Are you worried about losing your hard-earned SEO rankings during a website migration? You’re not alone. Website migration is a daunting process that can greatly affect your SEO if not executed properly. However, with the right strategies in place, you can safeguard your rankings, traffic, and online visibility during the transition.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through every step to ensure a smooth and successful migration without compromising your SEO efforts.
- Understand the SEO impact of website migration
- Learn different types of migrations and their risks
- Follow a step-by-step migration guide
- Implement key SEO considerations before, during, and after migration
- Monitor post-migration performance and optimize for SEO success
Understand Website Migration and Its SEO Impact
Website migration is more than just moving files from one server to another. It involves various changes, such as shifting to a new domain, redesigning the site, or switching to different content management systems (CMS). These shifts can disrupt your site’s SEO if not managed carefully.
When executed poorly, migrations can lead to a host of SEO issues such as broken URLs, loss of backlink equity, increased load times, and diminished user experience—all of which negatively impact your rankings and visibility on search engines.
How Website Migration Affects SEO Rankings
Website migration, whether for rebranding, a domain change, or a platform shift, is a complex process that can greatly impact your SEO. When done properly, it can boost site performance and user experience. However, if mishandled, it can lead to drops in search rankings, decreased traffic, and disrupted user journeys.
Following SEO site migration best practices is crucial to ensure that changes like switching domains or moving from HTTP to HTTPS are carefully managed. Search engines rely on URLs to understand site structure, and technical issues such as broken links and slow indexing can also harm SEO. A strong SEO strategy is key to a smooth transition.
In this guide, we’ll discuss how migration affects SEO and offer steps to minimize risks. Let us handle your migration to protect your traffic and rankings.
Book a free consultation for:
- Seamless transition with no downtime
- Preserved SEO rankings
- Minimized traffic and conversion loss

Types of Website Migrations
Before diving into how to execute a migration, it’s crucial to understand the different types of migrations and their unique SEO challenges:
- Domain change: Moving from one domain to another (e.g., from example.com to newexample.com).
- URL structure updates: Restructuring URL paths, such as changing from /category/page to /page-category.
- CMS change: Switching from one CMS platform (e.g., WordPress) to another (e.g., Ucraft).
- HTTPS protocol change: Migrating from HTTP to HTTPS to enhance security.
- Site redesign or rebranding: A complete overhaul of the design and branding, which may include changes in content, navigation, and user experience.
Each of these migration types comes with its own set of risks and SEO implications. Identifying your migration type early on helps in planning the appropriate SEO strategy.
How to Migrate a Website: Step by Step

Pre-Migration Preparation
Now that you understand the impact of website migration on SEO, let’s get into the nitty-gritty details of how to migrate a website without losing SEO. Before you begin the migration process, it’s essential to have a solid plan in place. This stage sets the foundation for a smooth transition. Here’s what you need to do:
Conduct a Comprehensive SEO Audit
Performing a thorough SEO audit is the first step to understanding where your current site stands and what could potentially go wrong during migration. Focus on the following:
- Indexability: Make sure all important pages are indexed and visible to search engines.
- Crawlability: Check for any roadblocks that might prevent search engines from crawling your site, such as incorrect robots.txt settings or noindex tags.
- Content quality: Look for high-performing content that drives traffic and conversions. This content needs to be preserved and protected during migration.
- Backlink profile: Do backlink audits. This identifies pages with valuable inbound links. These pages are priority candidates for 301 redirects.
- Google Search Console: For index status and crawl errors.
- Google Analytics: To understand current traffic patterns and user behavior.
- Screaming Frog: To crawl your site and look for technical issues.
- Ahrefs or SEMrush: Comprehensive backlink profile.
Benchmark Key Metrics
Before making changes, always document current site performance SEO metrics. This serves as your basis of comparison for successful migration without losing SEO rankings.
