SEO for Laravel websites is the work you do to improve their visibility in organic search. The strategy usually covers the technical base, on-page decisions, content quality and structure, internal linking, and the elements that help search engines understand how the project is organized.
Since many business owners and teams are unsure which framework or CMS supports their goals better, we created this guide to explain how Laravel projects work from an SEO perspective and share some exclusive tips:
- Laravel gives tighter control over routing, metadata, schema, and indexing, which supports stronger SEO success than most CMS setups.
- A solid technical base in Laravel creates a clear URL structure and a framework that scales cleanly as content and features grow.
- Laravel supports AI SEO through answer endpoints, model-based summaries, context blocks, and a unified data layer that feeds generative engines.
What Laravel SEO Means and Why It Requires a Different Workflow
The platform you choose builds your search engine optimization workflow from the start. A CMS pushes you toward plugin-driven mechanics. A Laravel project (which powers full web applications rather than template-bound sites) relies on code-level implementation. This changes the entire structure of the optimization work. Here’s how!
SEO for a Laravel website grows from the application’s internal logic, which follows the MVC architecture. Every decision in the codebase influences how the project performs:
- Routing becomes the first technical layer that guides crawlers.
- Metadata can appear through helpers, controllers, or view components, depending on how the team organizes the flow.
- A schema often works as a set of compact modules that support multiple templates. Sitemaps may run through background jobs or small service classes. Pagination follows query scopes, which keeps large collections predictable during scale.
Key elements inside Laravel often include:
- Routing rules the team created manually
- Metadata logic linked to controllers and components
- Custom modules used for schema
- Background processes for sitemaps
- Query scopes for pagination patterns
CMS platforms take another approach. They offer built-in panels for metadata, visual tools for redirects, preset sitemap modules, and ready schema templates. Editors get instant access to these features, so the initial setup moves quickly. Growth plays out differently, though. Plugin stacks influence speed. Template rules shape URL behavior. More complex projects totally depend on how flexible the system remains.
We arranged both approaches side by side. It gives a smooth read on how each one behaves:
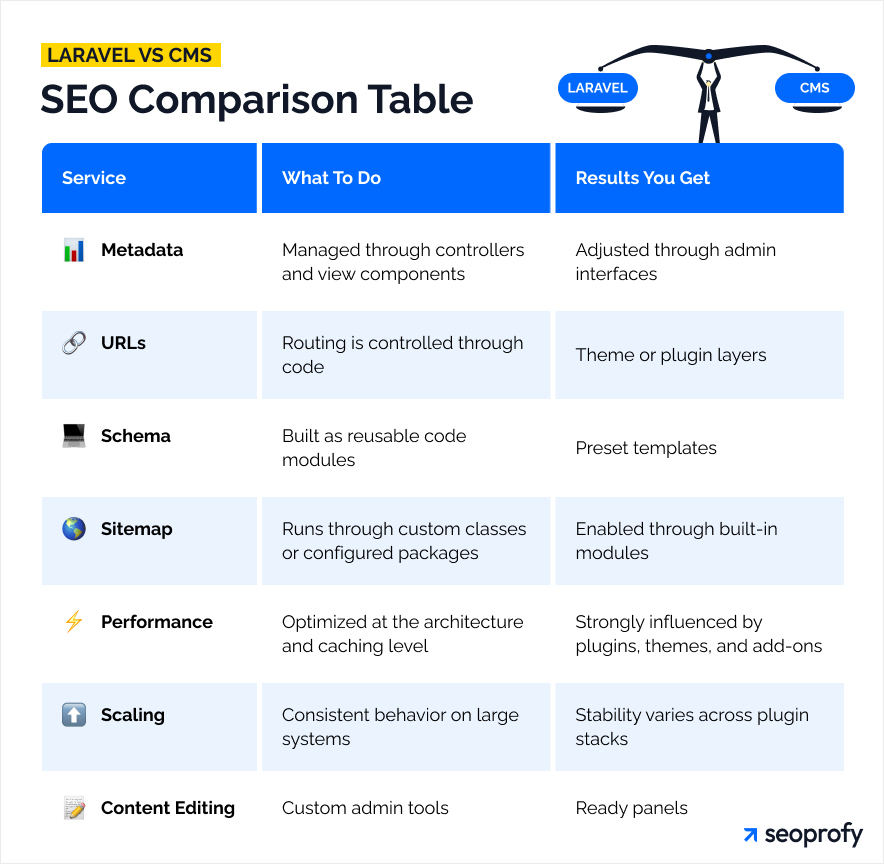
Key SEO Challenges in Laravel Projects

After reviewing the comparison table, you may feel that Laravel provides an excellent foundation for SEO through its flexibility and developer control. In many cases, this impression holds true. Even so, Laravel projects encounter their own set of challenges that deserve attention.
