Ecommerce SEO is the process of optimizing your online store so it shows up higher in unpaid search engine results pages (SERPs) when people search for products like yours. This includes improving page content, product descriptions, metadata, and site structure to follow Google’s best practices and match what shoppers are actively looking for.
This ecommerce SEO guide combines core principles with expert-level tactics, making it useful for both business owners and SEO professionals. It walks you through essential areas like keyword targeting, site architecture, technical SEO, and link building — all customized to drive real results.
Every improvement, no matter the size, helps boost your search rankings and attract users actively looking for your products. The guide includes actionable tips and pro strategies to help you convert visibility into sales and build a stronger market position.
- Prioritize category and product pages — they bring in the most traffic and need strong optimization.
- Fixing technical SEO issues alone can greatly boost visibility.
- Target long-tail keywords with buying intent to drive more conversions.
- Blogs can support SEO but are not essential for ecommerce, as product pages convert better.
What Is Ecommerce SEO?

Ecommerce SEO is a strategic approach to driving traffic to your online store by enhancing its visibility on search engine results pages (SERPs). Achieving higher rankings is essential, as well-ranked pages attract more visitors, ultimately increasing sales potential. This approach mainly focuses on practices like:
- Finding the best keywords
- Fixing technical issues
- Writing SEO-friendly content
- Getting links from authoritative sites
- Improving on-page elements
Why Is SEO Important for Ecommerce Websites?
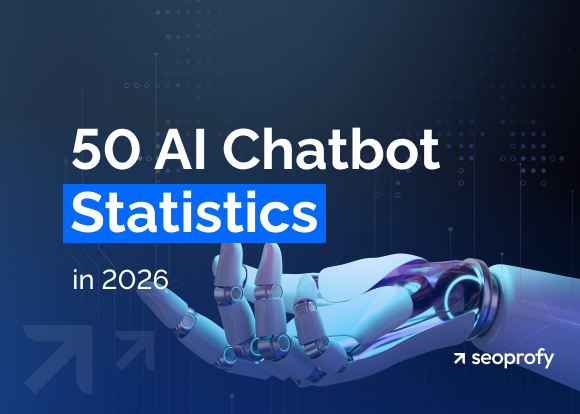
Data shows that 93% of internet users start their research in search engines. So when you optimize your store for relevant keywords, more people can find your products and consequently buy from you.
Moreover, 23% of overall orders in ecommerce come from search, which shows that SEO not only brings more visitors, but it also converts them. As for the other benefits, a well-executed SEO strategy can help store owners see:
- Better long-term ROI in contrast to ads
- Faster loading pages and smoother UX
- Increased brand authority and credibility
And now, let’s see the exact steps on how to do SEO for an ecommerce website.
7 Steps to Improve Your Ecommerce SEO

Ecommerce Keyword Research
The first step in every SEO campaign is keyword research. This is the process of finding the exact terms and phrases your potential customers use when searching for your products online.
It sets the basis for all the following optimization tasks on your website. For example, you need to have a list of your keywords ready before you start to optimize your product and category pages. That said, here’s how you can find search terms for your site:
Explore Keyword Research Options
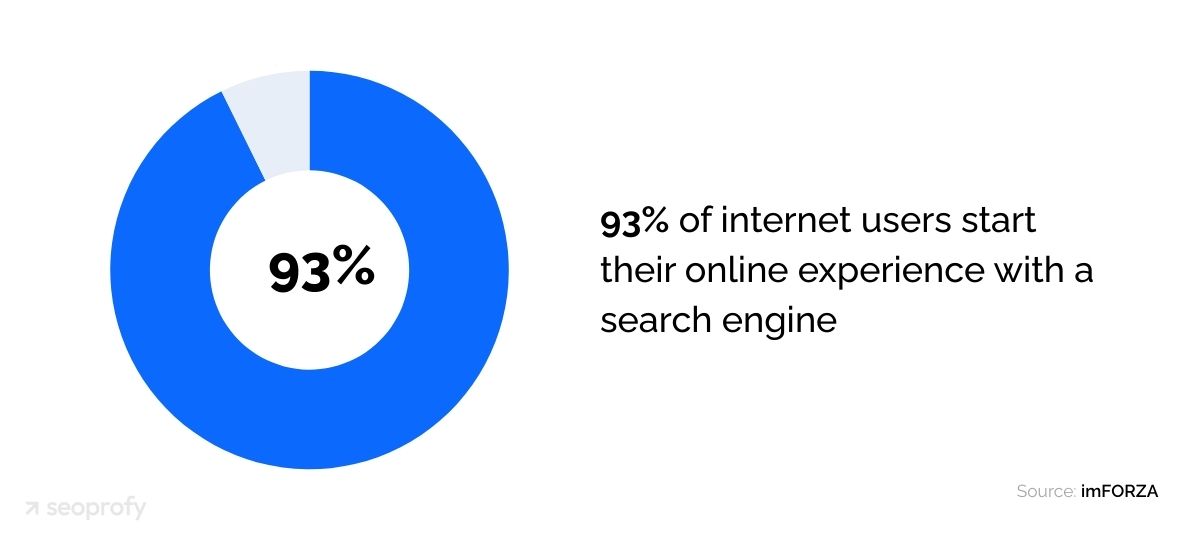
There are several ways to do keyword research for ecommerce. You can start with Google Keyword Planner. It’s free, and you can use it to check average monthly searches for your terms and see how much marketers are bidding for them.
High cost-per-click usually means better buying intent. So, even if keywords have lower search volume but higher CPC, they can still lead to more sales for your store. Here’s how the report looks in Google Keyword Planner:
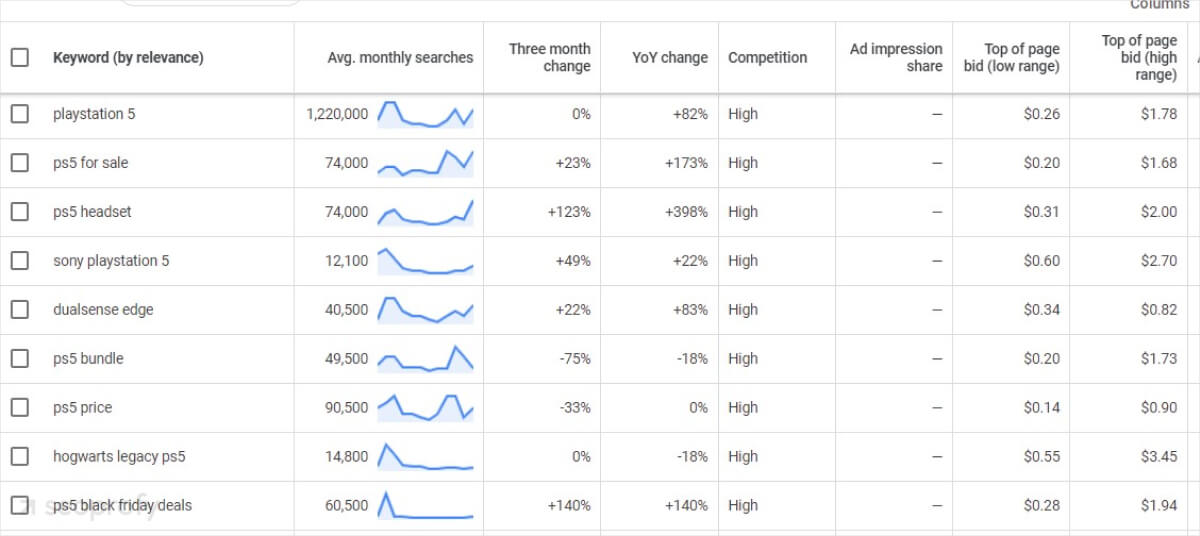
Another free way to find keywords for your product and category pages is Amazon’s suggestions. To do this, go to Amazon and type your main product terms in the search bar, followed by each alphabetical letter. You’ll find specific features and variations people are searching for.
For example, when selling office chairs, you might find that people frequently search for “office chair with lumbar support.” This can be a perfect product filter opportunity for your store.
You can also check out how Amazon and other big ecommerce sites organize their sites. Look at their product menus for keyword and category ideas.
For example, if you have a jewelry store, you can type in “engagement rings” to see how other shops sort and organize products in your niche.
