BigCommerce SEO is a set of optimization tactics that help online stores hosted on this platform to rank for high-value product keywords and get more organic traffic and sales. It blends BigCommerce’s native features with proven SEO practices like technical fixes, on-page improvements, and link building.
To help online stores make the most of their SEO efforts, we wrote this guide based on 13+ years of experience in this niche. You’ll learn tried-and-tested SEO tactics along with specific tips on what to prioritize in your strategy to increase visibility of your products and grow revenue from search.
- BigCommerce SEO consists of four pillars: technical SEO, on-page optimization, link building, and site structure, all of which need to work together to build long-term store authority.
- Online stores often deal with technical issues caused by faceted navigation and filters, which need to be taken care of because they can drain your crawl budget if not managed properly.
- A lot of attention in BigCommerce optimization should go into category and product pages, as these are the primary organic growth drivers for ecommerce brands.
- One of the best ways to spread authority is through strategic internal linking and topic clusters, which help build topical authority and lead search bots and users to your most important pages.
BigCommerce SEO Strategy Framework
BigCommerce SEO framework differs from other ecommerce SEO tactics because this platform has distinct rules around URL generation, category structures, faceted navigation, and content templates.
That’s why online stores should follow a platform-specific approach. We’re talking about controlling exactly how search engines crawl and rank your BigCommerce pages in search engine result pages (SERPs).
The Four Pillars for BigCommerce Stores
At a high level, every SEO BigCommerce strategy falls into four connected pillars, which together have the biggest impact on your product and category visibility. Here’s a brief overview of each:
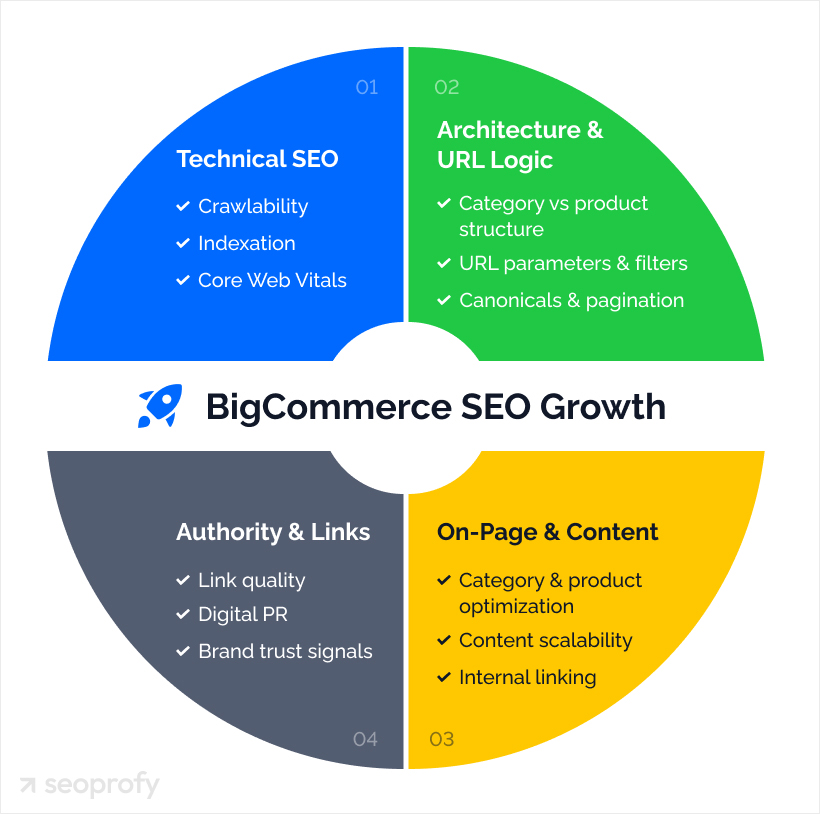
- Technical SEO: Crawlability, indexation, schema markup, and site speed. This work helps search engines move through your store efficiently and avoid indexing issues as catalogs expand.
- Architecture and URL logic: Category and product structure and URL parameters. Decisions here influence how Google prioritizes pages and how navigation flows from categories down to individual products.
- On-page SEO: Unique content on category and product pages, optimized for relevant keywords and supported by structured data. This helps pages show up more prominently in search and get more clicks.
- Authority and link building: Off-page signals such as backlinks and brand mentions. Google still takes these into account when ranking pages, and they matter for AI optimization, too.
Now that you have a general view of how a BigCommerce strategy comes together, let’s look at each area in detail.
Technical SEO for BigCommerce Stores
Technical SEO sits at the core of BigCommerce SEO optimization. Stores on this platform frequently run into issues caused by faceted navigation and pagination, which can generate a large number of duplicate URLs. The good news is that the platform gives you a decent foundation out of the box to fix those, though it also introduces a few limitations.
Crawlability, Indexation, and Platform Constraints
BigCommerce automatically generates XML sitemaps for products, categories, and content pages. These sitemaps update as items get added or removed, which keeps discovery for search engine bots fairly reliable without manual work.
