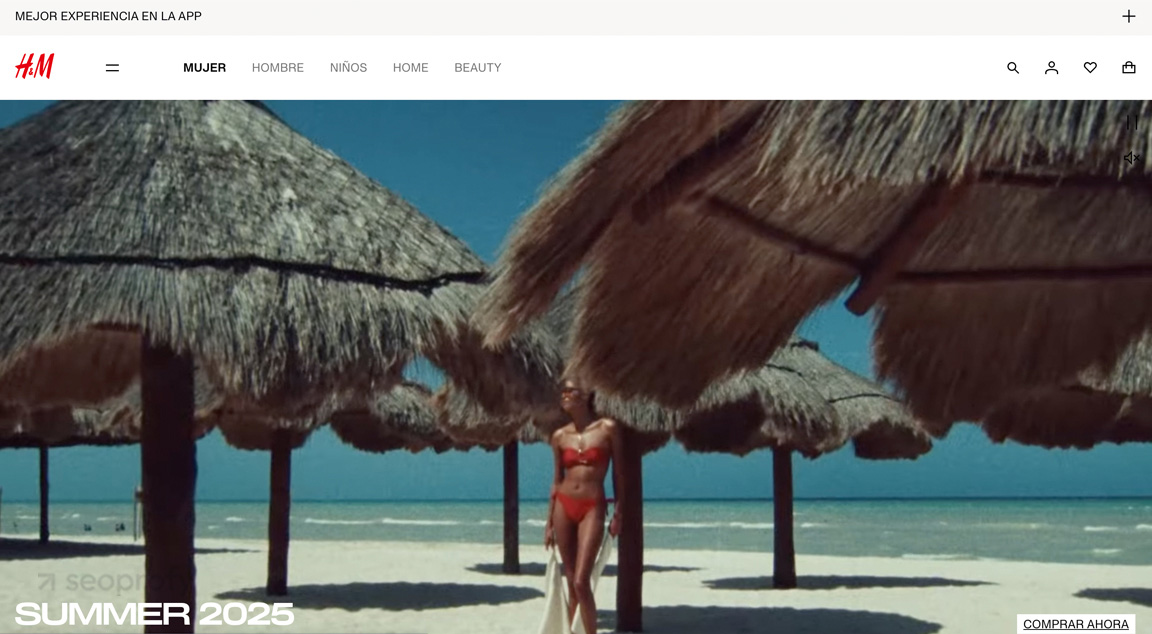
In the UAE, where modesty norms differ, the same season is represented with covered shoulders and a more reserved presentation.
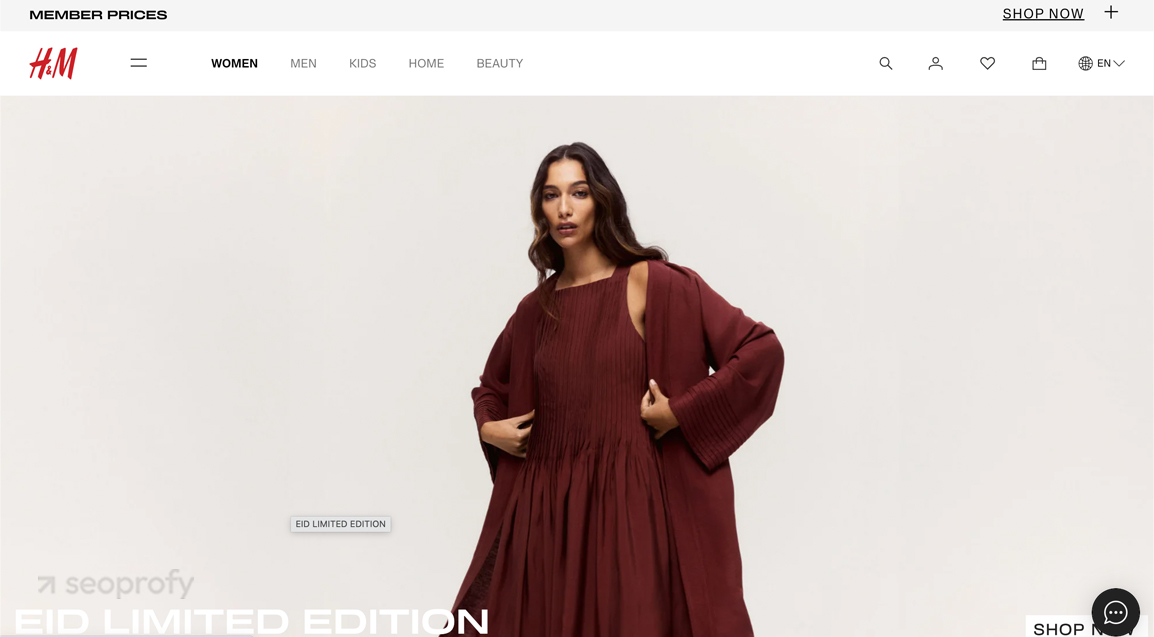
In China, the entire campaign adopts a different visual style that reflects local aesthetics and cultural expectations.
Airbnb adjusts not only language but also category labels, host guidelines, and search filters to reflect how users search in different countries. Even tech companies like Apple adapt SEO metadata and feature descriptions across their landing pages to match regional vocabulary and other cultural differences. Additionally, numerous well-known examples of successful localization strategies exist.
Why does this matter? 40% of global consumers will not buy from websites in other languages at all. A well-executed SEO localization strategy can directly influences trust, engagement, and conversion, and, as a result, dramatically improve click-through rates, lower bounce rates, and increase purchases from potential customers by making your content feel genuinely relevant to them.
SEO Localization vs. SEO Translation
Let’s take a closer look at where localization ends and direct translation begins. The table below breaks down the core differences between these two approaches.
|
Aspect |
SEO Translation |
SEO Localization |
| Goal | Make existing content readable in the target language | Make content relevant and competitive in local markets |
| Process | Directly translate text without considering local nuances | Customize structure, messaging, visuals, and technical elements based on local SEO behavior |
| Keyword Optimization | Often missed or done post-translation | Based on local keyword research from the start |
| Content Adaptation | Keeps original structure and tone | Adjusts tone, idioms, measurements, currency, examples, etc. |
| Search Engine Alignment | May not account for local SERP differences | Built to match local SEO algorithm behavior and user expectations |
| Outcome | Grammatically correct content that may not rank or convert | Regionally optimized pages that align with search and intent |
Key Benefits SEO Localization Offers for Global Businesses
Good SEO (search engine optimization) gets you found. Great SEO makes you feel local. That’s where localization comes in — and it’s one of the smartest moves a global brand can make. Here are the key outcomes of a well-executed localized SEO strategy:
1. Higher Visibility in Local Search Results
Localized pages use region-specific keywords, URLs, and meta tags, making them more likely to appear in local SERPs. Google favors content that matches user intent and location — localization helps meet both.