- Organic traffic: Focus on key landing pages and top-performing content. Look for pages that contribute most to organic visits. These are your top priorities to keep safe during the move. Compare and contrast traffic patterns over the last three to six months to understand seasonality and trends.
- Keyword ranking: Use tools like Moz Pro or SEMrush to track rankings before and after the migration process. Pay attention to high-volume, high-competition keywords, as any negative movement could significantly impact your traffic and visibility.
- Backlinks: Note the total number of backlinks and their distribution across your pages. Identify pages with the most valuable inbound links and protect them during migration to maintain their SEO equity.
- Conversion metrics: Track user engagement metrics such as conversion rates, bounce rates, and session duration. Analyze how users interact with your most critical pages. Once the migration process is done, any negative changes in these metrics can indicate issues with content layout or user experience on the new site.
Develop a Migration Plan
How do you make a plan if you want to migrate a website without losing SEO? Your plan should have the following:
- Scope of migration: Clearly define what is being migrated. The entire domain? A few specific sections? This allocates resources and sets expectations.
- Timeline: Set realistic deadlines, from pre-migration audits and staging to post-migration testing. Break down tasks into manageable chunks. Assign specific dates for each. Plan for delays to keep the project on track.
- Resources: Make sure everyone knows their role—developers, SEOs, content managers—everyone needs to be on the same page.
- Risk assessment: List risks, such as lost traffic, dropped rankings, or technical hiccups. Prepare for each risk and have a communication plan to inform stakeholders and users if problems occur.
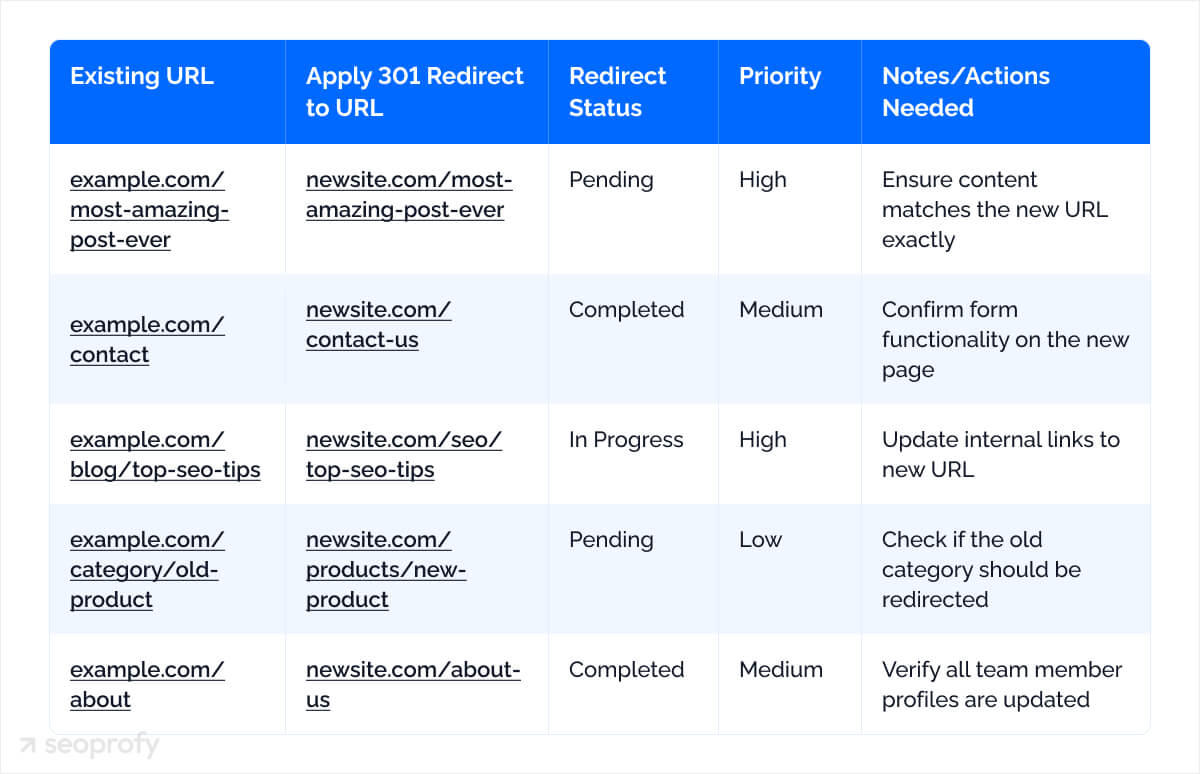
- Redirect map: Craft a detailed redirect map that lists old URLs alongside their new destinations. This ensures all link equity is preserved and users are seamlessly directed to the correct pages. Check the map for errors or conflicts to avoid redirect loops or dead ends.