1. Routing Logic That Becomes too Fragmented
Large Laravel projects often grow through contributions from many developers, and routing patterns drift apart over time. Similar pages end up using different structures or parameter rules. Crawlers lose consistency, and the site begins to feel unpredictable from a mapping perspective.
2. Metadata Spread Across Multiple Layers
Metadata can originate in helpers, controllers, view components, or middleware. Each option works, yet the mix creates uncertainty about where a specific tag is generated. Teams struggle to maintain stable title tags and meta-descriptions when logic lives in too many places.
3. Pagination Behavior That Varies Across Sections
Laravel encourages custom query scopes, which support clean data handling. Different scopes produce different pagination formats across categories, filters, and search results. Crawlers face inconsistent URL patterns, especially when parameters behave differently from section to section.
4. Rendering Loads That Grow Faster Than Expected
Blade templates expand as features progress. Teams add nested components, conditional blocks, and layout fragments. Rendering time rises, and the cost becomes visible as organic traffic grows: users wait longer for pages to load, and performance issues start to hold back better search engine rankings. Projects require early planning for caching techniques implementation and efficient layout structure to keep performance steady.
5. Schema Components without a Unified Pattern
Schema often begins as a set of small modules. Over time, teams create new versions, duplicate older ones, or update only certain parts. Pages start using different data models, and structured information loses clarity, making it harder for search engines to understand entities consistently.
Each of these challenges stays fully manageable with the right team. The project gains a stable technical foundation. From here, the article moves into the hands-on work and explains the main steps for SEO.
Build a Strong Technical SEO Foundation in Laravel

A strong technical base in Laravel gives your digital marketing project the stability it needs for confident SEO work, so this stage deserves real attention. The next steps cover the essentials that influence online visibility at the deepest level, including routing logic, metadata handling, indexing signals, performance, security, and readiness for mobile devices.
Implementing SEO in a Laravel Application
Implementing SEO in a Laravel application means aligning your technical setup with how search engines evaluate structure, speed, and relevance. Before you optimize routes or metadata, start by finding relevant keywords and planning a content structure that supports them. This helps you create meaningful pages that follow SEO best practices rather than patching issues later.
Your service provider or internal team should also monitor page load times and overall page speed, since performance improvements can significantly boost visibility and user engagement. Clean Blade templates, predictable layouts, and lightweight components help search engines understand your pages more easily. When needed, you can generate meta tags or schema programmatically so every new page stays optimized without extra manual work.
This approach gives your Laravel project a strong, scalable base that search engines can crawl and rank with fewer issues.
Set Up SEO-Friendly URLs
Clear URL structure supports consistent crawling and helps search engines map the site without confusion. It also gives the project a stable base for large content sections and future expansion.
Laravel routes let you define exact patterns for every content type. For example, category pages can follow a fixed format like /products/{category}, while detail pages rely on clean slugs through route model binding, such as /products/{category}/{itemSlug}. This structure also simplifies internal linking for large teams, because editors and Laravel developers rely on the same predictable patterns across the entire Laravel app.
Configure Canonical Tags
Canonical tags guide crawlers toward the preferred version of a page, which prevents the system from spreading authority across duplicates. This step is especially important for projects with filters, pagination, or multiple access paths to the same content.
In Laravel, canonical logic can sit inside a compact utility method. It picks the clean version of the page, forms the final address from slug data, and sends it straight into the template.
Imagine a user opens a product through a filtered listing, such as /products/shoes?color=black. Another user opens the same item from a category like /products/footwear/shoes. Both paths lead to the same product. Laravel’s canonical method sends a single clean URL to search engines, for example /products/shoes, so the system knows which version carries the main value.
This approach prevents parameter-based duplicates from inflating the URL inventory. It’s a core part of the Laravel SEO services setup that keeps the project easier to maintain.
Manage robots.txt and sitemap.xml
Robots.txt and sitemap.xml give search engines a clear route through your site and help the system focus on pages that matter. How does this work, and what does the setup look like in practice?
Take a store with thousands of products updating daily. The structure changes often, so crawlers need guidance. In Laravel, robots.txt usually lives as a simple static configuration file, while the sitemap is generated through a small script that pulls fresh URLs from your models and organizes them into a current list. For this kind of store, the sitemap holds only active product pages, and robots.txt directs crawlers away from internal areas and filter views.