If you want a more in-depth analysis of your keywords, you can go with a leading market tool, Ahrefs. In addition to advanced ecommerce SEO metrics, it shows you the exact search terms your competitors rank for. You can find these by doing the following:
- Open Ahrefs’ Site Explorer
- Type in the competitor’s domain
- Navigate to the Organic keywords report
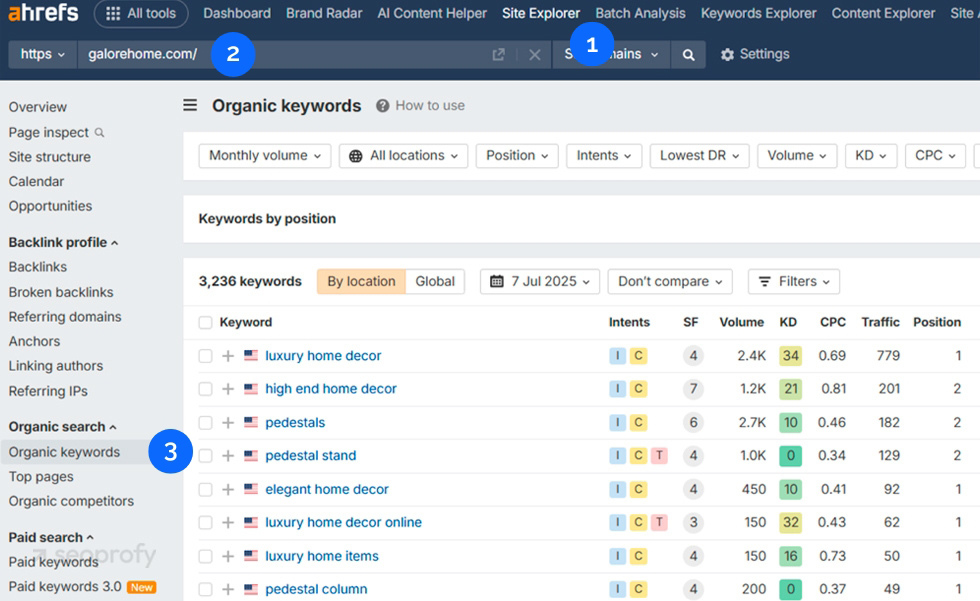
To check pages that bring your competitors the most traffic, simply go to the Top Pages report:
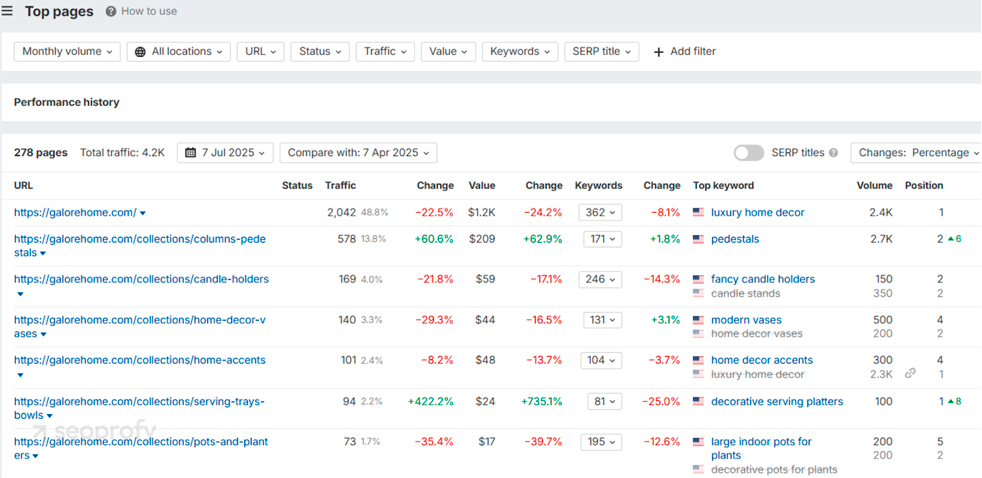
Once you’re inside the report, here’s what you can do:
- Check which categories are driving the most traffic
- Look for specific product pages that attract a lot of visitors
- View the keywords these pages rank for to find new opportunities.
While in Ahrefs, you can make use of another helpful feature: competitive analysis. This shows you the keywords that other ecommerce stores in your niche rank for that you don’t. All you need to do is add the URLs of your competitors’ sites.
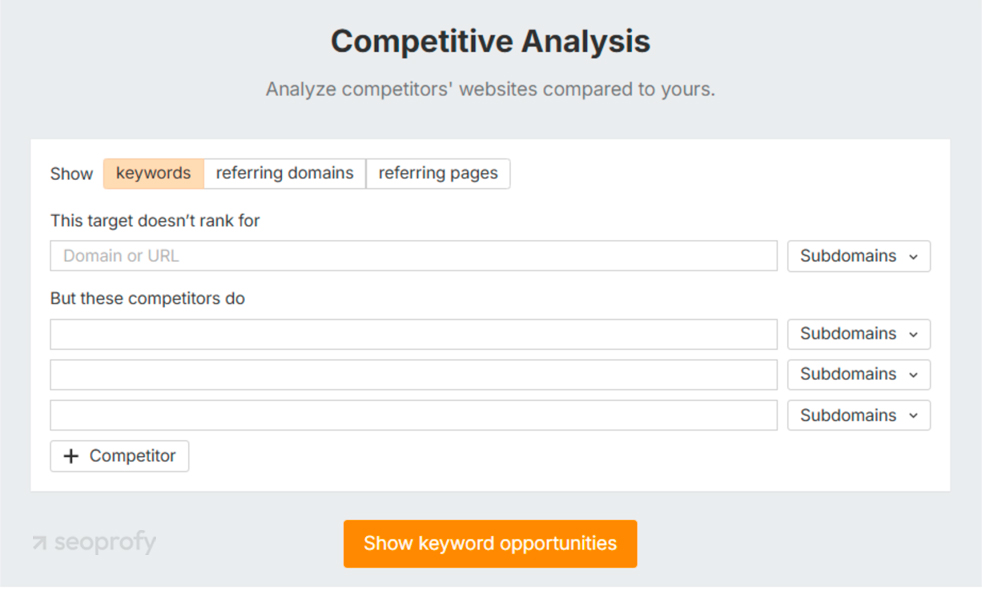
Although these tools show you data, understanding buyer intent makes you money. This brings us to our next section.
Define Search Intent
A big part of keyword research is analyzing search intent, which is the reason why someone searches online. The most common types of search intent in ecommerce are:
- Informational: Users are just looking around for information. These searches get tons of traffic but rarely lead to quick sales. For example: “How to pick a coffee maker“.
- Transactional: People want to compare certain products and are almost ready to buy, e.g., “Nike vs Adidas running shoes.“.
- Commercial: Users know what they want and have their credit card ready. These are your best searches. For example: “buy an iPhone 16.“

Why is it important for your ecommerce SEO strategy? Google strives to provide users with the most relevant content that matches their intent. So if the content on your site doesn’t align with what people expect to see, you won’t be able to rank well in search engine results pages.
One way to define the user intent is to look at Google’s first page for your keyword. You can also see the intent in a keyword research tool. Here’s how it looks in Semrush:
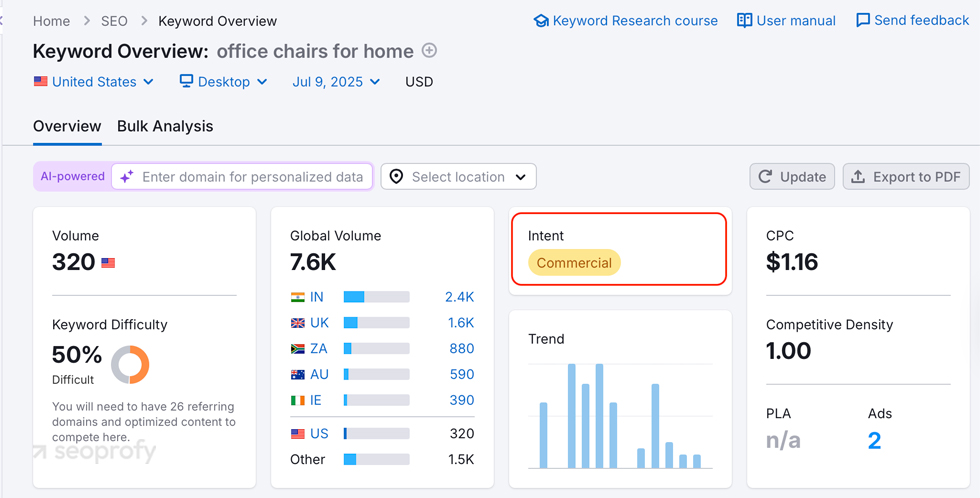
Your best bet is to focus primarily on long-tail keywords with a commercial intent. This way, you can zero in on those searches that are most likely to result in conversions.
Choose the Right Keywords for Your Ecommerce Website
Now that you have a list of keyword ideas, the next step is to analyze them to see if they are worth going after. For this, you’ll need to check their search volume, keyword difficulty, relevance, and competitiveness.
Search volume tells you how many people look for this term each month. A keyword with many searches might seem great, but sometimes it can be too broad and very competitive.
So the optimal approach is to find the ones that have decent search volume and low keyword difficulty (more on that later). This is how these metrics are shown in Ahrefs:
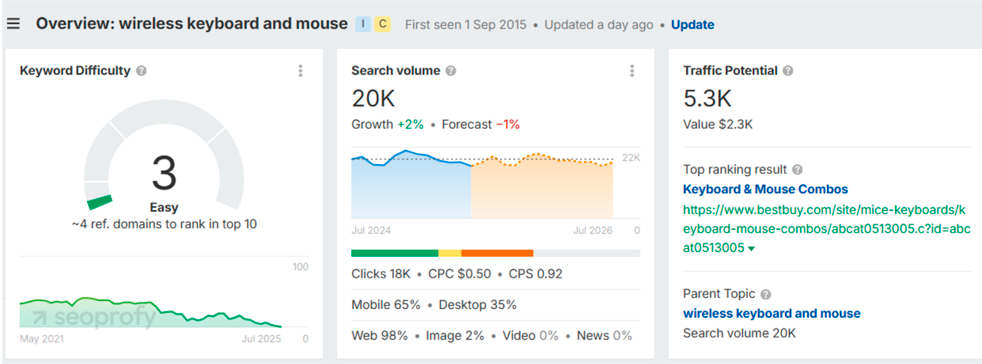
The other thing worth mentioning is traffic potential. It’s different from search volume because instead of just showing how many times a specific keyword is searched, it gives you an estimate of the total traffic you could attract if you rank for that search term.
Next, you would want to check how competitive the keyword is. How to do it? Simply go to Ahrefs’ Keyword Difficulty Checker.

It’s a helpful tool that shows you how hard it would be to rank for a certain search term. The best part? You can use it for free.