The platform also allows direct editing of robots.txt, which gives you control over crawl access. However, these features do not prevent indexation issues on their own. Here’s a short checklist of what you’ll need to keep an eye on:
- Check if your priority category and product URLs are indexable (GSC → Indexing report)
- Align canonical tags with the pages meant to rank (page HTML + URL Inspection in GSC)
- Watch for orphaned pages created by filters or navigation (GSC → Indexing report)
- Review sitemap URLs and confirm they reflect indexable pages (BigCommerce sitemap + GSC)
These general checks keep indexation under control and are often included within broader SEO audit services. The next step is dealing with the URL variations BigCommerce creates by default.
Pagination, Canonicals, and Parameter Handling
Category pages often generate multiple URLs through sorting, filtering, or page numbers, all pointing to similar product sets. While this might not seem like a big deal, it can create duplicate content issues for your store, diluting crawl budget and splitting ranking signals.
Filters can create thousands of URL combinations, which means Google has to crawl and may also index all of them. This isn’t good because the crawl budget is limited. When most of it goes into low-value pages, priority pages can end up without being indexed.
Luckily, canonical tags help address this issue directly. They consolidate duplicate URLs and tell search bots which version of a page should take priority. BigCommerce handles them automatically, though it doesn’t know which filtered URLs matter for search and which ones exist only for navigation.
Depending on how your store uses filters, canonicals can be managed at the template level or adjusted through Script Manager. A default for BigCommerce stores looks like this:
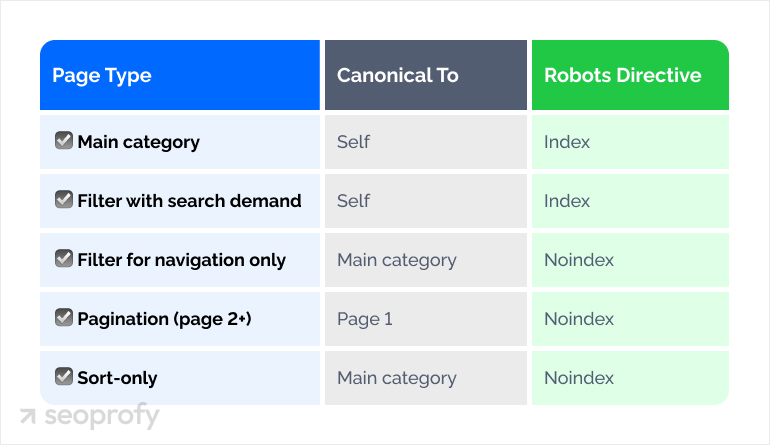
| Page Type | Canonical To | Robots Directive |
| Main category | Self | Index |
| Filter with search demand | Self | Index |
| Filter for navigation only | Main category | Noindex |
| Pagination (page 2+) | Page 1 | Noindex |
| Sort-only | Main category | Noindex |
This structure keeps your store easy to crawl while protecting the pages meant to rank. It also reduces long-term cleanup once catalogs expand and filters multiply.
For situations where filtered pages serve real search demand, canonicals can remain self-referencing while other variants get restricted. In contrast, purely navigational filters often work better with noindex directives to prevent duplication.
BigCommerce Site Architecture and URL Logic
Site architecture is how your online store’s pages are organized and how they connect through internal links. At our ecommerce SEO agency, this is one of the first areas we review, since it affects crawl paths, internal linking, and page discoverability across the entire store. A good example of site structure for ecommerce stores looks like this:
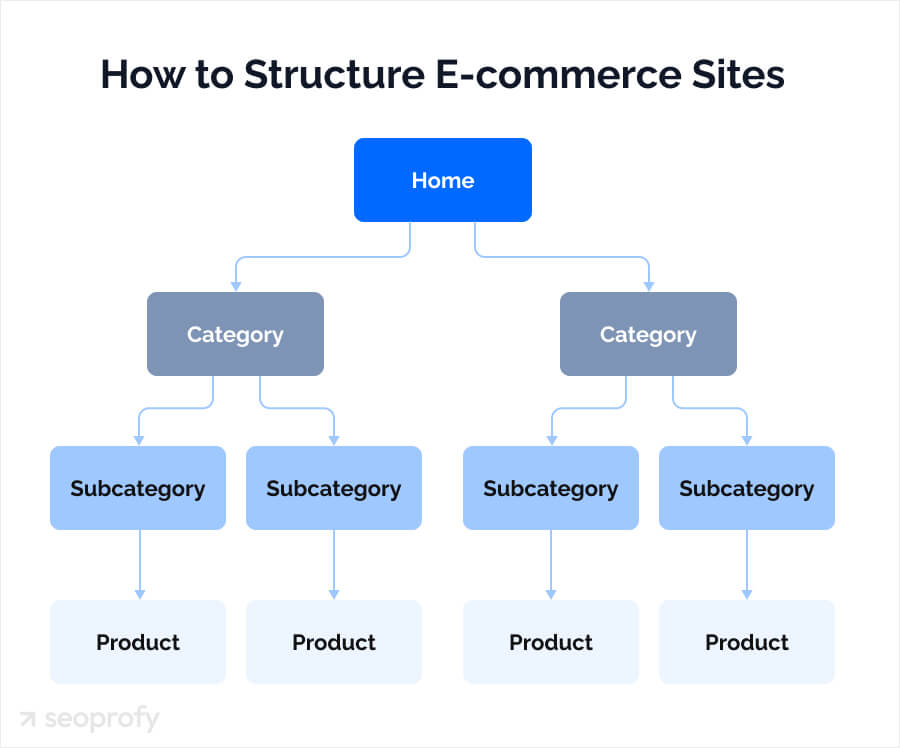
This layout works because it gives search engines a clear hierarchy. At the same time, users don’t have any trouble navigating and browsing your catalog.