A U.S. site optimized for “car rentals” won’t perform as well in the UK, where people search for “hire cars.” SEO localization bridges this gap.
2. Stronger User Engagement
Users are more likely to trust and interact with content that feels familiar. Localization adjusts not just the words, but also tone, imagery, date formats, currencies, and cultural references.
A CSA Research report showed that 76% of consumers prefer purchasing products with information in their native language, even if they speak English.
3. Improved Conversion Rates
Tailored messaging leads to higher trust, reduced bounce rates, and more completed conversions. When a user sees a checkout page in their native language with local payment options and currency, they’re more likely to finalize the purchase.

4. Competitive Edge in New Markets
Most businesses expanding globally underestimate local competition. Search engine optimization localization ensures your site doesn’t just show up — it stands out.

Competing locally means ranking alongside native brands. SEO localization is your gateway to parity.
5. Better Compliance and Market Fit
Local laws, product standards, and accessibility requirements vary. A localized site allows you to adhere to regional SEO guidelines and legal expectations, like cookie banners in the EU or content accessibility in Canada.

A smart SEO localization strategy helps your brand feel local from the start. It builds trust, boosts visibility, and turns potential customers into loyal ones — often before your competitors even show up.
Build an SEO Localization Strategy
Effective SEO localization for international markets starts with execution. A strategic approach involves identifying optimal target keywords, tailoring messaging to suit local cultural nuances, and ensuring search engines can properly crawl, index, and rank your localized pages. Here’s a more hands-on, technical breakdown to guide you through the process:

Use Best Practices for Local Keyword Research
Localized keyword research starts with understanding how people actually search in a given region. You need to identify native phrasing, spelling variations, slang, and local search behavior specific to that market.
Check Real Search Volume
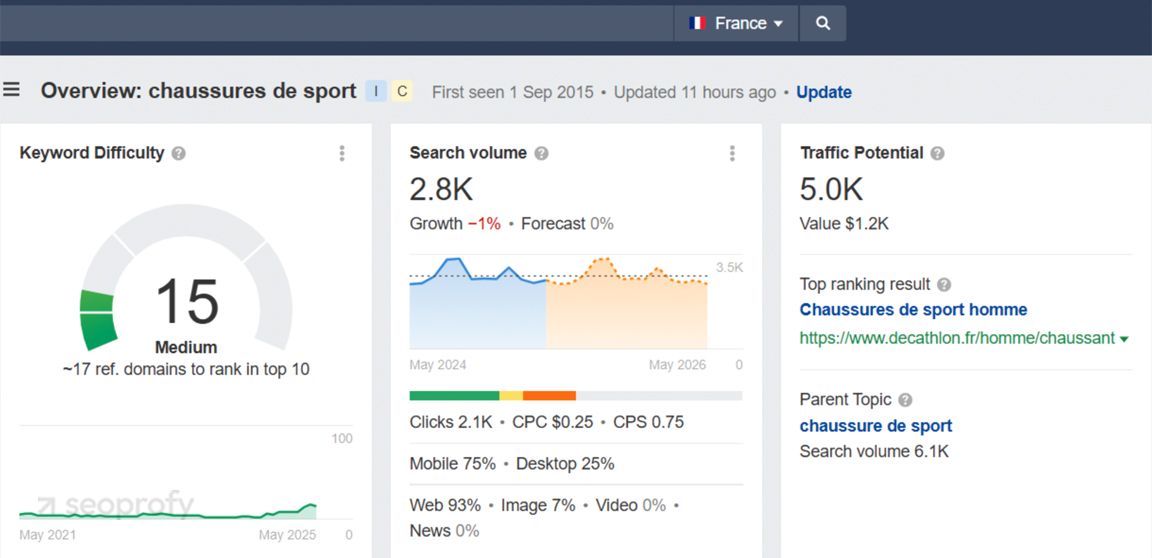
Start by setting your location and language settings in tools like Google Keyword Planner, Ahrefs, or Semrush. Use the same country and language that your target audience uses. For example, a keyword like “sneakers” may translate to “chaussures de sport” in French, but locals might search “baskets” instead.
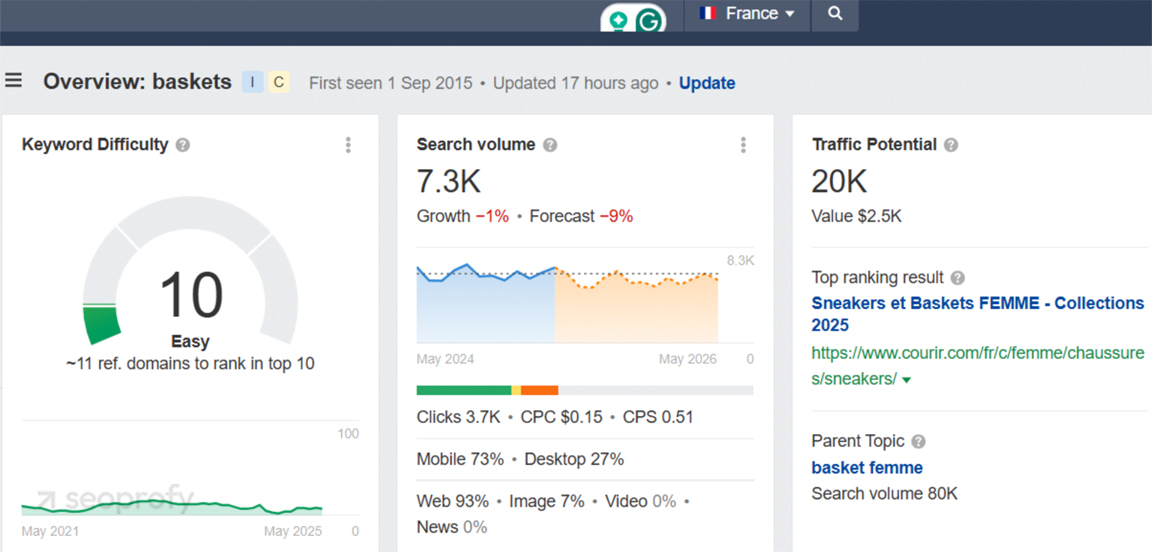
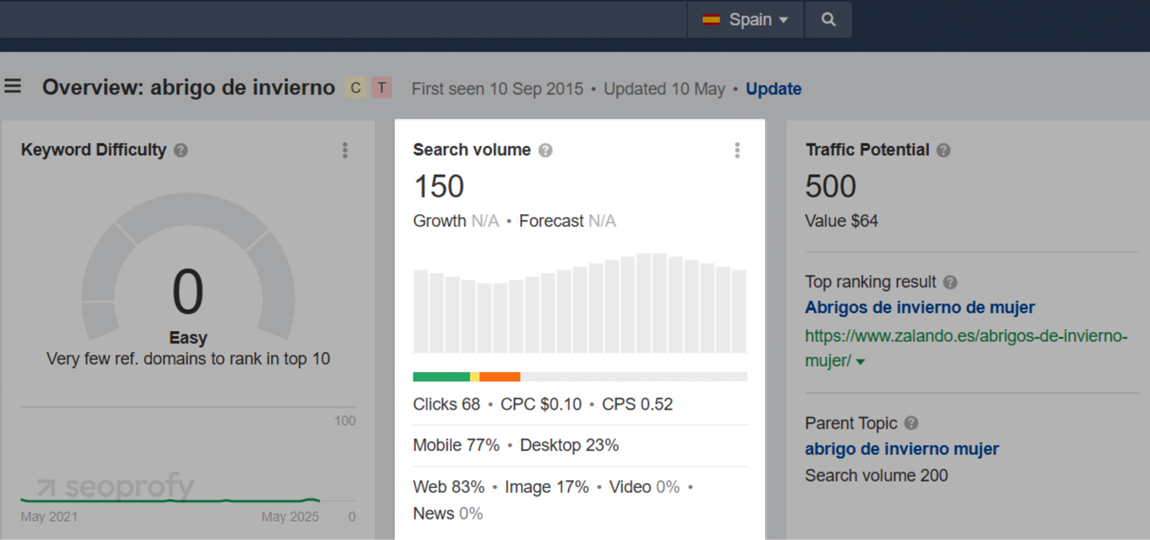
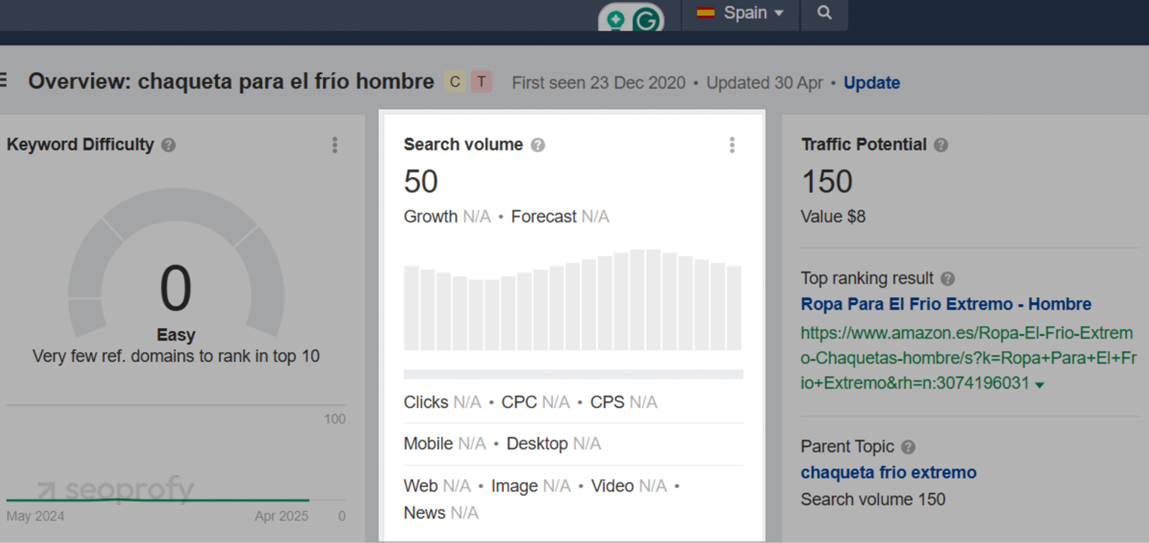
In Spain, users might search for “abrigo de invierno” (winter coat) but sometimes use informal phrases like “chaqueta para el frío hombre” or even “ropa que abrigue.” These variations don’t follow textbook phrasing, but they show up in real queries and should be reflected in your keyword list. Without researching local usage, you will miss real search volume.
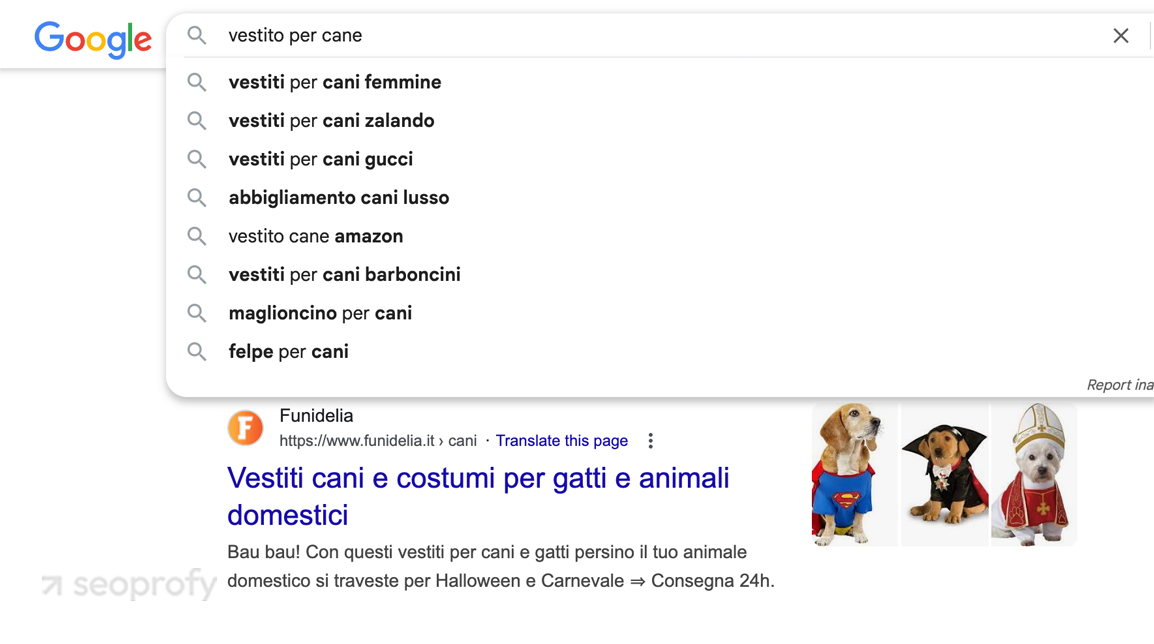
Use Google Search Console to review actual queries by region if you already have international traffic. Pair that with autocomplete and “People also ask” results from the local version of Google (such as google.fr or google.de) using a VPN or location emulator like Valentin.app or Nightwatch.io.