Ensure Proper Indexing and Crawlability
Indexing improves when search engines understand how your Laravel project exposes content and how each section connects. The framework gives full control over routing and page output, so the quality of indexing depends on clear technical choices from the team.
A solid setup usually includes these steps:
- Controllers return consistent status codes
- Pagination follows one predictable pattern across all listings
- Listings point to detail pages through clean, stable paths
- Public routes remain open for crawling
- Robots meta tags control which pages should stay out of the index.
Optimize Performance & Core Web Vitals in Laravel

According to Google’s research on mobile landing pages, when load time grows from 1 second to 10 seconds, the probability of a mobile user bouncing increases by 123%. Laravel gives enough control to raise website speed at the technical level:
- Route caching for quicker server responses
- Compact Blade components
- Controllers with tuned queries and eager loading
- Optimized assets and compressed images.
Improve Security
Security matters for SEO because Google flags hacked pages, applies Safe Browsing warnings, and can remove compromised URLs from results until the issue is fixed. These actions come straight from Google’s own security policies, so the impact hits a website’s visibility immediately.
Laravel helps SEO teams prevent this by offering strict request validation, protected routes, and controlled access to admin tools. These safeguards stop spam pages and injected links from slipping into the index.
Ensure Mobile Friendliness
Google now uses the mobile version of a site as the main reference during evaluation. Plus, research shows that 88.5% of respondents leave when the site’s speed is low, and 73.1% mention poor mobile friendliness and responsiveness as key issues. Laravel fits these realities well, because the framework lets teams build mobile layouts with far more freedom than most CMS tools.
Blade helps with this. It’s Laravel’s built-in templating system, and it controls how each part of the page appears on different screens. When the device changes, Blade rearranges text blocks, shifts buttons into reachable positions, and scales images through simple template rules. The mobile view stays clear for users and is easier to optimize for SEO.
Create SEO-Friendly Content and On-Page Optimization
Now that the technical setup is sorted, we can move to the part that feels more creative and hands-on. This section focuses on building SEO-friendly content and tightening the on-page elements that support it.
Title Tags and Descriptions
Meta title and description are what users see in search when deciding if your page matches what they’re looking for, so they have a direct impact on clicks. In Laravel, developers or agencies can set these fields through Blade components or SEO packages by passing the title and description as simple parameters.
The system inserts them into the layout and keeps them consistent across templates. This frees your SEO firm from manual edits every time the content changes. CMS platforms can offer similar tools, but the level of automation depends on specific plugins and settings, so the process often requires more checks.
Structured Data and Schema Markup
Structured data helps search engines discover elements on the page: a FAQ block, a product, a review, or an article. This kind of clarity often improves how the page is shown in search and can push you toward richer snippets and AI-driven answers that rely on clean signals.
You can test any Schema implementation through tools like Schema Markup Validator. They show whether:
- The markup is valid
- Required fields are filled.
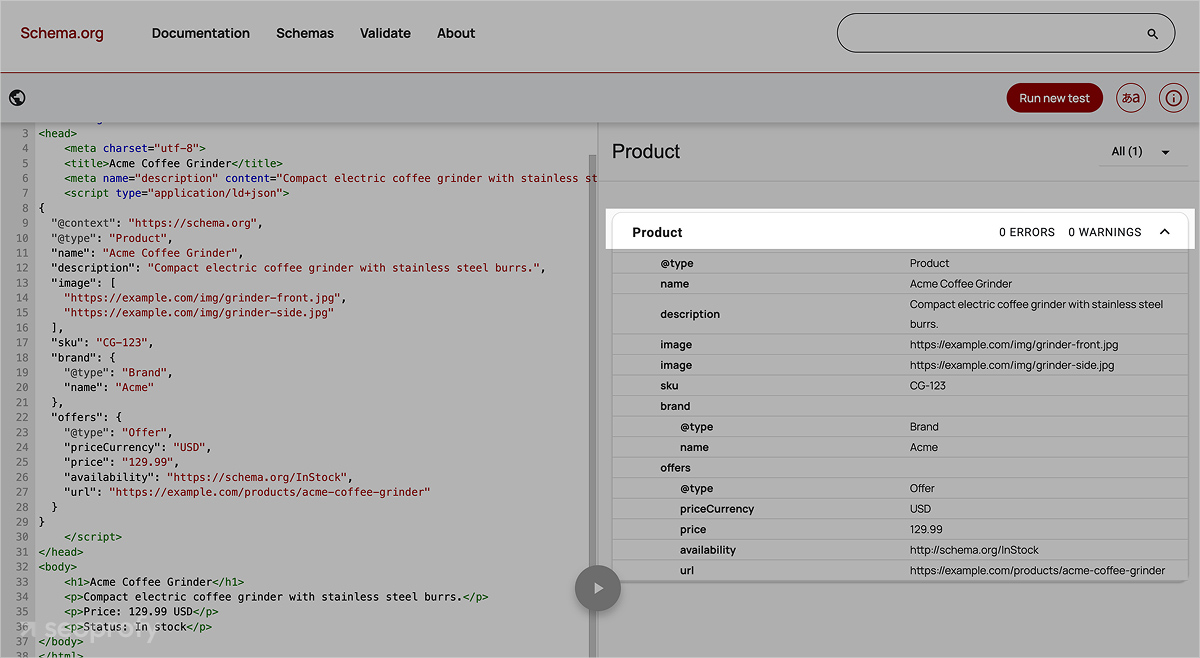
In Laravel, structured data can be added in a few simple ways. Developers often generate JSON-LD in a helper or service class and pass the final snippet into the view or rely on SEO packages that are implementing schema markup automatically.