First, you need to enter your keyword into the search field. Then, click “Check keywords.” Here’s what you’ll see once you hit the button:
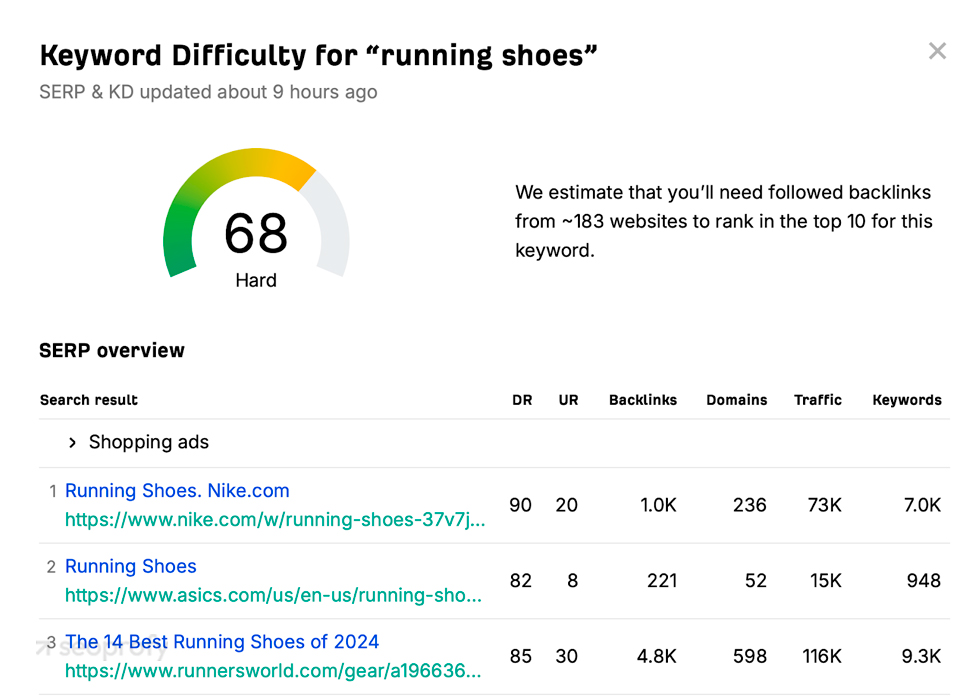
As a rule of thumb, the higher this number is, the harder it’ll be for you to rank for it. So, try to focus on search queries that have a score between 20 and 40. These are your winning tickets to rank well on Google.
The other thing that matters when choosing keywords for your ecommerce SEO is relevance. If the search term isn’t a close match for your products, you’ll likely attract visitors who aren’t interested in buying what you’re selling. So when looking at your keyword ideas, ask yourself the following questions:
- Does it match what I sell?
- Is it related to my product categories?
This way, you can know for sure that you’re targeting the right audience.
Make the Most of Keyword Clusters
Once you have the list of your search terms at hand, it’s important to organize them to maximize the results of your ecommerce SEO efforts. For this, you’ll need to identify keyword clusters and parent topics.
Keyword clusters are groups of similar or related search terms. For example, if you’re selling dog food, you might also include variations like “chewy dog food” or “fresh pet dog food.”
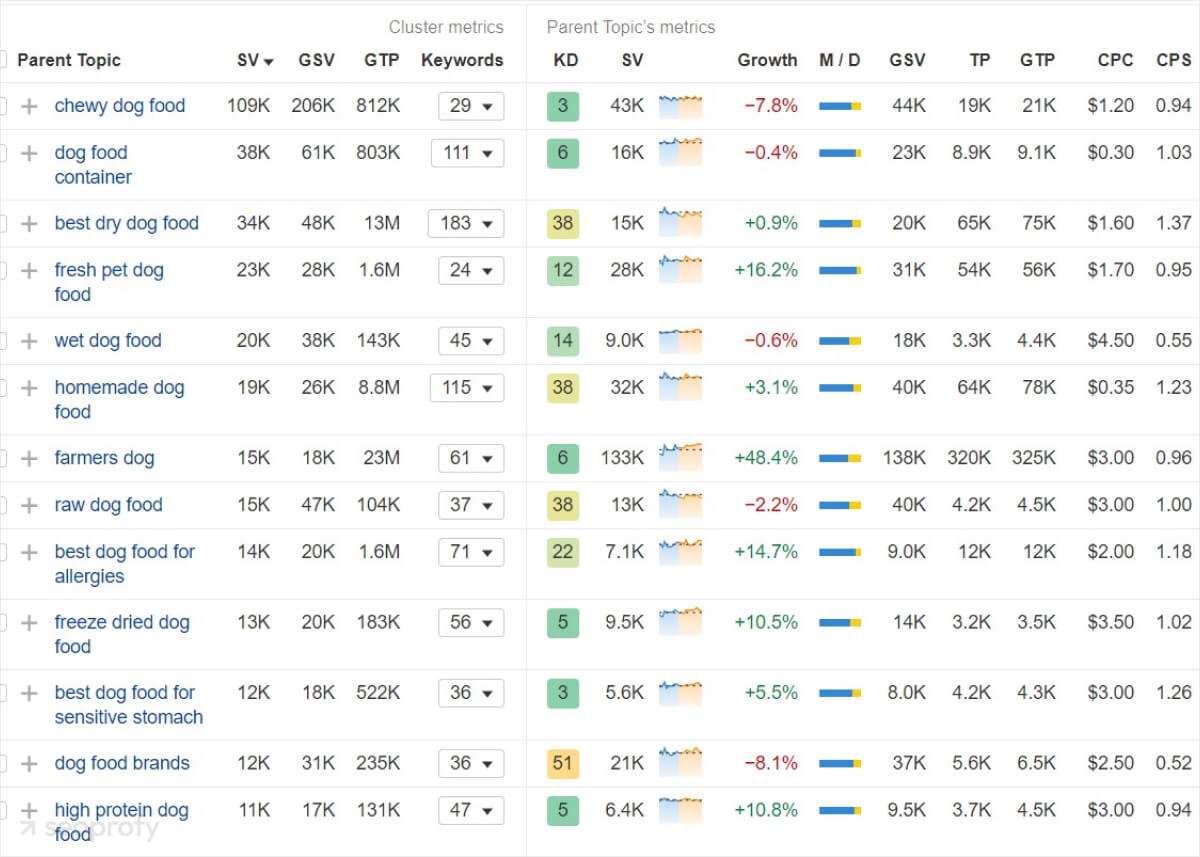
This clustered structure is an important part of a content strategy for ecommerce wesbsites. It shows which pages to build first, how to organize product and category content, and where internal links should connect ideas, which leads us naturally to the next section.
Site Architecture for Ecommerce
Site architecture is responsible for how your pages on your site are organized and arranged. It’s super important for both user experience (UX) on your site and also for Google. Mostly because an optimized architecture helps search engines find and crawl all of your product and category pages and show them in search results.
As a rule of thumb, you need to organize your site in a way that enables visitors to reach any product from your homepage in 3-5 clicks. Here’s how to do this:
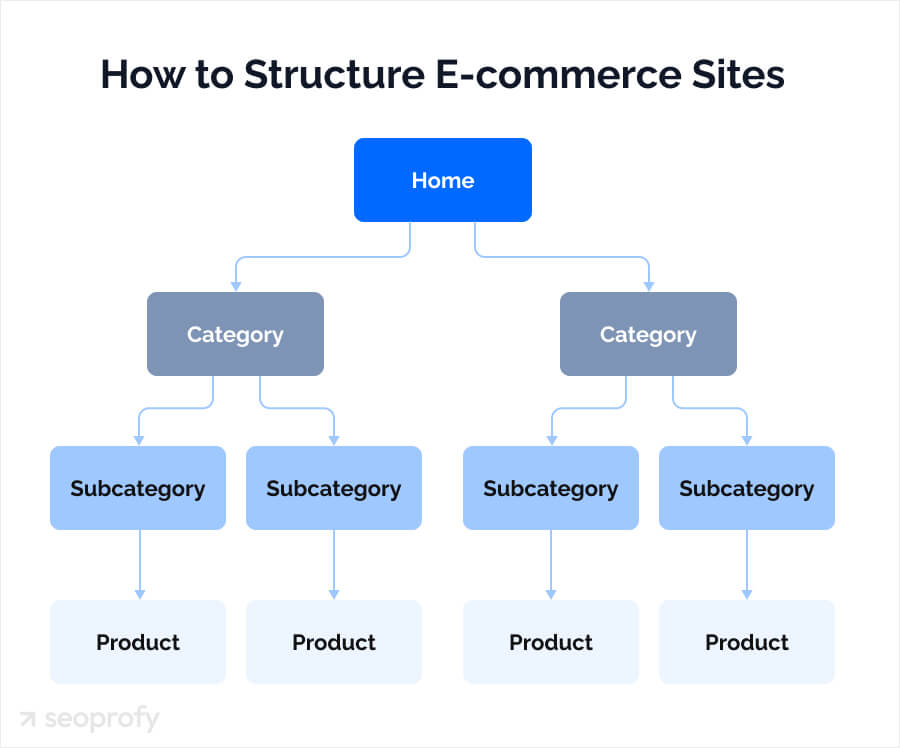
For example, SEO for fashion brands relies on clear navigation, so their site structure could look like this:
Homepage > Women’s > Dresses > Wedding Guest Dresses > [Product Name]
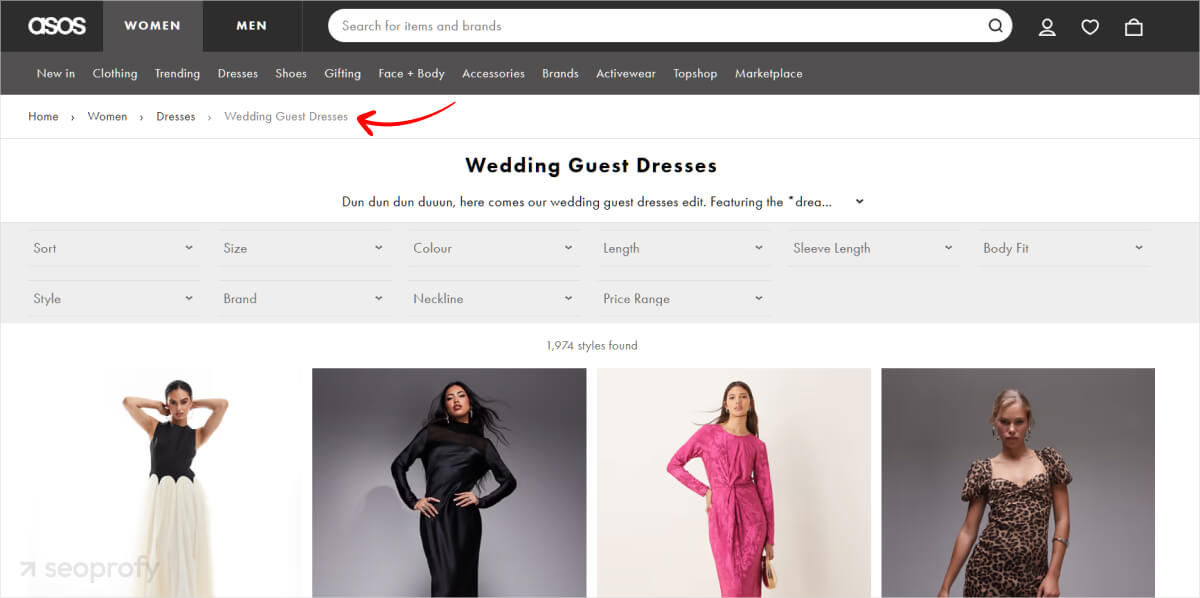
Put your best-selling categories in the main navigation.