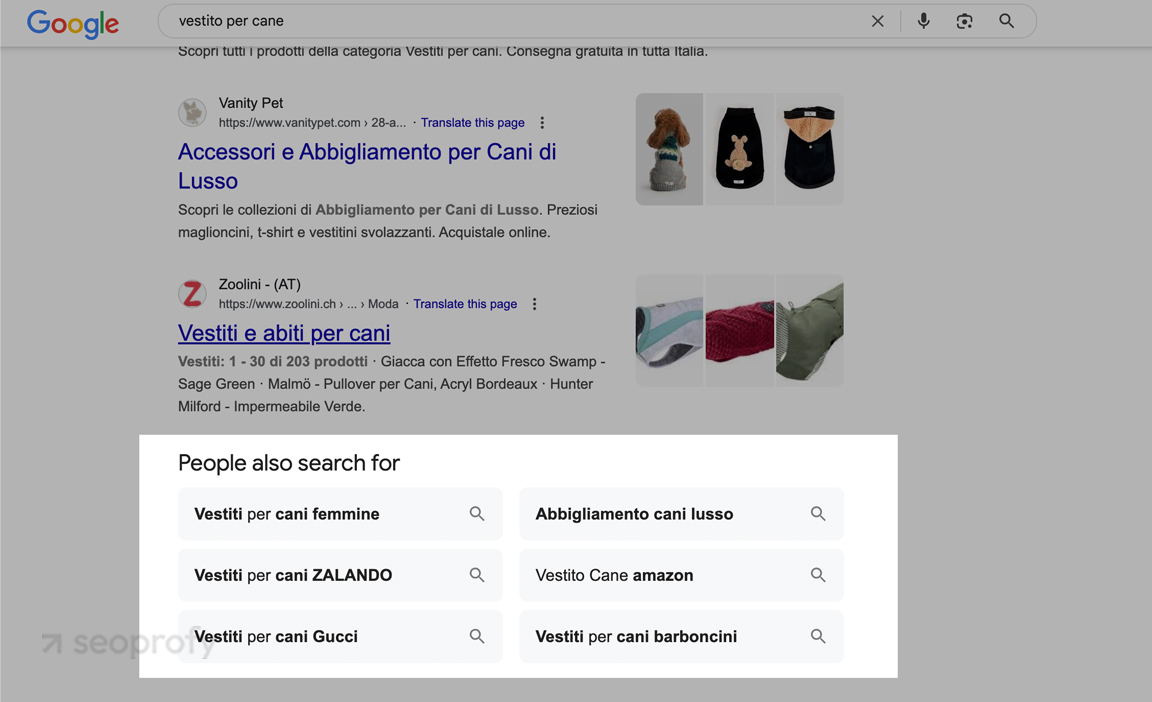
Find Gaps in Local Search Coverage
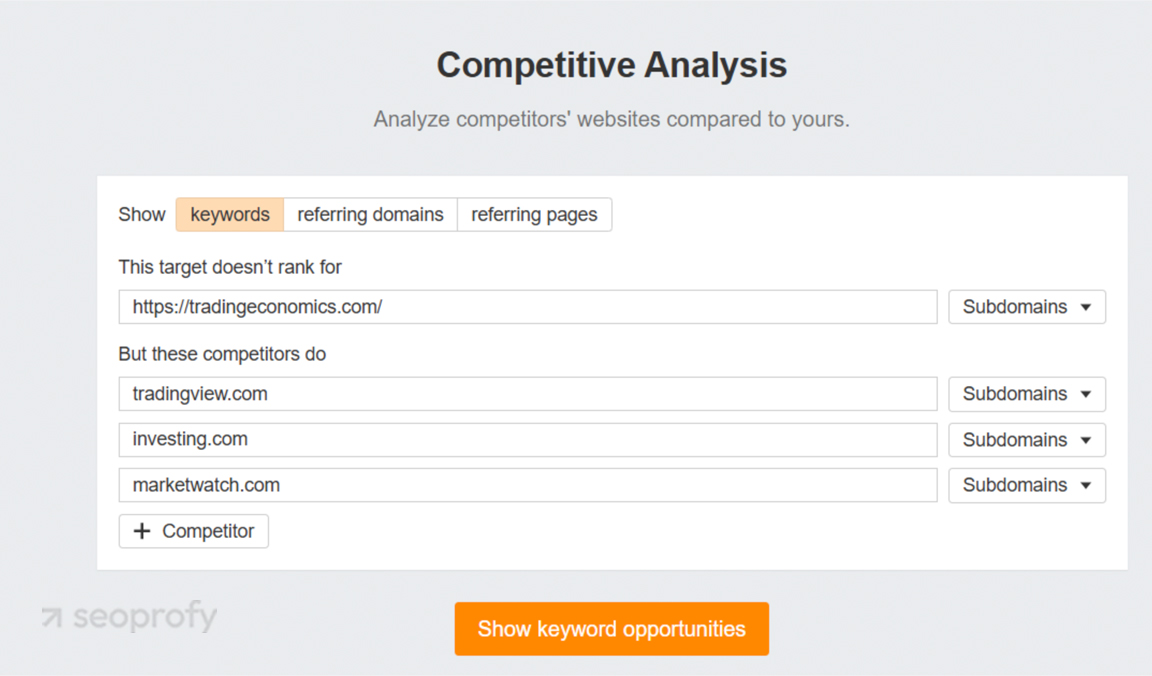
Check local search competitors’ sites. Use Ahrefs’ “Content Gap” feature to compare their ranking keywords against yours.