Build Semantic, Well-Structured Pages
Search engines rely on page structure to figure out what matters, so a clear hierarchy helps both crawlers and users. Laravel doesn’t force a specific layout, which gives your team freedom to build clean H1 H3 chains, simple HTML, and accessible images without fighting the framework.
You can keep the structure steady by:
- Setting one H1 in the main layout template
- Using H2 and H3 blocks inside Blade views for clean flow
- Adding alt text directly in the image tag.
Use Topic Clusters and Strong Internal Linking
Topic clusters help search engines understand the depth of your expertise and see how individual pages connect to a broader subject. When the main article links to supporting pages, and those pages link back, the whole cluster sends a signal that you cover the topic fully. Strong off-page SEO signals earn authority, and internal linking spreads authority across the cluster instead of leaving each page on its own.
But how do you actually set this up in Laravel? You can store relationships in the model (for example, belongsToMany for pages within one topic), pull related high-quality content with a simple query, and print those links in the view with route() so the URL is always correct. When someone adds a new page to the cluster, the system can fetch it automatically, so there’s no need to update links by hand.
Use Clear Formatting & Visuals That Improve Engagement
Readers stay longer when the page is easy to scan. Clear formatting helps both people and crawlers understand what’s going on, especially on long guides or product pages.
A few things that work every time:
- Short paragraphs that stick to one idea
- Subheadings that explain what comes next
- Screenshots, diagrams, or code snippets are placed near the point they support
- Short examples that show how something works instead of describing it abstractly
With Laravel, this structure is easy to maintain because each block can live in its own partial or component. Your team can reuse these pieces across pages, and formatting will stay consistent.
As you can see, Laravel usually:
- Takes longer to build
- Has a more complex architecture
- Costs more at the start
But once the system is in place, SEO work becomes calmer and more predictable because the framework gives you more control, fewer plugin surprises, and consistent behavior at scale.
SeoProfy upgrades the technical base of Laravel sites so they attract organic traffic, convert better, and build long-term trust with search systems.
- Cleaner architecture signals
- Faster indexing
- Stronger topic relevance
- More qualified leads

Multilingual and International SEO
International pages need accurate signals so the search engine can index each version correctly and avoid mixing languages or showing the wrong page to the wrong market. In Laravel, you can manage multilingual SEO through routing, localization files, and structured page rules that keep every version separate and traceable.
What to focus on:
- Set language-specific URLs using Laravel’s routing (/en/page, /de/page) so each version has its own crawl path.
- Generate hreflang tags dynamically based on your language config or database fields and print them in the layout for every page.
- Store localized content separately instead of duplicating text, using language models or JSON translation files.
- Assign unique meta tags to each version through your controller or SEO service to prevent duplicate signals.
- Map relationships between versions in the model so the system knows which pages are equivalents across languages.
Essential Laravel SEO Tools and Packages
For any serious multilingual or large-scale SEO setup, you need a basic toolkit. Manual work won’t cover all technical requirements, so we grouped the core packages into a simple table for quick reference.
|
Laravel SEO packages |
What Solves |
Why Helps |
| spatie/laravel-sitemap | Generates XML sitemaps | Keeps your crawl paths updated, no manual edits |
| artesaos/seotools | Manages meta tags and Open Graph data | Central point for titles, descriptions, social tags |
| spatie/schema-org | Builds JSON-LD schema | Let’s you create structured data programmatically |
| Laravel Localization (mcamara) | Handles multi-language routes | Automates URL versions for international pages |
| Astrotomic/laravel-translatable | Stores and retrieves translated content | Keeps language versions separate inside your models |
Laravel also makes it easy for developers to automate how these tools and other tools work inside real projects. For example, when using a sitemap generator like spatie/laravel-sitemap, teams can update the file automatically during deployment or regeneration using the following command provided by the package.