- Staging environment: Set up a staging site that mirrors your live site exactly. Use it to test all elements—redirects, internal links, and on-page SEO—before going live. This lets you catch and fix issues in a controlled environment.
Communicate with Stakeholders
Ensure all stakeholders are informed about the migration schedule and potential impacts.
- Internal teams: Developers, SEO specialists, and content managers should be in sync regarding the migration plan.
- External partners: Notify partners, affiliates, and vendors who may be affected by the migration.
- Users: For larger migrations, consider informing your user base about potential downtime or changes they might experience.
If the pre-migration plan is done correctly, it protects your site’s organic search traffic and maintains your position on the search engine results page.
SEO Considerations During Migration
When migrating a website, managing the critical SEO elements is essential to ensure a smooth transition without losing search engine visibility. Focusing on SEO aspects such as proper 301 redirects, preserving meta tags, and maintaining URL structures will help prevent a drop in rankings and protect your website’s SEO value.
Ignoring these aspects can become one of the major reasons of dropped traffic post-migration, as broken links, missing redirects, or slow indexing can negatively impact your visibility. These elements ensure your site remains visible to search engines and users alike during and after the migration process.
Create a URL Mapping Strategy
A solid URL mapping strategy carefully maps out every old URL to be redirected to its new counterpart, allowing each old URL to have a corresponding new destination. Here’s how to do it:
- List all current URLs: Use a tool like Screaming Frog to crawl your current site and extract all URLs.
- Categorize URLs: Decide which URLs will be kept, redirected, or removed.
- Create a redirect map: For each URL being redirected, create a 301 redirect rule. This tells search engines that the content has moved permanently and retains most of the original link equity.
- Check for redirect loops and chains: Your redirects should not create loops or long chains, as these can harm SEO and user experience.
Implement 301 Redirects Effectively
One of the most common reasons for dropped traffic is poorly set up 301 redirects (or lack thereof). Setting up 301 redirects is crucial to preserving SEO value when URLs change. It ensures all old URLs point to new counterparts, transferring link equity and preventing 404 errors.
- Preserve SEO value: 301 redirects ensure that the authority and SEO signals associated with old URLs are passed on to the new URLs.
- Prevent 404 errors: Without 301 redirects, users and search engines will encounter 404 errors, which can harm both your rankings and user experience.
- Avoid redirect chains: Multiple redirects can slow down page load times and dilute the SEO benefits of the redirect. Ensure your 301 redirects go directly from the old URL to the new one.
- Regular monitoring: After implementing 301 redirects, continue monitoring for any broken redirects or errors using tools like Google Search Console or Screaming Frog.
Preserve On-Page SEO Elements
During migration, preserving critical on-page SEO elements is essential to maintaining the SEO strength of your website. Focus on:
- Meta tags: Ensure all your page titles, meta descriptions, and keywords are carried over to the new site.
- Headers: Keep your H1, H2, and other heading tags consistent, as they play a significant role in SEO and user readability.
- Alt text: Preserve image alt texts, which are critical for accessibility and SEO rankings, particularly in image search results.
- Internal links: Make sure that all internal links are updated to reflect the new URLs and still direct users to the correct pages on the site.