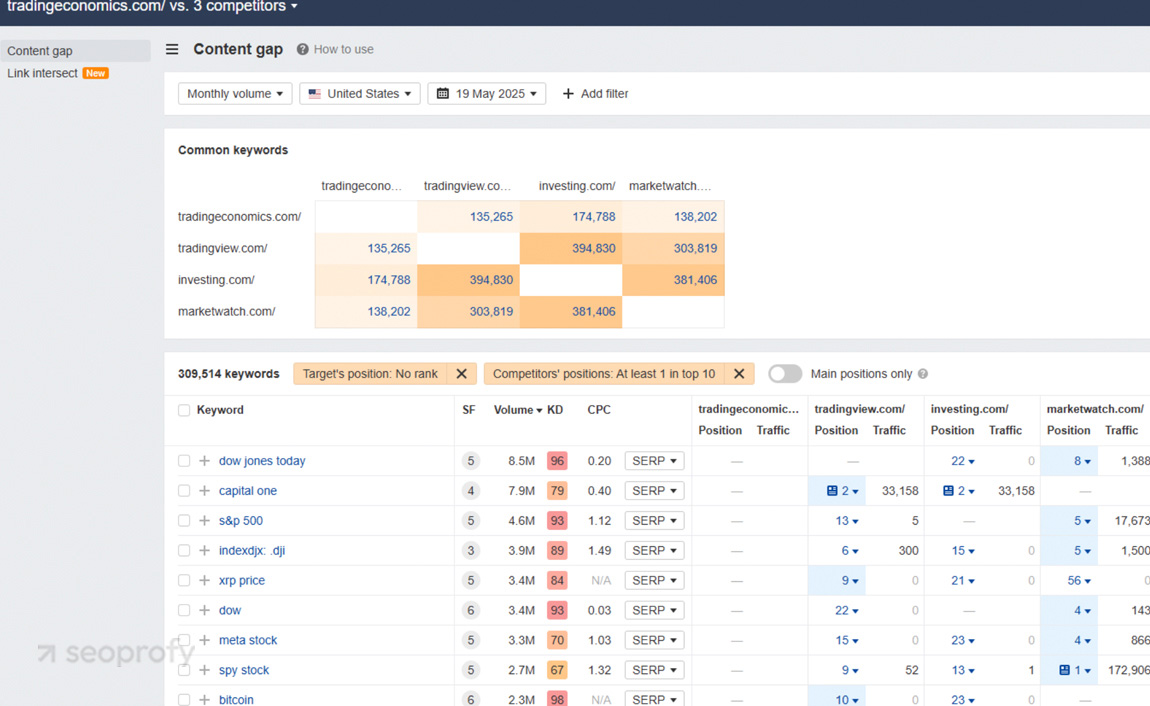
Here’s an example. We ran TradingEconomics.com against three competitors: TradingView, Investing.com, and MarketWatch. All of them have region-specific visibility.
We filtered by the US market and lower keyword difficulty to find missed opportunities. The screenshots below highlight both high-volume and low-competition gaps, such as “voo” and “bbai stock,” where competitors already get traffic but TradingEconomics has no global online visibility.
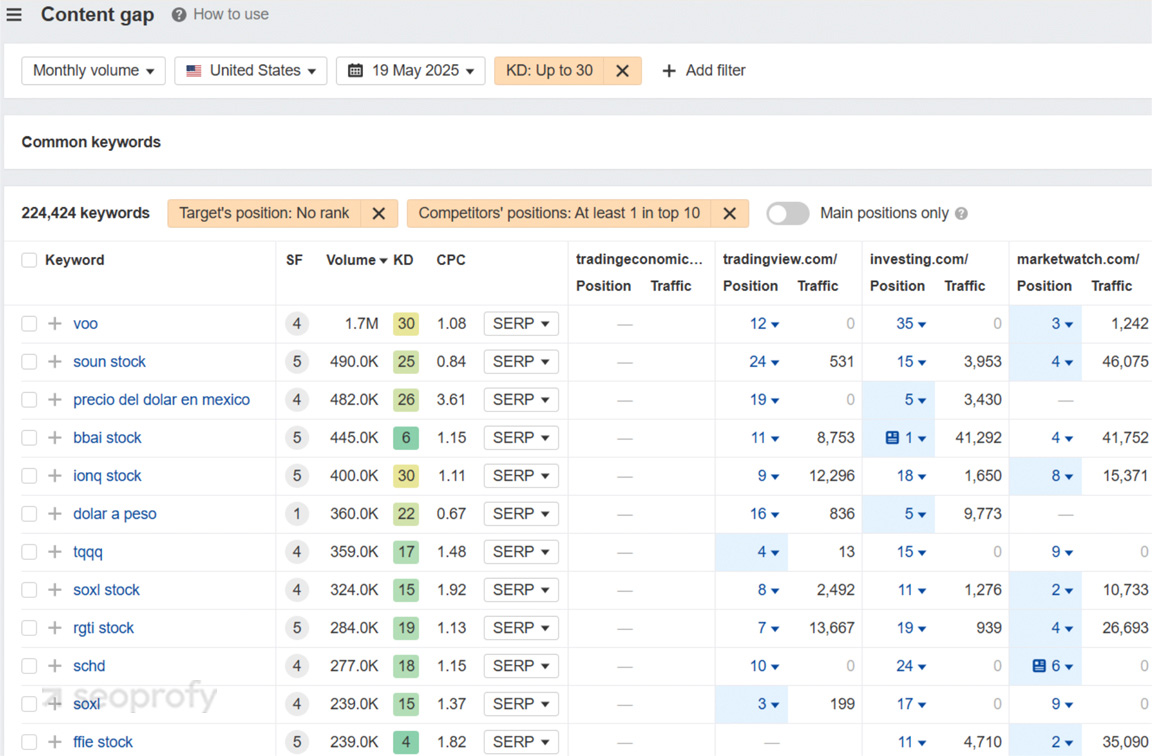
Pay attention to long-tail terms and modifiers as well as direct short queries. Locals often include geo, product specifics, or even holidays in queries. These keywords may have lower volume, but they often signal stronger intent and are easier to rank for. Moreover, on average, longer search terms receive 1.76 times more clicks than queries made up of just one word. To build an SEO strategy that performs across regions, combine both short and long-tail terms to balance search volume with intent to convert.
Compare Search Intent Market by Market
Once you build your keyword list, check search intent. A term might have informational intent (seeking answers or education) in a specific target market and transactional intent (ready to buy) in another. Ahrefs highlights this visually with colored intent labels.
For example, the word “purse” in the US usually refers to a woman’s handbag, while in the UK it often means a wallet and can apply to men as well. So, the local search results are completely different in structure and target audience.