Category vs Product Indexing Strategy
BigCommerce lets the same product appear in more than one category. This can create duplicate URLs and cause pages to compete with each other in search. To avoid that in your SEO strategy, use keyword research to define which pages should rank for which queries. For most stores:
- Categories should rank for broad and mid-tail keywords
- Products should rank for long-tail and transactional queries
As a general tip, when filters or alternate URLs exist, canonicals should point to the page intended to rank rather than allowing multiple URLs to compete. On that note, it’s worth looking at how BigCommerce handles URL structure and where that can create additional SEO risk.
URL Structure Best Practices
The in-built functionality on BigCommerce creates readable URLs by default and allows removal of extra slugs and .html endings. That flexibility helps shorten URLs, though it also makes it easier to create duplicates when changes happen without redirects or canonical. As for tips on how to create SEO-friendly URLs, here are a few best practices:
- Keep URLs short and descriptive
- Use hyphens to separate words
- Avoid dates, timestamps, and session strings
- Maintain a consistent category-to-product path
If some of your products move between categories or category paths change, canonicals and redirects should update at the same time. That keeps signals consolidated and avoids leaving outdated URLs indexed.
On-Page SEO for BigCommerce Category and Product Pages
On-page SEO means optimizing all the elements on your page: title tags, meta description, headings, copy, and images. These details tell Google what the page is about, and also influence user experience (UX) on your site.
Category Page Optimization
If you check the performance of your online store, you’ll likely find that your category pages drive the majority of organic traffic. They represent broad buyer intent and usually target head terms with the highest search demand, which is why they often attract the largest share of potential customers. To make category pages your most valuable SEO assets, here are some tips you can try:
Use Unique, SEO-Friendly Category Names
Your category names are one of the strongest relevance signals on the page. They appear in the URL, navigation menus, breadcrumbs, and internal links. In practice, they should:
- Target high-volume, product-focused keywords
- Match common search phrases used by buyers
- Clearly describe what products are included
Those category names then set the stage perfectly for faceted navigation, which takes that relevance further.
Make the Most of Faceted Navigation
BigCommerce supports filters such as brand, size, color, price, and material, and many stores extend this further with attributes specific to their products. Having these on your website improves usability and helps shoppers narrow down large product assortments quickly. Here’s a good example from Ted Baker on how you could do it:
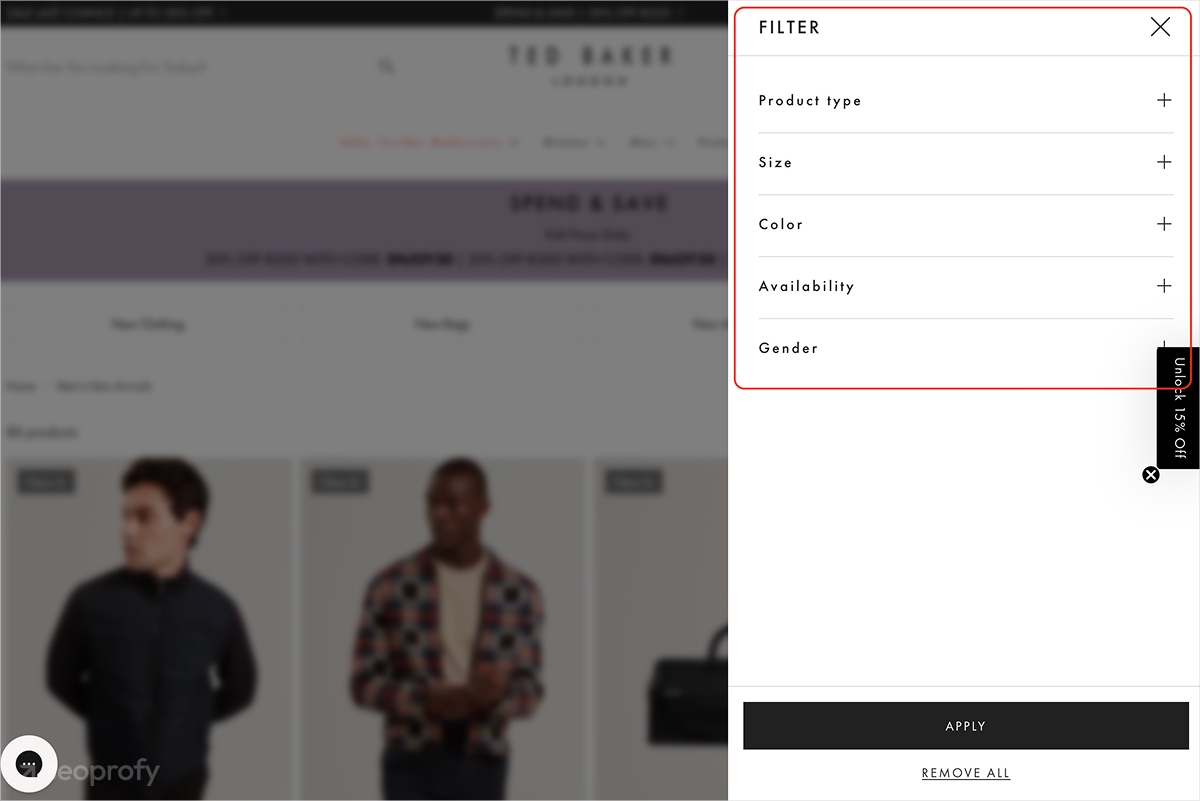
But again, while filters improve UX, they can also generate large numbers of URL variations. To keep category authority consolidated, remember to use canonical tags and noindex directives, as we’ve mentioned in the earlier sections.
Optimize Meta Tags
Titles and meta-descriptions are one of the few things you fully control, and they have a direct impact on how people click your listing in SERPs. Here’s an example of what they look like:
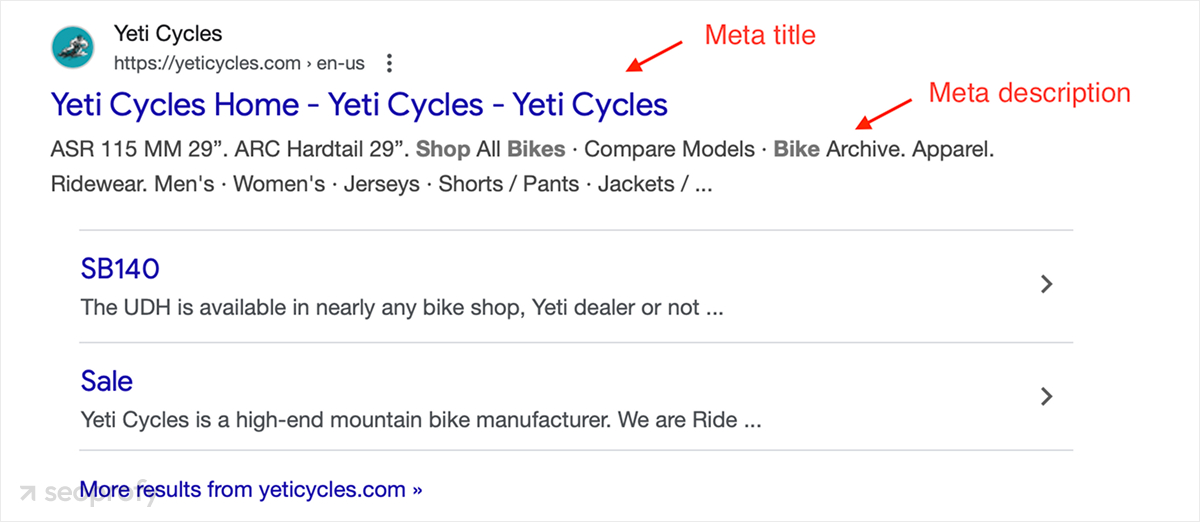
Even though BigCommerce can auto-generate page titles, they might not always be well-optimized, which is why we recommend taking the time and editing them manually. Here’s how:
- Keep title tags short (meta titles under 60 characters, meta descriptions under 160 characters)
- Place the primary keyword early in the title, ideally in the first half
- Add specific details, like key features and unique value props
- Make the description actionable and use words like shop now
One thing to keep in mind is that Google doesn’t always show the meta description you write. If another part of the page matches the query more closely, Google may use that instead.
Product Page Optimization
The next logical step of your on-page optimization efforts is your product pages. So, below we’ll look at a handful of ways to optimize them in your Big Commerce SEO campaign.
Create Detailed and Unique Descriptions
Similar to category pages, you need to include your primary and secondary keywords in the product descriptions. Additionally, add relevant details about the product and describe all the benefits and features users might be interested in. This practice works well for search engines, and Google’s AI overviews often pull details from such descriptions into their responses.