Prepare for Technical SEO Needs
Update your robots.txt file, XML sitemaps, and canonical tags to reflect the new URL structure if you want to migrate your website without losing SEO. Submit the updated sitemap to Google Search Console and monitor for any indexing issues and technical SEO metrics.
Technical SEO website migration checklist:
- Robots.txt: Update the robots.txt file to reflect the new site structure. Make sure no important pages are blocked.
- XML sitemaps: Create a new XML sitemap and submit it to Google Search Console. This helps search engines discover your new URLs more quickly.
- Canonical tags: All canonical tags must point to the correct pages on the new domain to prevent duplicate content issues.
Testing SEO for Website Migration Impact in a Staging Environment
Website migration is always a tense moment, especially for SEO. This is where a staging environment can help. Having a staging environment allows your team to test everything out before going live. This lets you see any issues that would have creeped up when you do the real thing, whether you’re checking redirects, user experience, or SEO elements.
Importance of a Staging Environment
A staging environment is a replica of your live site that allows you to test changes before they are deployed. This step is essential when migrating a website to avoid SEO pitfalls and ensure a seamless transition.
- Catch errors early: A staging environment helps identify broken links, missing pages, or incorrect redirects before they affect the live site. This way, you can resolve issues before they impact users or search engine crawlers.
- Safeguard SEO: By testing SEO elements such as meta tags, internal links, and canonical tags, you ensure that your site’s SEO remains intact post-migration.
- Test redirects: Staging allows you to verify your 301 redirects and ensure they are pointing to the correct new URLs without creating redirect loops or chains.
- User experience: Not just to protect search engine results, you have to simulate user interactions to test for broken user journeys, slow page load times, or other problems that might affect engagement and conversions.
- Prevent indexing issues: Testing your robots.txt file, XML sitemaps, and canonical tags ensures that search engines can properly crawl and index your new site structure without issues.
- Ensure technical compatibility: Whether you’re migrating to a new platform, domain, or protocol (e.g., HTTP to HTTPS), testing in a staging environment verifies that all technical aspects, such as server configurations, are functioning correctly.
- Minimize downtime: Staging helps minimize the risk of unexpected downtime during the migration process, allowing for a smoother go-live experience.
A staging environment is a vital safety net, ensuring all aspects of your migration—from technical SEO to user experiencec x —are in place and optimized before the launch.
Execute the Migration
Now that you’re gearing up to migrate your website, it’s time to talk about making the transition as smooth as possible, from managing the go-live process and keeping an eye on your SEO performance with the help of SEO experts afterward to tackling any issues that come up post-migration. We’ll also include tips on fine-tuning your backlink strategy and updating external links to preserve SEO.
Manage the Go-Live Process
The go-live process is the final, make-or-break phase if you want to migrate a website without losing SEO.
- Choose a low-traffic period. This ensures minimal website migration SEO impact on users while you monitor issues in real-time.
- Use Google Analytics and other tools to monitor spikes in 404 errors or sudden traffic drops.
- Always have a backup plan. Keep a copy of your old site just in case, and have a rollback strategy if things don’t go as planned.
If critical issues happen, revert to the previous version fast. Launching during off-peak hours gives your team enough time to troubleshoot and fix issues without disrupting many users.
Post-Migration Monitoring and Optimization
After migration, you still have to do monitoring and further optimizing for SEO performance. To avoid any surprises and recover from penalties, keep an eye on new website traffic and fix any issue that may have popped up during the platform migration process.
Track SEO Performance After Migration
Use the following tools to measure SEO performance of your website’s post-migration:
- Google Analytics: Check for sudden traffic drops or spikes.
- Google Search Console: Monitor indexing issues, crawling errors, and keyword performance.
- SEO tools: Tools like SEMrush or Ahrefs can help track keyword rankings and backlink health.
Identify and Resolve Common Post-Migration Issues
Watch out for the following issues after site migration:
- Traffic drops: Check all your redirects and indexing status. See that none of your top pages are being blocked by the robots.txt file.