Make Navigation User-Friendly
Use clear and descriptive menu labels on your website so that your visitors can effortlessly find products they need. Consider the following:
- Visible search bar
- Easy-to-use filters
- Breadcrumb navigation
In the screenshot below, you can see what it can look like for a pet store:
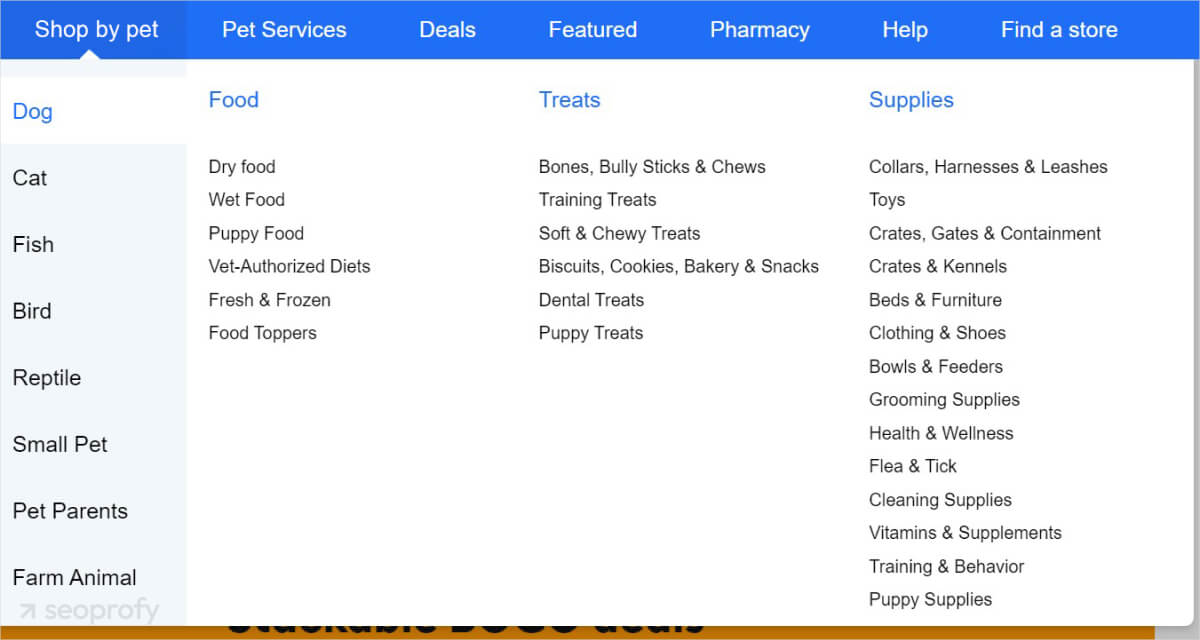
Remember that if customers can’t find your products, they can’t buy them. Every extra click on your site can cost you sales.
Some websites have HTML sitemaps where you can find the site structure.
Technical SEO
Technical SEO has a direct impact on how your ecommerce site performs in search and on the ROI you get from your entire SEO strategy. It affects everything from how fast your pages load to how easily users can move between product pages. On top of that, crawl budget and indexing logic determine which pages show up in search results, so when filters generate thousands of unnecessary URLs, your most valuable products get buried.
Given the complexity and scale of ecommerce sites, which often include a vast number of pages, technical issues are more likely to arise and can impact the user experience and search engine crawlers’ ability to navigate your site efficiently. This all makes technical SEO for ecommerce a central part of your strategy. Let’s now look at the main areas you need to keep in check.
Crawling and Indexing
For your product pages to appear in search engine results pages (SERPs), Google first needs to find, crawl, and index them. The problem with the ecommerce stores is that search bots often have problems crawling them. Here are a few reasons why:
- Many ecommerce sites are built with JavaScript, which can be slow for Google to index.
- They often have thousands of product pages that are updated frequently.
- The site structure of ecommerce stores is more complex, with lots of categories and product types.
- They tend to have duplicate content issues (more on that later).
If not addressed, these technical SEO issues can significantly impact your website’s visibility, potentially leading to missed traffic and sales. You can check why your web pages are not indexed in Google Search Console:
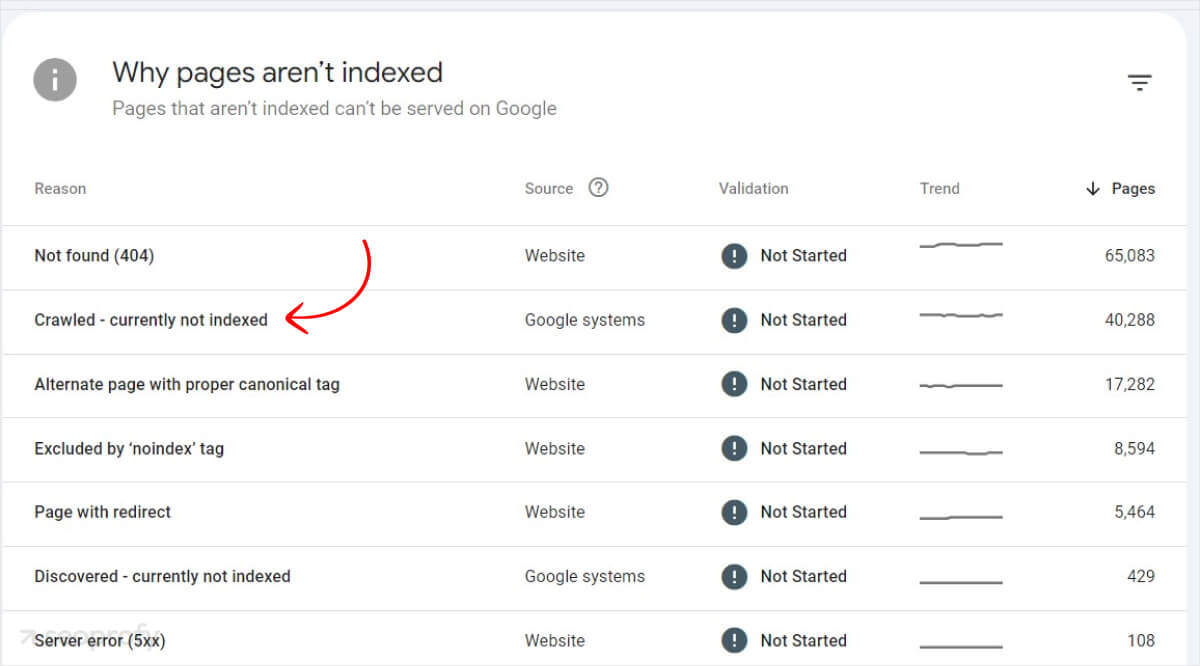
Here are some ecommerce SEO best practices to prevent this:
- Speed up your pages: Fast-loading pages enable Google to crawl your site more efficiently, enhancing your SEO performance. Additionally, a faster site greatly improves the user experience, keeping visitors engaged and satisfied.
- Create clean URLs: Make your URLs simple and descriptive. Use keywords and keep them short, like “domain.com/shoes/running-shoes.”
- Optimize meta tags: Each product page should have a clear title and unique meta description to help Google understand what the page is about.
- Use XML sitemaps: An XML sitemap gives Google a clear map of your site and helps it find and index your pages.
- Write unique product descriptions: Make sure every product has a detailed description with relevant keywords to help Google categorize your products.
Core Web Vitals and Page Speed
Core Web Vitals are a set of factors that Google uses to evaluate user experience on your pages. It considers the following:
- Largest Contentful Paint measures how long it takes for the largest element on your site to load. A good score is under 2.5 seconds.
- Interaction to Next Paint checks how quickly your site responds to user interactions. Ideally, this should be 200 milliseconds or less.
- Cumulative Layout Shift looks at how much the layout shifts while the page loads. A score of less than 0.1 indicates good visual stability.
Page speed is a critical ranking factor in your ecommerce SEO strategy, as it determines how quickly a page loads for users. Slow-loading pages can deter visitors, who are likely to leave the site and seek alternatives, leading to higher bounce rates and missed sales opportunities.