Add High-Quality Visuals
Images of your products are just as important as descriptions. They help browsers evaluate what they’re buying and reduce purchase hesitation. Try to add multiple images and, if possible, videos. Show the product from different angles, in use, and with size references where relevant, similar to how Black Diamond does it on their product pages:
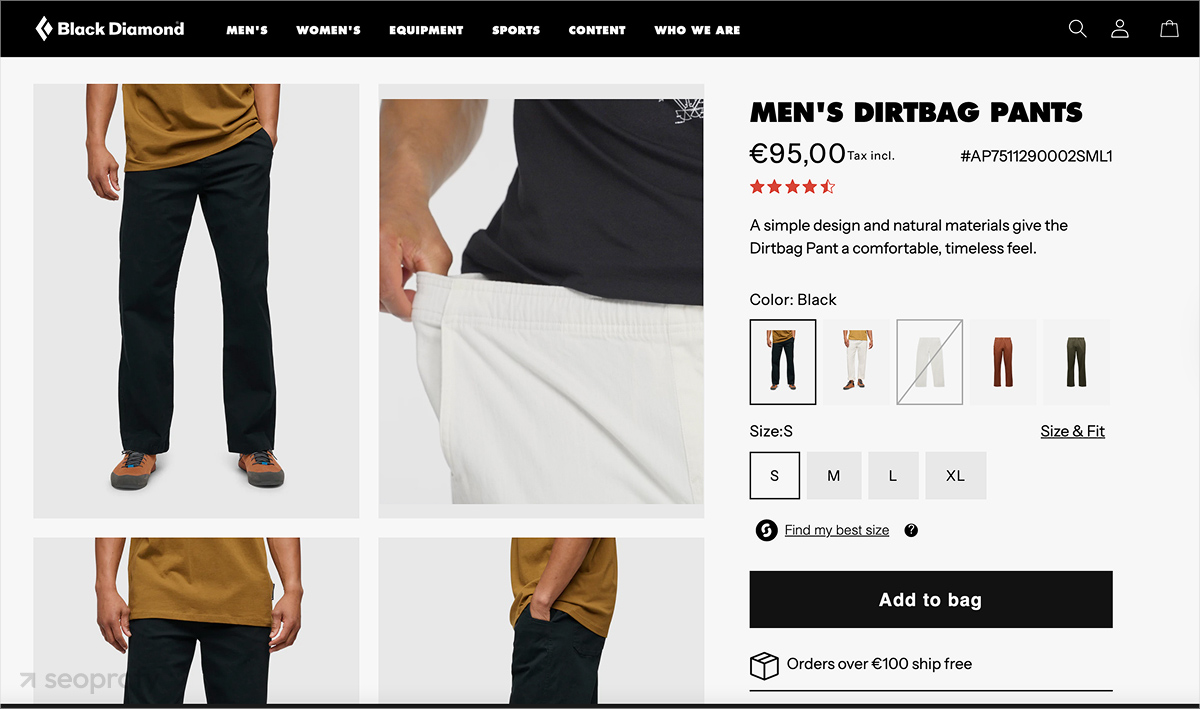
At the same time, remember to add alt text to each image. Google uses alt text to understand image content, and it also supports accessibility.
Embed Testimonials and Customer Reviews
A great and proven way to improve conversions on your pages is the so-called social proof signals, like reviews from people who already bought an item. When shoppers see that others have had a good experience, they’re much more likely to trust the product and follow through with a purchase.
Optimize Product Metadata
We’ve already shared some best practices on how to write meta titles and descriptions for category pages, but product pages have their own specifics:
- Product titles: Include brand, product type, and key attributes (size, color, model).
- Meta descriptions: Mention what makes the product distinctive and add a call-to-action.
- URL structure: Remove unnecessary parameters and use your primary keyword.
- Header tags: Match your product name and primary keyword.
Additionally, follow the same character limits mentioned earlier for optimal display in search engine results pages.
At SeoProfy, we help ecommerce brands grow organic traffic and sales through hands-on execution and data-driven tactics. Our team works directly with the platform’s limits and strengths to aid stores in getting:
- Better visibility for product and category searches
- More qualified traffic that converts into sales
- Scalable SEO systems that grow with your catalog

BigCommerce Blogging and Content Strategy
Even though the majority of organic traffic in ecommerce comes from category and product pages, blogging can still be a useful tactic in your search engine optimization efforts.
You can use it to support your commercial pages, build topical authority, and capture informational searches that could potentially lead to purchases. Let’s look at how to approach this using built-in features and external options.
Blog as an SEO Support System
BigCommerce includes native blogging functionality, though it’s fairly basic compared to dedicated content platforms. It supports standard blog posts, categories, and tags, which is enough for stores that publish occasionally. At the same time, it comes with constraints, like:
- Limited control over page layouts
- Basic taxonomy limited to simple categories and tags
- No built-in editorial workflows for scaling content
Because of this, many ecommerce teams choose a headless setup using BigCommerce with WordPress. This combination gives more flexibility around layouts, internal linking, content organization, and long-form publishing, without changing the checkout or product infrastructure.