- Crawl errors: Use Google Search Console to identify and fix any crawl errors. Look for 404 errors and rectify them with proper redirects.
- Backlink issues: If backlinks are pointing to non-existent pages, reach out to the linking sites and request updates. Use a tool like Ahrefs to monitor your backlink profile.
Update External Links and Backlink Strategy
Once migration is complete, the next step is to update external links pointing to old URLs. This maintains your backlink profile and avoids dead links that harm your SEO. Additionally, it’s crucial to know how to update page URLs after site migration, ensuring both external and internal links are correctly directed.
Reach out to high-authority sites linking to your old or duplicate content and request updates to the new URLs. This is also an excellent opportunity to enhance your link building strategy by fostering relationships with these sites. SEMrush’s Backlink Analytics can let you see who’s linking and make sure your link profile stays strong and healthy. Routine auditing and updating your backlinks after migration helps in maintaining your site’s authority and relevance.
Advanced Tips for Site Migration Without Losing SEO
Handling large-scale and complex website migrations requires more advanced strategies and customized approaches. Whether you’re migrating a multilingual website or a site in a specialized industry like e-commerce or SaaS, planning and execution are needed to preserve SEO progress.
Handle Large-Scale and Complex Migrations
Handling large-scale and complex migrations, especially for multilingual or multi-regional sites, requires meticulous planning. Focus on hreflang tag implementation to guide search engines on regional or language-specific pages. Ensure regional URL structures are clear and consistent while preserving local SEO elements like keywords and meta tags.
Set up 301 redirects tailored for each region, avoiding chains, and update backlinks for localized sites. Use a staging environment to test regional versions and monitor regional traffic post-migration using tools like Google Search Console. Leveraging CDNs or regional hosting can also enhance performance for local users.
Considerations for Specific Industries
Different industries have unique requirements for SEO during migration:
- E-commerce: Make sure product pages retain their SEO value by preserving user-generated content such as reviews and ratings.
- SaaS: Ensure a seamless transition for pricing pages and service information to maintain conversions.
- News sites: Pay special attention to URL structure changes that could affect the freshness of news articles in search engine results.
FAQs on SEO Migration
Can I revert back to the old website if there are issues after migration?
Yes, reverting is possible but should be a last resort. Always maintain a full backup of your old site before migration. Rather than fully reverting, it’s often more efficient to troubleshoot specific issues while keeping the new site live.
How can I monitor the success of my website migration?
Use tools like Google Analytics and Google Search Console to track key metrics such as traffic, search engine rankings, and indexing. Monitoring performance helps identify any drops or errors that need addressing.
What should I include in a URL mapping strategy?
A thorough URL mapping strategy includes a list of old URLs matched to their new counterparts, with proper 301 redirects to ensure users and search engines find the new pages without encountering 404 errors.
Is it necessary to set up a custom 404 page during migration?
Yes, a custom 404 page is important to maintain the user experience in case of any broken links. A well-designed 404 page can also guide users back to relevant parts of the site.
How can I ensure all important SEO elements are preserved during migration?
Export and track important SEO elements like meta tags, headers, and alt text before migration. Verify that these are correctly imported and functional post-migration to retain SEO value.
Why is it important to update internal links after migration?
Updating internal links ensures that users and search engines navigate smoothly to the correct new pages, avoiding broken links that could negatively impact SEO and user experience.
How do I handle broken links after a website migration?
Regularly crawl the new site using tools like Screaming Frog or Search Console to identify broken links. Implement or update 301 redirects to fix broken links, ensuring users and search engines are directed to the correct content.
Conclusion
Migrating a website is a complex task, but it doesn’t have to lead to a loss in SEO performance. By following this comprehensive guide and implementing the website migration best practices, you can safeguard your SEO and maintain your rankings.
Need expert help? Let’s ensure your migration is smooth, safe, and successful. Contact us for a free site migration consultation.