For ecommerce businesses, improving page speed is an essential element of an effective SEO strategy. It not only enhances search rankings but also ensures a smooth, engaging experience that keeps customers on the site and drives conversions.
The first thing you could do is check your current site speed and Core Web Vitals. For this, use tools like PageSpeed Insights or GTmetrics.
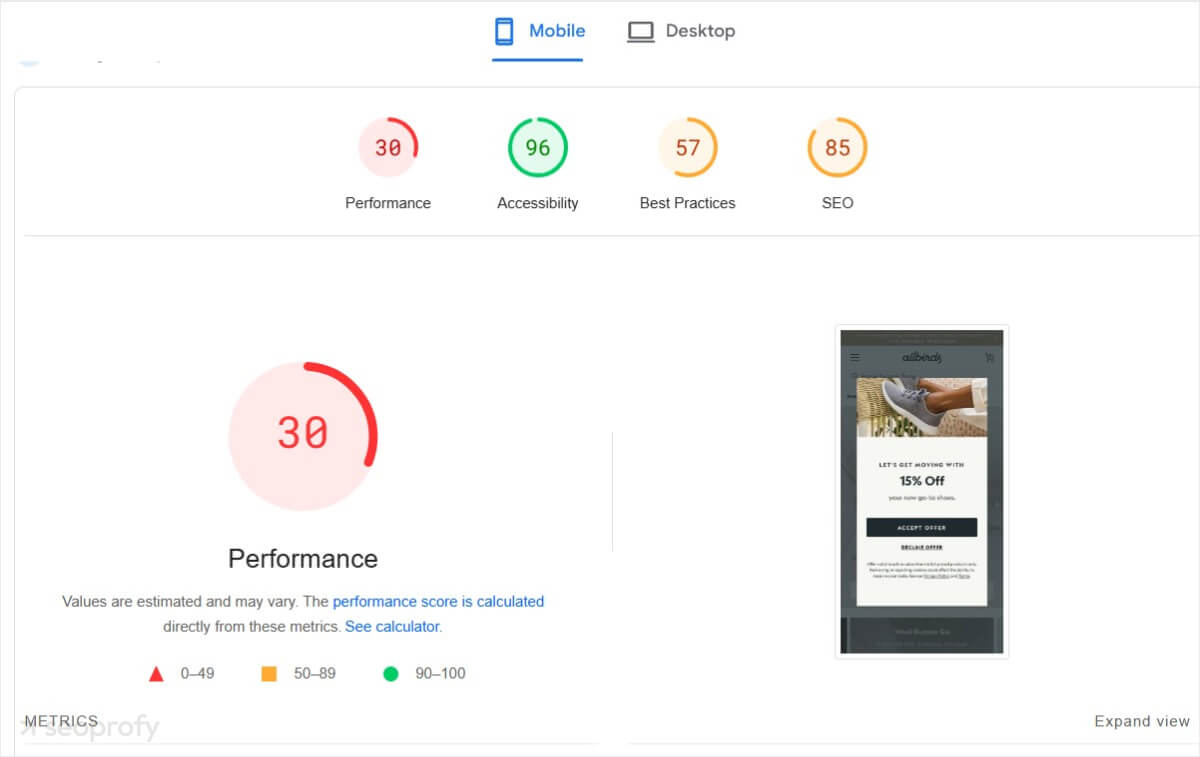
You’ll get a score from 0 to 100. The higher the score, the better. If the result isn’t as great as you’d like it to be, here are a few ecommerce SEO tips to improve it:
- Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN) to spread your site’s content across servers around the world.
- Reduce the number of HTTP requests your site makes. Each element on your page, like images or scripts, requires a request, and too many can slow things down. Combining files and using image sprites can help.
- Set up caching so static files are saved on a user’s device. Plugins or platform settings can help with that.
- Optimize images to keep file sizes small without losing quality. Formats like WebP work well. You can use a free tool called Squoosh App for this.
- Check if your server is set up correctly to help your site load faster. If it’s still slow, upgrading your hosting plan can help handle more traffic and improve speed.
Broken Pages and Redirects
Technical SEO for ecommerce frequently addresses issues like broken pages or 404 errors, which can occur if a URL is misentered, a page is removed, or content is relocated without setting up the correct redirect. For stores, broken pages disrupt the user experience, often leading to visitor drop-offs and potential sales losses. Additionally, search engines detect these errors, which can negatively impact your ecommerce site’s ranking and overall SEO performance.
To fix broken pages, regularly check for them using tools like Screaming Frog. If you find any:
- Set up 301 redirects to send visitors to the right page
- Fix any links that lead to broken pages
- Restore deleted pages if they’re still useful
Redirects play a key role in this process, as they send users and search engines to a different URL than the one they initially requested. Make sure there’s a clear connection between the old URL and the new one you’re redirecting to. This relevance helps maintain your rankings and keeps you visible to potential customers.
Duplicate Content
Ecommerce sites often face a common issue: duplicate content. This happens when similar text appears across different product or category pages, which can confuse search engines and impact your SEO. To prevent this problem, you can “noindex” less relevant pages to hide them from search engines. The other effective solution is to use canonical tags. These tell Google which page version is the primary one to show in search results and help you avoid ranking dilution.
Add schema markup to your product pages so they can appear as rich snippets in search results.
Our technical SEO experts will analyze the most common issues ecommerce sites deal with and help you:
- Fix broken links and apply redirects
- Set canonical and noindex tags
- Speed up the load speed of your site

On-Page SEO for Ecommerce Websites
When it comes to getting your online store noticed, on-page SEO is where it all begins. Mastering it can help you not only attract more visitors but also improve their shopping experience. From title tags to internal links, here’s a guide on how to optimize each aspect of your ecommerce site:
Title Tags and Meta Descriptions
Title tags and descriptions are what people first see within search results. You need to optimize them to be between 50 and 60 characters and always include the main keyword to grab user attention. The more enticing it is, the more users will click on it. When it comes to SEO for online shops, here’s the best way to write your titles:
- Put the main keyword in the first half
- Add modifiers that show value: “with free shipping,” “on sale”
- Include the current year for seasonal items
Since ecommerce stores have a lot of pages, using templates for meta tags would be most convenient. Here’s a sample template for a meta description:
{Product} for Sale – {Shop-name]
{Product} – [Shop-name]
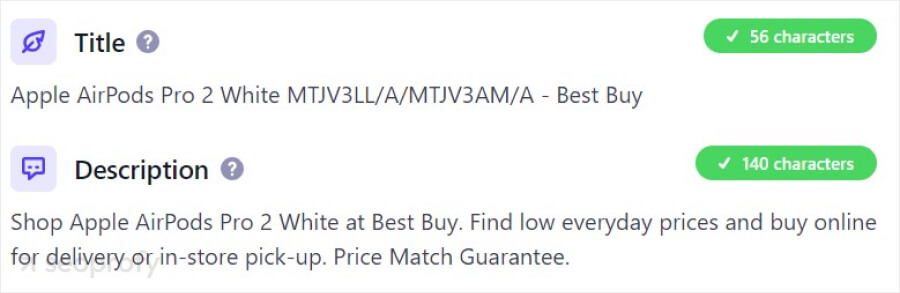
Keep in mind that templates can sometimes lead to generic descriptions that don’t look enticing enough to drive clicks. For the best ecommerce SEO results, try using templates for most pages but write unique meta tags for the ones that matter most to your store.
Headings
Headings structure your content to make each section clear and accessible for both visitors and search engines. Start with a primary heading, or H1, that includes your main keyword to define the focus of the page. Then, use subheadings like H2 and H3 to organize content into logical, easy-to-navigate sections, enhancing readability and SEO performance. It can look like this:

Your headings act as a guide for search engines. The more organized the page, the easier it is for Google to crawl and rank it.
URL
A good URL structure is short, descriptive, and includes your target keywords. Here’s an example of how to write SEO-friendly URLs:
- Instead of yourstore.com/p-12345, use yourstore.com/womens-leather-boots.
- Include categories for broader pages: yourstore.com/shoes/womens-boots.
Using clear URLs with breadcrumb navigation reinforces your page’s relevance, helps users understand the site’s hierarchy, and contributes to higher click-through rates on SERPs.
Product Page Descriptions
Descriptions on your ecommerce product pages matter not only for SEO but also for driving conversions. Clear, detailed copy shows your potential customer all the benefits your product has to offer and can encourage purchases.
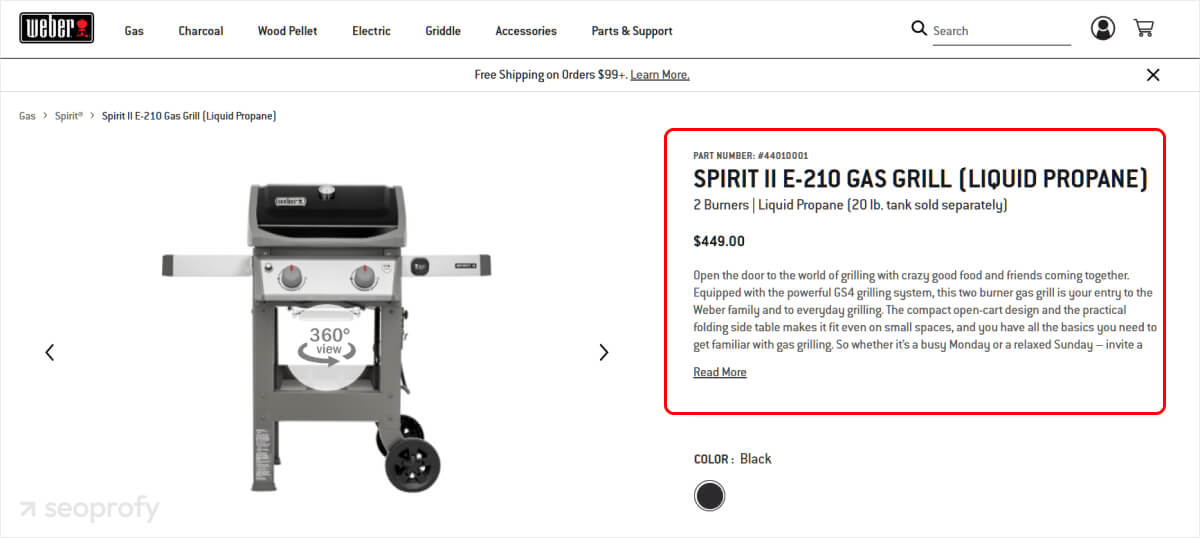
You can use AI tools for initial drafts to make this process easier, but don’t forget to go through each text and polish it to sound natural and unique. The following are some tips that will help you do better at ecommerce product page optimization:
- Include your primary keyword naturally in the title.