Additionally, you can use an external CMS, though this separates your content from the main domain and requires more complex integration. Here’s how three of those options compare:
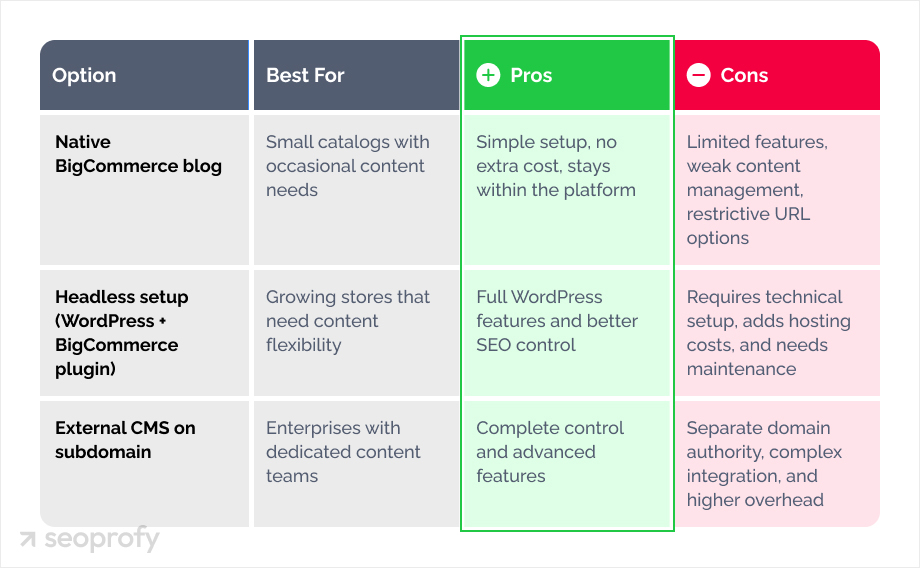
| Option | Best For | Pros | Cons |
| Native BigCommerce blog | Small catalogs with occasional content needs | Simple setup, no extra cost, stays within the platform | Limited features, weak content management, restrictive URL options |
| Headless setup (WordPress + BigCommerce plugin) | Growing stores that need content flexibility | Full WordPress features and better SEO control | Requires technical setup, adds hosting costs, and needs maintenance |
| External CMS on subdomain | Enterprises with dedicated content teams | Complete control and advanced features | Separate domain authority, complex integration, and higher overhead |
If your needs are basic, a native blog can be a good option. For more advanced content strategies, a headless WordPress setup through the BigCommerce WordPress plugin makes more sense. You get WordPress’s content capabilities while keeping your store on BigCommerce.
Content Planning and Entity Coverage
To get the most SEO benefits from your content strategy, it needs to be organized around entities and topic clusters. You can build them around three core search intent types: buyer-intent queries, informational guides, and product tutorials or comparisons.
Say you sell kitchen appliances. Your main category is “stand mixers.” A topic cluster around this might include:
- How to choose a stand mixer for different baking needs (informational)
- Stand mixer vs hand mixer comparison (commercial)
- Best stand mixer attachments and how to use them (informational + product links)
Each cluster should have one main commercial page (usually a category) and 5–20 supporting pieces that interlink horizontally and point back to that main page as the canonical “hub.” This structure builds topical authority and shows Google your site covers the subject comprehensively.
As for the content formats you can use, BigCommerce gives you several options:
- Blog posts for informational content and guides
- Landing pages for campaign-specific content or buying guides
- Category descriptions for commercial content that sits directly on product pages
The way you can approach it in SEO for BigCommerce is to design every article or guide to either establish topical breadth around your main themes or capture and nurture earlier-stage visitors so they eventually land on your core product and category URLs.
BigCommerce Schema and Structured Data
Schema markup or structured data is the code you add to your web pages to help search engines understand what your products are, so they can appear in rich snippets and carousels, and get more clicks.
BigCommerce handles most of the schema types automatically via Stencil themes, but you will need customization or apps for a full ecommerce impact, like star ratings or FAQ expansions.
Required Schema Types
There are many schema types ecommerce stores can use, so below we’ll share the ones with the most impact on your product visibility in Google search:
- Product schema tells search engines about your product name, price, availability, and SKU. BigCommerce handles this automatically, though you can extend it with additional properties like color, size, or material through template customization.
- Review schema (aggregateRating) displays star ratings and review counts in search results. BigCommerce includes basic product schema, but doesn’t add review markup by default. You’ll need apps like Yotpo or Stamped to implement this properly.
- Breadcrumb schema shows your site’s navigation path in search results and helps Google understand your site structure. BigCommerce supports this natively, though you may need to verify it’s properly implemented in your theme.
- FAQ schema triggers expandable FAQ snippets in search results. BigCommerce doesn’t include this by default. You can add it manually through custom code or use apps like Schema Plus.
- Organization schema provides information about your business, including logo, contact details, and social profiles. This needs to be added manually or through schema apps.