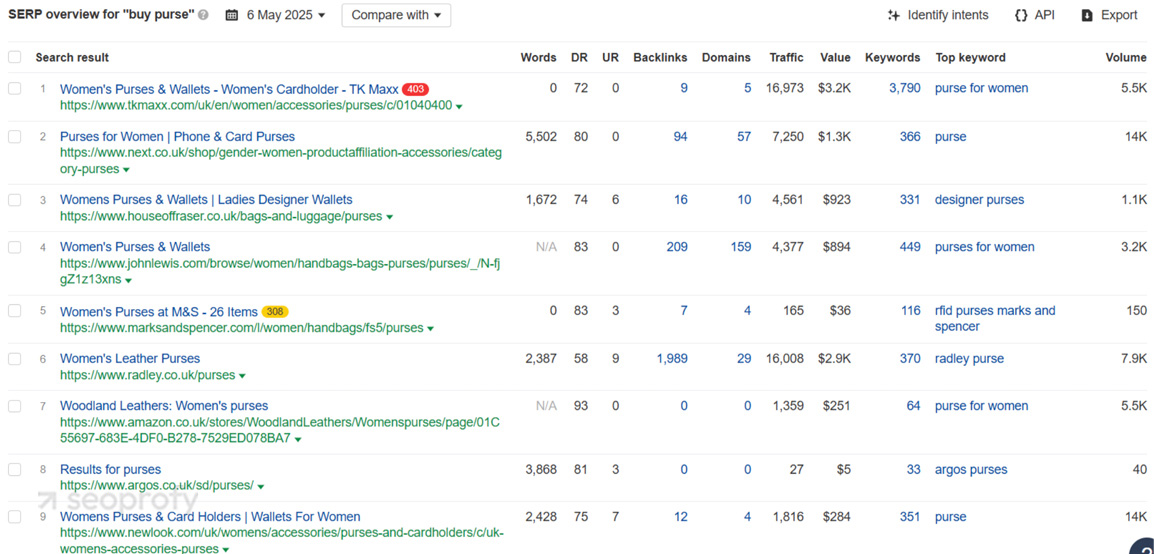
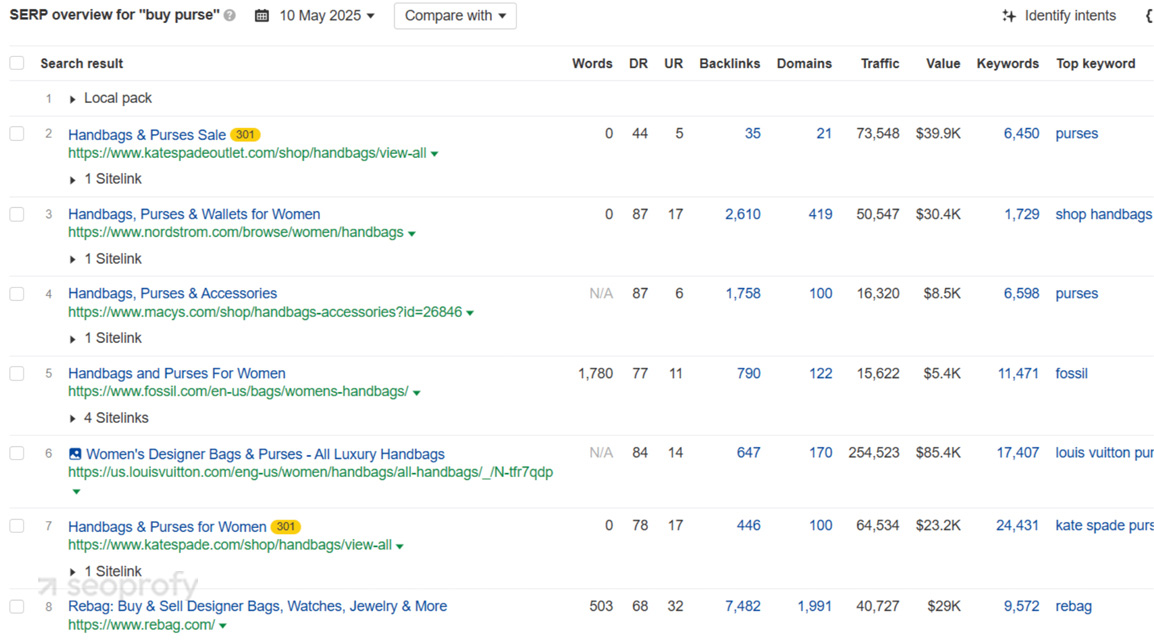
Group Search Terms to Guide Local Content Strategy
Finally, cluster relevant keywords by target language, region, and intent. This will guide your content structure and prevent cannibalization (when multiple pages target the same query and compete against each other). Below is a sample keyword cluster for skincare in Spanish search engines to show how this might look in practice.
*Please note that this is a hypothetical example created for illustration, not a research-based cluster.
|
Keyword |
Language |
Region |
Intent |
Notes |
| crema hidratante piel seca | Spanish | National | Informational | Blog or comparison page |
| comprar sérum ácido hialurónico Madrid | Spanish | Madrid | Transactional | Local landing page |
| mejores cremas antiedad 2025 | Spanish | National | Informational | Year-specific, content for seasonal updates |
| oferta protector solar Valencia | Spanish | Valencia | Transactional | Regional promo query |
| cómo aplicar contorno de ojos correctamente | Spanish | National | Educational | FAQ or how-to section |
Adapt Your Content for Local Culture
Content that ranks is content that feels local. That perception has a direct impact on engagement, relevance, and international SEO performance in the region.
Tone and Phrasing
Tone and phrasing must match local context and expectations. In some markets, informal language and idioms create trust, while in others, users prefer neutral or formal communication. For example, an English CTA like “Grab yours now” might sound friendly and urgent in the US but could seem unprofessional in Germany, where “Jetzt kaufen” or “Jetzt bestellen” is more appropriate. Meanwhile, in Japan, overly assertive wording may feel disrespectful or pushy.
Currencies, Units, and Formatting
Pay attention to currencies, units, and formatting. An American reader might hesitate if a product description uses centimeters or liters, like here:
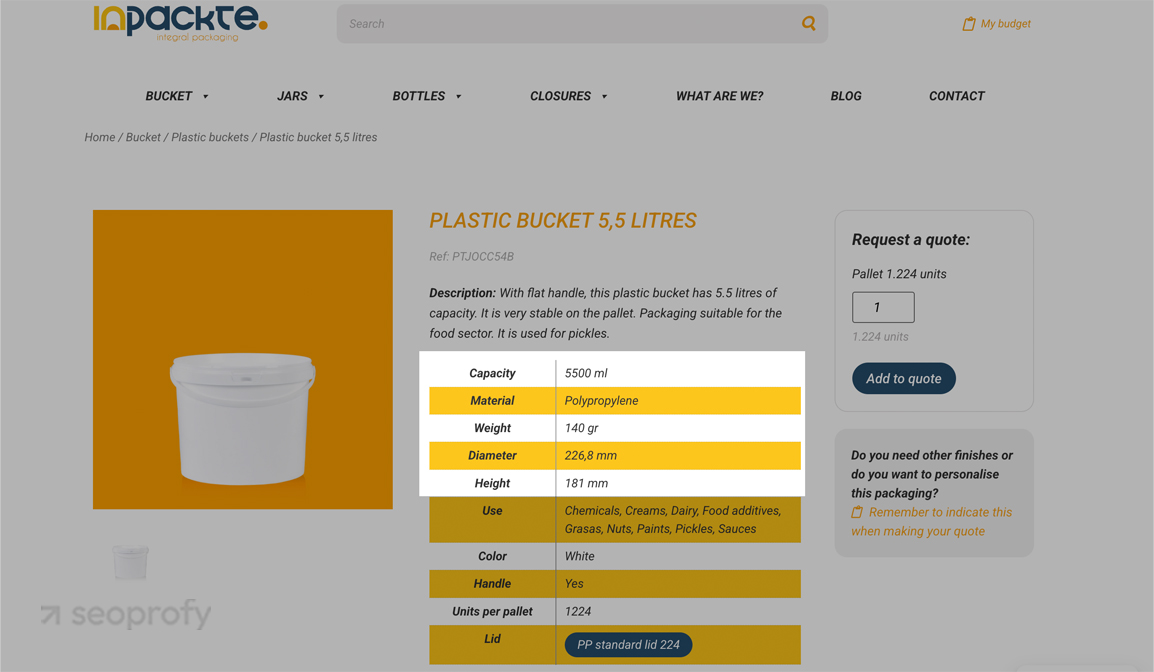
At the same time, a European audience may struggle with feet, ounces, or dollar pricing. These small mismatches affect how comfortable users feel and may lower engagement or trust without them even realizing why.