- Mention the real-life uses customers care about most.
- Add social proof like customer reviews and testimonials.
Internal Linking
Every SEO strategy for ecommerce websites should include internal linking. Internal links guide both customers and search engines through your store, helping users discover related products and content. Additionally, these links distribute link equity across your pages, potentially boosting their search engine rankings and overall site authority.
Let’s look at how Walmart handles internal linking. In their main menu, they display primary product categories and sections:
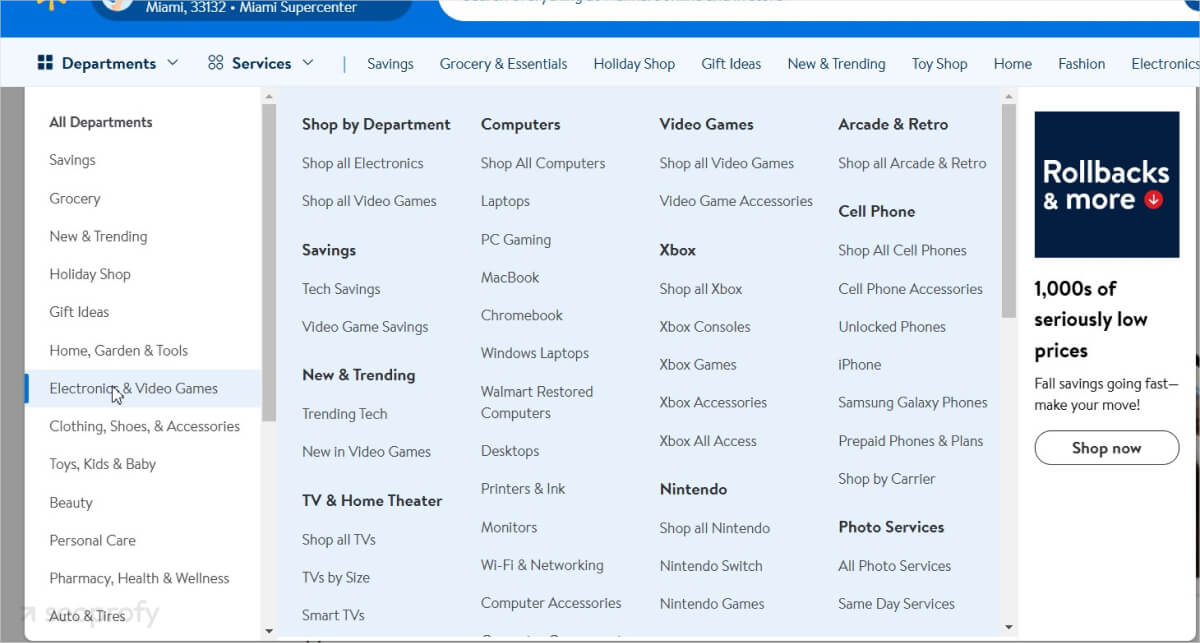
When the user clicks on one of those categories, they are taken to a page that displays the subcategories within it:
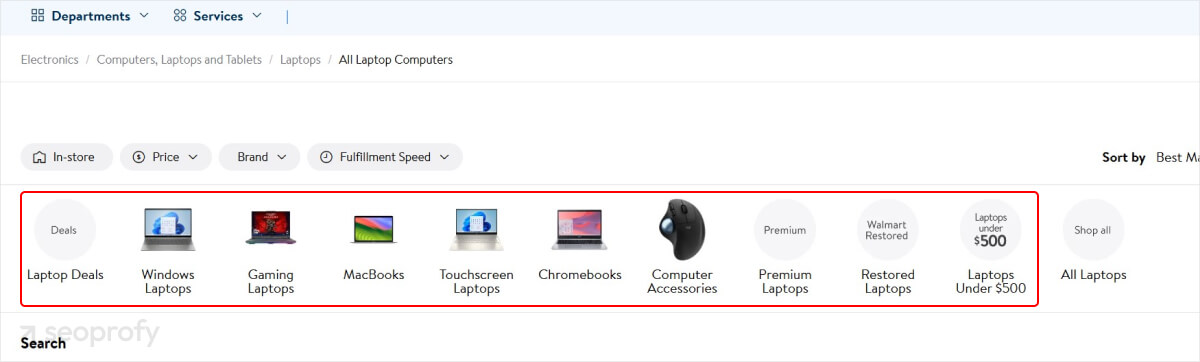
This structure helps users quickly find specific products within a broader category and also helps search engines better understand your site. Then, when users view a specific product, they’re shown a selection of similar products:
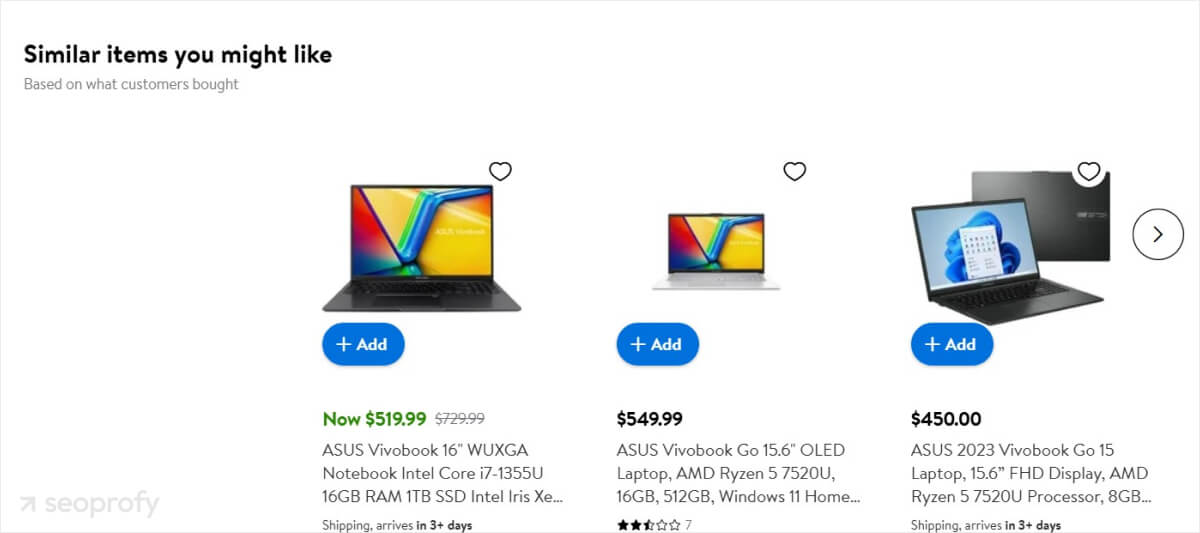
We recommend that you link to your high-priority pages first when interlinking. Here are a few other ecommerce best practices you can try:
- Link related products on product pages
- Use keyword-rich anchor texts
- Create “You might also like” sections
- Link between complementary categories
Link Building
Another important aspect of search engine optimization for online stores is ecommerce link building. Building reputable backlinks signals to search engines that your site is credible, improving rankings and visibility. Quality links boost your brand’s authority and help drive qualified traffic, making link building a critical part of standing out in crowded search results.
Here’s a checklist for your ecommerce link building strategy:
- Prioritize high-value pages: Focus on pages that bring in the most sales or have the potential to. Plan to promote these top categories and product pages over the next 6–12 months.
- Analyze competitors’ links: Identify where your competitors get their links from and if they’re ranking well for similar products. Use tools like Ahrefs or Semrush to look at their link sources, such as relevant blogs, industry sites, or influencers. Then, make a list of potential sites to contact for links.
- Develop a link building strategy: Create a structured plan to build links to your key pages. For example, if you’re promoting high-end furniture, reach out to design blogs, or if you’re in fitness gear, look for health-related websites.
- Monitor links and update regularly: Track which links are performing well and if they’re helping your pages rank. Check your anchor text and link placements with tracking tools to make sure they’re active and relevant. Adjust your plan as needed to improve results over time.
One mistake most stores make in their ecommerce strategy is trying to build backlinks to every single page with a limited budget. As much as it feels right to get visibility on as many pages as possible, this will inevitably water down your effort.
Especially since SEO pricing for link building is on the higher end, it’s far more effective to focus on a few high-priority pages.
Set up backlink alerts in LinkChecker.pro for both gained and lost links to your priority pages.