In the table below, you get a more succinct overview of the purpose of each in the BigCommerce SEO strategy:
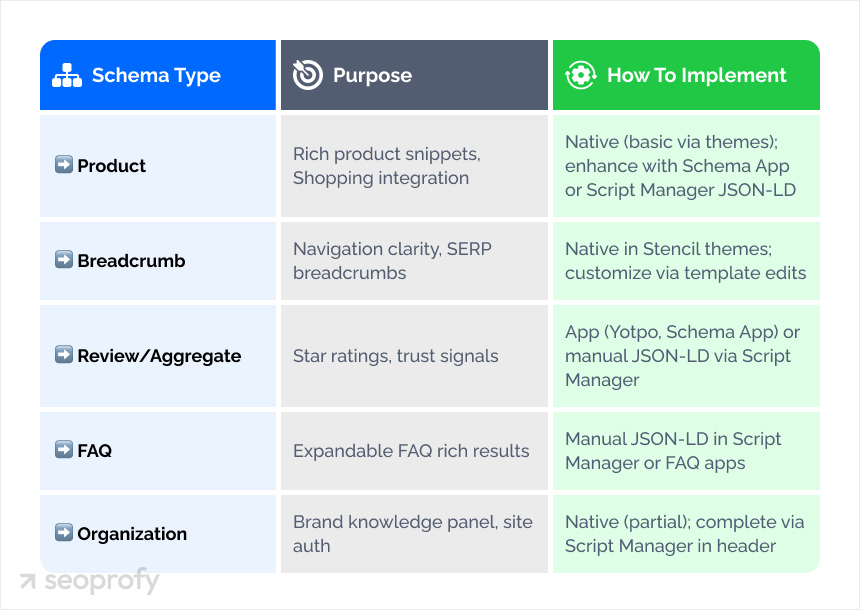
| Schema Type | Purpose | How to Implement |
| Product | Rich product snippets, Shopping integration | Native (basic via themes); enhance with Schema App or Script Manager JSON-LD |
| Breadcrumb | Navigation clarity, SERP breadcrumbs | Native in Stencil themes; customize via template edits |
| Review/Aggregate | Star ratings, trust signals | App (Yotpo, Schema App) or manual JSON-LD via Script Manager |
| FAQ | Expandable FAQ rich results | Manual JSON-LD in Script Manager or FAQ apps |
| Organization | Brand knowledge panel, site auth | Native (partial); complete via Script Manager in header |
After adding schema, test every page in Google’s Rich Results Test and monitor Google Search Console’s Enhancements report.
Core Web Vitals & Performance Optimization
Google uses a set of metrics to evaluate the experience real visitors have on your website. These metrics are grouped under Core Web Vitals and look at three main things:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): How quickly the main content on the page becomes visible.
- Interaction to Next Paint (INP): How responsive the page feels when users interact with it.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): How stable the page layout stays while content loads.
These metrics have a direct impact on your search engine rankings (even if it’s small) and also influence how long people stay and interact with your site. So, it’s a good idea to check them regularly using PageSpeed Insights.
Speed Optimization in BigCommerce
Around 88% of surveyed users say that slow loading is one of the top reasons they abandon a website, which puts speed optimization high on the priority list for online stores.
Fortunately, BigCommerce serves storefront assets through a built-in content delivery network (CDN), which helps with load times across regions. In addition to that, you can try these best practices:
- Use WebP for product and category imagery where possible, and resize images to their rendered dimensions
- Turn on lazy loading for below-the-fold images and videos so the first screen loads faster
- Minify and compress theme assets, and reduce unused CSS and JavaScript where the theme allows
In your BigCommerce search engine optimization strategy, pay most attention to your priority pages first, since faster load times on those pages directly affect how many visitors stay long enough to browse and buy.
Internal Linking Strategy for BigCommerce
Internal linking is one of the most controllable ranking levers in your SEO campaigns. You can use it to funnel link equity from high-traffic web pages to money-makers and guide users and search engine crawlers through your content ecosystem.