Visual Content
Ensure visual content aligns with local cultural expectations. For example, beachwear might be appropriate in one market but could cause backlash in another. Research market sensitivities before using imagery.
There are many examples of poor localization leading to widespread criticism. For instance, in 2018, Dolce & Gabbana launched a campaign in China showing an Asian model awkwardly eating Italian food with chopsticks. It was widely seen as disrespectful and culturally tone-deaf. After the backlash and calls for a boycott, D&G’s market share in the Asia-Pacific region dropped from 25% to 22% within months. The long-term impact was significant, as D&G has yet to recover to its pre-incident market share levels in Asia-Pacific.
Use Technical SEO for Localization
Technical SEO for localization starts with choosing the right URL structure for each market. You have three main options:
- Subdomains (fr.example.com)
- Subdirectories (example.com/fr)
- Country-code top-level domains (example.fr)
Subdirectories are often easiest to manage and keep all authority within one domain. Subdomains often require extra SEO efforts, as search engines treat them as separate websites, which can complicate backlink strategies. Country-code domains offer the strongest geographic signal but require more resources to maintain and promote independently.
Next, implement hreflang tags to tell local search engines which version of a page to show users based on their language and location. Each localized page should reference all other variations using hreflang, including itself. Make sure every language version includes a canonical URL and matches the hreflang implementation to avoid duplicate content issues.
You can add hreflang tags in three ways:
- In the HTML head
- In HTTP headers (for non-HTML files)
- Via an XML sitemap.
For large sites, sitemaps are usually easier to manage and keep clean. Use tools like Merkle’s Hreflang Tag Testing Tool or Sitebulb to validate implementation.
Make sure your localized pages are indexed. Submit them in separate sitemaps per language if possible. Monitor crawl stats and indexing status in Search Console by country version.
From research to rollout, we make sure your site ranks and performs in every region you serve. You get:
- Better rankings in country-specific SERPs
- Local content that brings qualified leads
- Clean, SEO-ready structure for each locale

Common SEO Localization Pitfalls
Localized pages are a part of international SEO, and even if they can look polished and complete, but still fail to gain search visibility. The issue often lies not in the content itself, but in how the site signals that content to search engines. Below are the most frequent issues we encounter during audits and how to solve them before they start affecting results, especially when managing content in multiple languages.
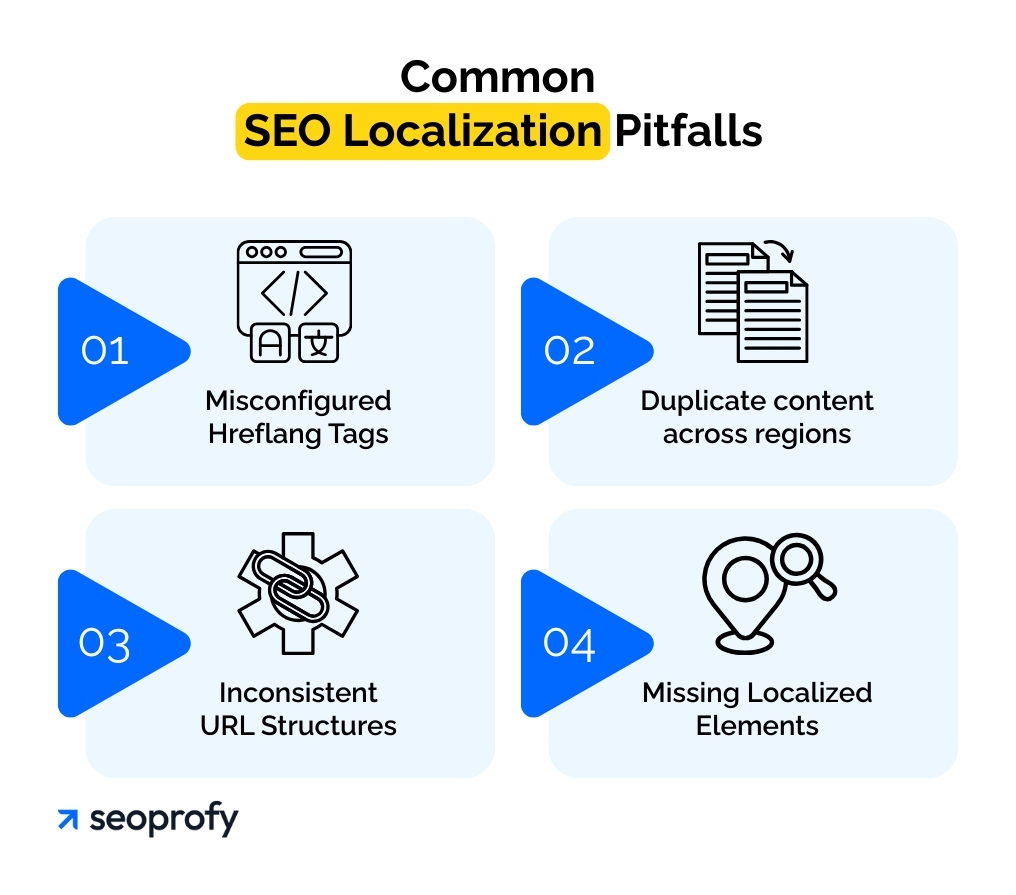
Misconfigured Hreflang Tags
Hreflang is one of the most misunderstood aspects of technical SEO. Pages often reference the wrong language or country code, skip self-referencing tags (telling search engines the page is part of the multilingual group), or fail to establish reciprocal links between variations. These gaps confuse search engines and can result in incorrect indexing or visibility issues.