Schema builders, SEO meta tools, localization utilities, and other tools follow the same logic — each one offers helper methods or Artisan commands that keep markup, metadata, and language versions consistent without manual edits. This practical workflow ensures your Laravel application stays aligned with SEO best practices as the project grows and search engines crawl new content.
SEO for Laravel in the Age of AI and LLM Search
Since most businesses are now actively working on AI SEO to appear in generative answers and capture traffic from AI-driven search, we also can’t skip this part of the strategy.
Key actions for effective generative engine optimization in a Laravel environment:
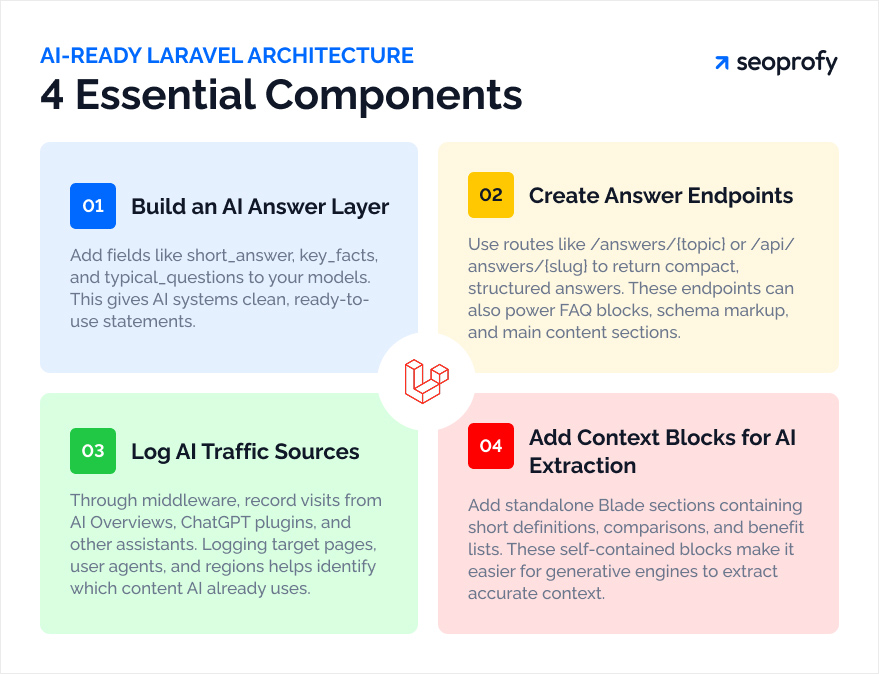
- Build an “answer layer” in your models. For key entities such as products, services, and articles, add fields like short_answer, key_facts, and typical_questions. These fields can be filled through the admin panel. Controllers deliver this data to Blade and to JSON. This will give AI systems ready-to-reuse statements.
- Create dedicated answer endpoints. Add routes like /answers/{topic} or /api/answers/{slug} that return a compact structured answer: a title, a few key facts, and links for deeper reading. The same data can support FAQ blocks, schema markup, and the main page.
- Log traffic from AI sources. Through middleware, write incoming requests from AI Overviews, ChatGPT plugins, and other assistants into a table: target page, user agent, and country. This helps you see which content blocks generative systems already pick up.
- Prepare “context blocks” for AI. In Blade, add separate sections with short definitions, comparisons, and benefit lists that are built from model data. These blocks stay self-contained and easy for generative engines to extract.
Track, Monitor, and Improve Your SEO Performance
And finally, you need to track SEO results and conduct performance optimization. Below, we outline the key KPIs and where to monitor them so you can see if the strategy moves in the right direction.

Next Steps Toward a Fully Optimized Laravel Website
Many teams choose a CMS because the launch feels faster and the setup looks simpler. That part makes sense. But over time, Laravel gives SEO implementation advantages that most CMS platforms can’t match: flexible data control and clear model logic. This creates a base that supports a confident and successful SEO strategy.
At SeoProfy, we genuinely enjoy working with Laravel projects. We understand how to organize the architecture so it helps the site grow instead of holding it back. If you want quality SEO services and a team that uses the strengths of this framework to their full potential, SeoProfy can take care of it.