Blogging for Ecommerce
Most ecommerce SEO guides push the idea that a blog is a must-have for online stores. And while blogging for ecommerce can help build brand awareness and drive relevant traffic, it’s not always as effective as other optimization strategies. To prove this, let’s look at some cases:
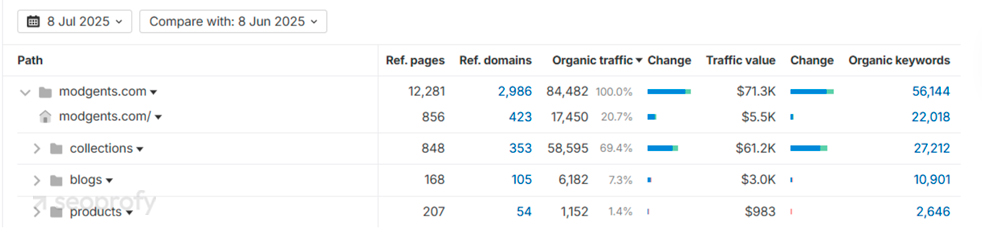
On the screenshot above, you can see that blogs only account for 7.3% of organic traffic for this store, which is quite low. Now, let’s look at a different example:
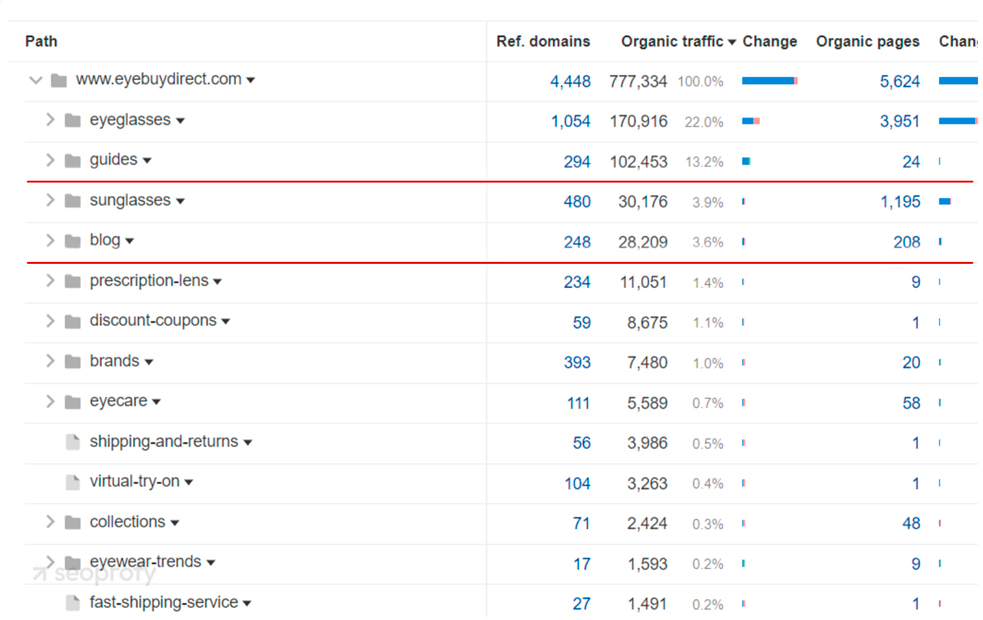
In this case, EyeBuyDirect’s blog, with 208 pages, accounts for only 3.6% of organic traffic. Meanwhile, their guides with just 24 pages bring in 13.2%, and the eyeglasses category page drives 22%.
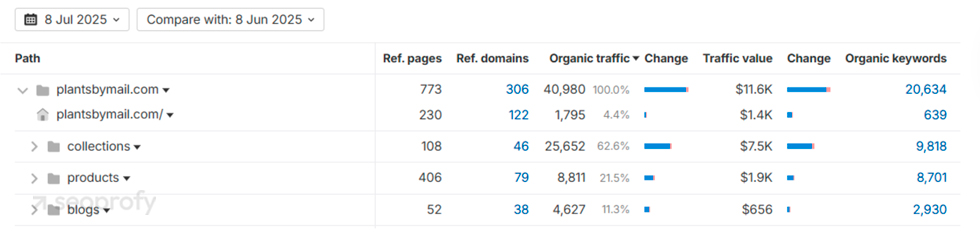
Our final example is from plantsbymail.com. As you can see in the screenshot below, their collections drive 62.8% of organic traffic, while their product pages account for 21.5%.
In comparison, blogs only bring in 11.3%. This shows that blog content for ecommerce is not as impactful as product and category pages. Therefore, your core goal should be to set up these pages first.
Once your category pages are optimized and start performing, blogging can help expand your reach. Here are the types of content that support that goal:
- Buying guides: This can attract people who are undecided and looking for help to make a choice.
- Product comparisons: A blog post, like “Brand X vs. Brand Y: Which Is Better for You?” targets shoppers who are trying to choose between similar options.
- How-to posts: Educational content provides practical advice, builds topical authority, and is an excellent way to reach searchers with informational intent.
- User stories and customer spotlights: Featuring stories from real customers or influencers shows how people use your products in real life. It builds trust and gives new visitors a reason to explore your products.
Invest in content marketing when you are already getting the desired SEO results on your landing pages and have a positive ROI from your SEO campaigns.
Measure SEO Performance
Now that you know how to find keywords, optimize your on-page elements, and fix technical issues, what’s next? It’s time to measure SEO results and check how these efforts are improving your visibility and sales. Here’s how to do it:
Monitor Your Organic Search Traffic
Keeping an eye on your organic search traffic provides a clear picture of how well your site attracts visitors through search engines. Use tools like Google Search Console and Google Analytics to monitor changes in traffic, user behavior, and conversions.
In Google Search Console, the “Performance” tab lets you track clicks, impressions, and average position over time, which shows you the direct impact of your SEO optimization efforts.
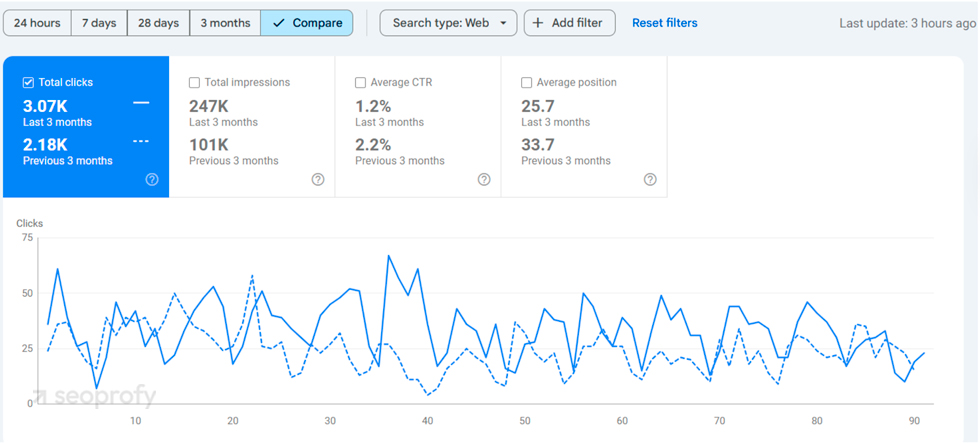
Meanwhile, Google Analytics offers real-time insights into organic traffic sources, devices used, and conversions.
Track Keyword Rankings
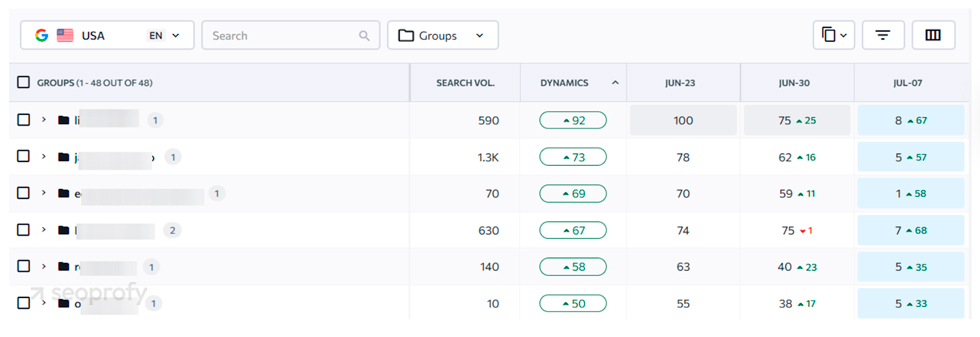
Keyword rankings show how visible your store is in search results for targeted terms. To check this, you can use Ahrefs’ “Rank Tracker” tool. You’ll need to set up a project, add your keywords, and specify a location. Ahrefs will track these terms and show their performance.
Another tool you could use for this is SE Ranking. It lets you track priority keywords and monitor changes in their positions over time. You can organize them by page type or product category to evaluate how different sections of the site perform.
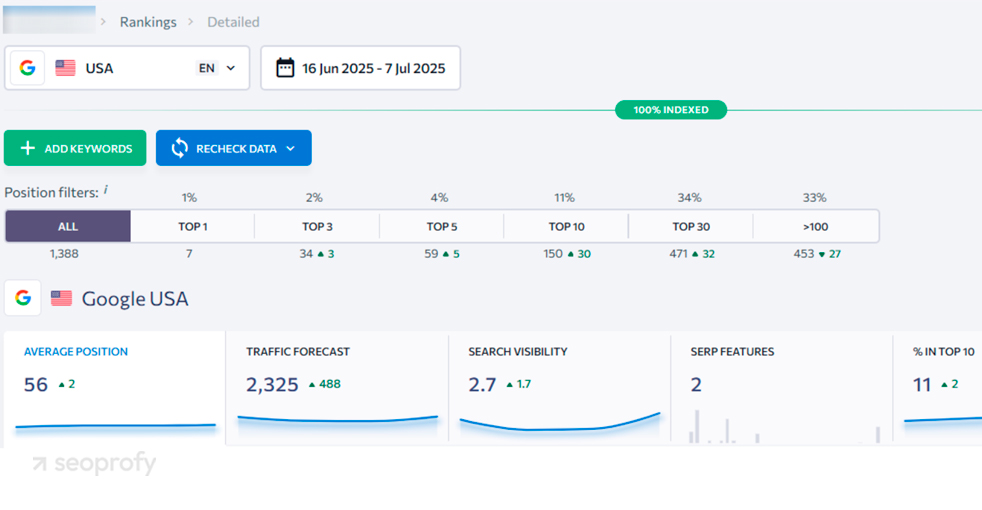
Additionally, you can track movements for specific keyword groups. For ecommerce sites with large catalogs or separate strategies by category, this helps monitor performance across different sections of the site.