Always use valid ISO 639-1 language codes and ISO 3166-1 country codes. Every localized page should reference all other versions, including itself. In large sites, one of the most reliable SEO localization tips is to implement hreflang in XML sitemaps rather than directly in HTML, especially when templates vary across regions. This minimizes human error and helps keep everything consistent across versions.
In the end, ensure correct ISO codes, self-referencing tags, and mutual referencing for all language versions. Use an hreflang testing tool like Sitebulb to catch errors before they affect your rankings.
Duplicate content across regions
Publishing translated versions of the same content without proper signals can trigger duplicate content concerns. This is especially risky if URLs are similar and hreflang is missing or broken. To avoid this, use hreflang and canonical tags together correctly. Canonicals should point to the local version of the page, not a global default.
If multiple regional versions exist with only minor language differences (such as UK vs. US English), canonical confusion becomes especially risky. Google may pick one version to index and ignore the rest.
Also, avoid auto-redirecting users based on IP without allowing search engines to crawl alternate versions. Instead, let Googlebot discover each localized version through internal linking and hreflang references. This approach follows white hat SEO practices and ensures that regional pages remain indexable, distinct, and aligned with Google’s guidelines.
Inconsistent URL Structures
Using a mix of subdomains, subdirectories, and ccTLDs across markets leads to confusion for both users and search engines. Stick with one structure and apply it uniformly across all localized versions. This choice impacts crawl management, reporting accuracy, and the way backlinks are distributed.
Changing structures mid-project (for example, moving one region from a subdirectory to a ccTLD) can break existing links and hreflang maps. Also, avoid URL naming that looks local but is not actually localized in content. For example, using the @type: Product schema with English-only fields on a Japanese page can reduce rich result eligibility.
Missing Localized Elements
Some pages carry over default metadata, headings, or visuals. These leftovers reduce relevance and make the content feel generic. This problem requires additional SEO localization efforts. Always check that language, titles, meta descriptions, and media match the target region.
Stock visuals with Western faces in content for Asian markets, or untranslated CTAs in a fully localized article, send mixed signals. Beyond visuals and text, even elements like structured data should match the local language, where supported. For example, using the @type: Product schema with English-only fields on a Japanese page can reduce rich result eligibility. Search engine localization must extend across visible and invisible layers of content.
Unchecked technical issues often explain why strong localized content fails to perform. A structured audit process helps surface these blockers early and keeps multilingual SEO performance aligned with your global strategy.
Track and Measure the Results and ROI of SEO Localization
To understand if your SEO localization strategy is working, you need to measure performance at the market level. Start by defining what success looks like for each region. This could be:
- More organic traffic
- Search engine rankings improvements
- Conversions
- Revenue tied to SEO content localization
Without clear SEO goals, you will struggle to attribute results.
Next, configure Google Search Console for international targeting. If you use subdirectories, make sure they are properly linked and crawled. If you use subdomains or ccTLDs, verify each property separately. Use the Performance report to segment data by country and query. Look for increases in impressions, clicks, and average position across your localized URLs.
Google Analytics (or GA4) lets you track behavioral metrics by a particular location. Segment your reports by country or language and watch for differences in bounce rate, average session duration, and conversion rate. If localized pages drive traffic worldwide but show poor engagement, it could be a sign that website content, UX, or expectations do not match the region.
Set up keyword tracking using a tool that supports geo-specific SERP data. In Ahrefs or Semrush, track your localized pages against region-specific search terms. Use different keyword lists for each market and monitor ranking movements over time. Combine this with URL-level data to catch mismatches between search engine rankings and actual traffic.
To calculate ROI, compare the cost of localization with revenue from the region. That includes:
- Translation
- Implementation
- Localized content
- Tool subscriptions
You can approximate regional ROI by looking at ecommerce revenue or goal completions by country in Google Analytics. If exact revenue data is not available, use proxies like lead volume or signups.
Regular reviews help catch drop-offs early. Schedule monthly check-ins to monitor changes and compare performance across international markets.
Tools for SEO Localization
While outlining SEO localization best practices, we mentioned a number of tools that simplify everything from multilingual keyword research to hreflang validation. For your convenience, we’ve collected all the best SEO tools in one table, along with notes on cost, functionality, and what each one is best used for.
| Tool | Purpose | How to Use | Cost | Notes |
| Ahrefs | Customized keyword research, backlink analysis, and competitor tracking | Find region-specific keywords and analyze backlinks of local competitors in target countries | Paid | Supports regional filters for most major markets |
| Semrush | Keyword tracking, site audits, localization insights | Track rankings by location and optimize content for regional keyword variations | Paid | Includes location-based SERP tracking |
| Google Search Console | Performance tracking by country/language | Monitor how your localized pages perform in different regions and languages | Free | Shows clicks, impressions, and query data per region |
| Google Keyword Planner | Keyword research by location/language | Discover popular local search terms and compare them across markets | Free | Requires a Google Ads account |
| DeepL | High-quality machine translation | Translate seed content before localization or use it to QA existing translations | Free with limits / Paid | More accurate than Google Translate for most languages |
| Weglot | Website translation management | Automatically localize your site structure and content with hreflang and language switcher setup | Paid | Integrates with most CMS platforms |
| Sitebulb | Technical SEO audits, including hreflang checks | Audit localized pages and check for missing or incorrect hreflang implementations | Paid | Visualizes site structure and hreflang clusters |
| Merkle Hreflang Tags Tool | Hreflang tag checks | Validate the hreflang tag setup to ensure the correct targeting of regional content | Free | Useful for spot-checking implementation |
For most global businesses, a mix of free and paid tools works best. Use GSC and Keyword Planner for foundational data, and layer on tools like Ahrefs or Sitebulb if you need deeper insights or more advanced audits.
Implement Your Localization Strategy for Global Success
Website localization best practices for SEO are what allow a business to grow internationally without losing control over structure, rankings, or conversions. But implementation rarely goes smoothly. Most teams face the same issues: no clear regional keyword lists, messy hreflang tags, duplicated content across markets, and analytics that cannot be segmented properly.
At some point, patching things manually stops working. That’s when expert SEO localization becomes essential. It involves setting up region-specific keyword tracking, creating content that aligns with local search preferences, and adjusting for variations in search engine market share. Additionally, addressing translation and localization, refining URL structures, and resolving indexation issues across multiple site versions are key steps in achieving a tailored and effective SEO strategy.
We help companies do exactly that. As an international SEO company, we audit what is already in place, define what is missing, and help build a process that works across markets. Whether you manage five country sites or twenty, we make sure your pages rank, convert, and scale without falling apart under growth.
If your team is already spread thin or stuck fixing the same issues every quarter, let us help you build an SEO localization system that holds together. Check out our SEO case study for an international website to see how we approach it in practice.