Check Conversions
In ecommerce, common conversions include completed purchases, add-to-cart clicks, and email signups. To track these in Google Analytics:
- Go to “Reports”
- Select “Life Cycle”
- Choose “Monetization”
- Click on “Ecommerce Purchases”
Analyzing your SEO conversion rate alongside traffic gives a more complete picture of SEO’s impact on your business goals. It helps you understand which keywords, pages, or user paths are the most effective in driving results. At the same time, you’ll be able to see which pages need more work to turn visitors into customers.
Best Ecommerce SEO Tools
There are more than enough tools on the market for tracking SEO results. And below, we’ll share the ones that are most useful for ecommerce brands.
Google Analytics
As you probably know, GA4 is a powerful tool for tracking visitor behavior on your site. For online stores, it shows what customers are clicking on, how long they stay, and which products get the most attention. Here’s how you can use it:
- Track user flow: Google Analytics 4 lets you track how visitors move from one page to another. By monitoring this flow, you can see if there are any “drop-off” points where people leave your site.
- Check engagement metrics: Look at the “Engagement” section to see metrics like “Engaged Sessions” and “Average Engagement Time” to understand how interested visitors are in your content.
- Look at conversions: Set up conversion goals for actions like purchases, add-to-cart clicks, or email sign-ups to learn how many visitors are converting.
Google Search Console
Google Search Console (GSC) focuses on how Google sees your website. It helps you monitor your search traffic, find and fix issues, and understand what keywords are driving organic visitors to your site.
- Search performance: Go to the “Performance” tab to see which search terms bring visitors to your site. Pay attention to high-impression but low-click keywords. These may be opportunities to improve click-through rates by tweaking your page titles and meta descriptions.
- Index coverage report: The report shows which pages Google can and can’t find on your site. Since this is very important in SEO for large ecommerce sites, make sure all your main pages are indexed and address any errors flagged here, like 404 errors or mobile usability issues.
- Backlink report: In the “Links” section, you can see which sites link back to yours.
Ahrefs
Ahrefs is an all-in-one SEO tool, excellent for researching keywords, analyzing competitors, and building links. It’s particularly useful for ecommerce sites to find out what keywords they should target and which competitors rank for similar terms. Some ways to use it are the following:
- Keyword explorer: Use the “Keyword Explorer” to find terms with a good balance between search volume and keyword difficulty (Ahrefs shows both metrics).
- Site Explorer: Enter your domain in “Site Explorer” to get an overview of your SEO health. Ahrefs shows metrics like “Organic Keywords” and “Organic Traffic.” You can also see which pages perform best.
- Competitor analysis: Ahrefs lets you analyze your competitors’ sites by showing their top keywords, backlinks, and traffic. Check this regularly to see if there are any valuable keywords you might have missed in your online store SEO.
- Backlink profile: The “Backlink” section shows all the sites linking back to yours, with an emphasis on high-quality links. If your competitors have strong links from credible sources, you can reach out to those sites for similar partnerships.
Screaming Frog (For a Technical SEO)
This is yet another tool that stores should use in their ecommerce SEO strategies. The main use case of this software is to find technical issues like invalid links and duplicate content that could impact your search engine ranking. Here’s how you can use it:
- Crawl your site: Start a crawl of your site, which will map out all your pages and show any issues like missing meta descriptions or duplicate content.
- Identify broken links and 404 errors: Screaming Frog highlights any links with 404 errors. A word of advice: try to fix these quickly, as they can negatively affect your user experience.
- Find duplicate content: This tool shows any pages with similar or duplicate content, so you can rewrite where necessary.
Ecommerce SEO Mistakes to Avoid
There are some common mistakes eCommerce stores make, which are the following:
- Not fixing technical issues: Broken links, crawl errors, and missing tags can impact the user experience and lower search rankings.
- Missing breadcrumbs: Breadcrumbs help shoppers (and Google) easily navigate your site. Make sure they’re in place.
- Not adding internal links: Linking related products and categories helps shoppers explore your site and boosts SEO.
- Not working on brand recognition and link building: Brand mentions and backlinks build authority, which helps your pages rank higher over time.
- Skipping schema markup: Adding schema can get you those rich search results, like product reviews and prices, which make your listings stand out.
- Stuffing keywords: Using keywords too much, especially on product pages, can make your content feel spammy to users and search engines.
- Not handling out-of-stock products properly: Removing out-of-stock pages without redirects can create broken links and a bad user experience.
The Future of Ecommerce SEO
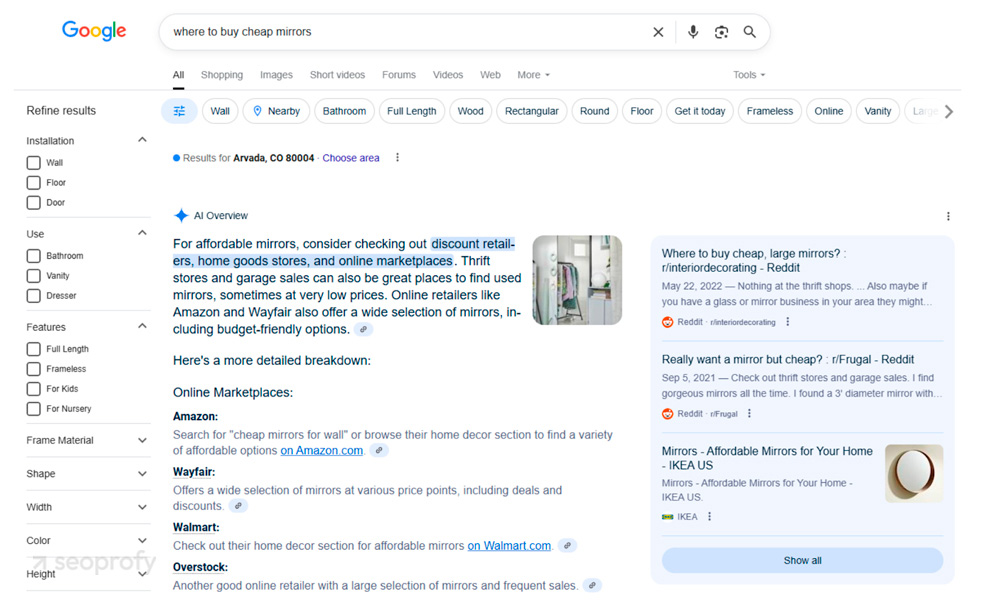
At SeoProfy, we don’t know exactly what the future holds, but one thing’s clear: ecommerce search is changing fast. Not so long ago, search results were simple lists of blue links. Now, with Google’s AI-driven overviews, users can get instant answers without even clicking.
In addition to that, LLM models like ChatGPT and Perplexity now have shopping features that show users personalized product recommendations directly inside the conversation.
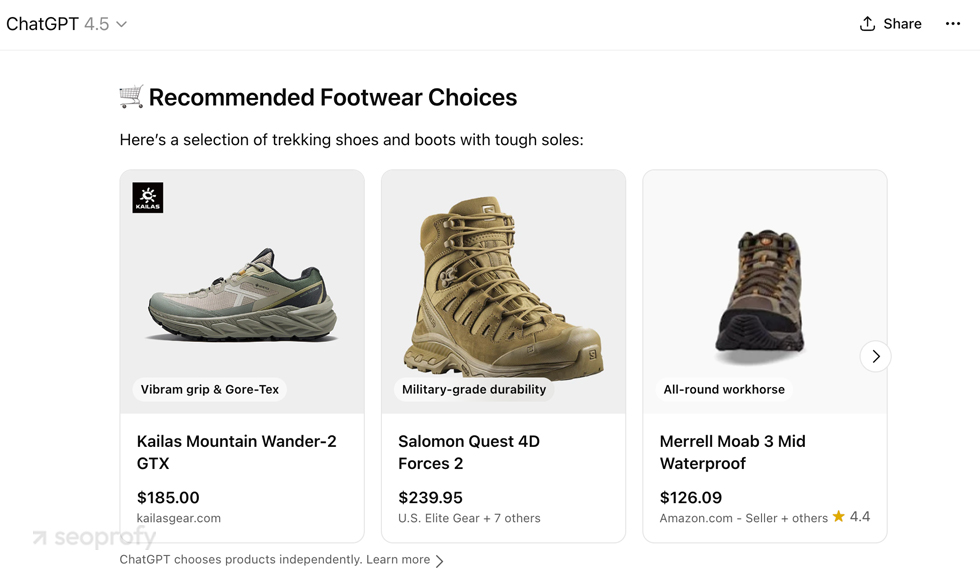
For online stores, this shift means they’ll need to keep an eye on SEO trends in ecommerce and find ways to rank within these new overview formats and LLM models. The good news? We’ve noticed that if a site is well-optimized and performs well in organic search results, it has better chances of getting featured in AI models as well. So, doubling down on SEO for ecommerce will be more important than ever.
Bottom Line
SEO continues to be an important marketing channel for online stores that want more visibility and sales. And the strategies we shared in this article should give you an idea of how to find the best keyword opportunities, fix technical issues, and build links to priority pages so you can increase sales without relying on ads.
In case you need any help with optimizing your store, schedule a free call with SeoProfy. We offer professional ecommerce SEO services to help stores improve rankings and reach more customers. Get in touch with us today, and let’s build an SEO plan that fits your business perfectly.