The simplest way to think about internal linking is to follow your store’s structure. Here’s how you can do it:
- Category pages link to relevant products and supporting content
- Product pages connect back to their main category
- Blog posts reference categories and products where they fit naturally
This tactic keeps topics grouped and creates tight clusters that signal expertise to Google around your core entities, like product types or brands. Here’s a practical example from Ted Baker:
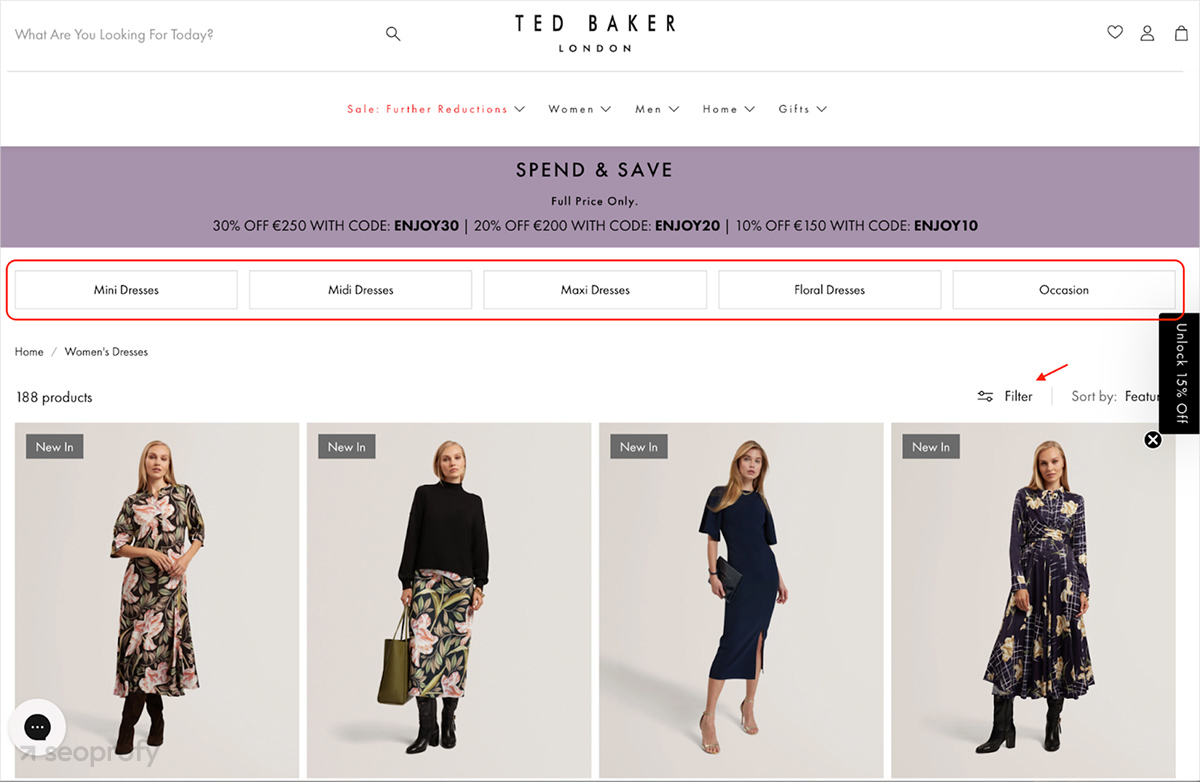
In the screenshot, the Women’s Dresses category links straight to high-value subcategories like Maxi Dresses, Mini Dresses, and Occasion. That turns the parent category into a navigation hub that passes internal equity into the collections you want to rank, while also guiding shoppers to the dress type that matches their intent.
For bigger stores, there are also automation tools that can help you speed up this process. Apps like LinkBoss or Customs APIFlow can scan your content and suggest context-based links. These usually pull from target keyword matches or topic models to connect blogs with products at scale.
However, if you decide to use such tools, always review them manually. Automation can introduce spammy anchor text or irrelevant jumps that hurt usability and, over time, create risk around over-optimization.
Off-Page SEO and Authority Building for BigCommerce Brands
High-quality backlinks have always been one of the primary indicators of authority for Google. Data also suggests that a site’s overall link authority, known as Domain Rating, has a strong connection to higher rankings.
The problem, though, is that product or category pages are harder to earn references to organically. So, below we’ll look at a few ecommerce link building strategies that work specifically for online stores.
Link Acquisition Strategy for Bigcommerce Stores
Just like in any other niche, the quality of backlinks always beats quantity. Your store will get much more SEO value if the mentions come from topically relevant and authoritative domains. Here are a handful of off-page SEO methods to get those for your store:
- Get featured in buying guides (“best [product type] 2026”)
- Write guest posts for affiliate and comparison sites
- Earn resource page links from authoritative blogs in your niche
- Partner with influencers who review products
In the eyes of search engines, such mentions of your brand or products help reinforce E‑E‑A‑T signals (experience, expertise, authoritativeness, and trust). And it’s not just a win for traditional SEO either.
AI tools like Google’s AI Overviews and ChatGPT often pull product recommendations from reviews and roundups. So, having your products mentioned, even without a backlink, can help you appear in generative answers as well.
Steer away from paid link schemes and networks that exist purely to sell those, as they can lead to penalties from Google.
Data-Driven SEO KPIs for BigCommerce Stores
The only way to tell if your SEO work is paying off is by tracking the right data. Below, you’ll find the most relevant KPIs for BigCommerce stores, along with where to track them and what each one helps you understand.
In general, SEO performance tracking should be baked into every part of your BigCommerce strategy. And as you analyze your data, always look past the rankings and traffic and pay attention to how that visibility contributed to your sales and overall revenue.
BigCommerce SEO in 2026: AI, Entities and Search Evolution
All of the tactics we shared today give you a good foundation on how to make SEO a growth lever in your digital marketing campaigns. But as we look ahead, it’s impossible to miss the massive shift ecommerce is going through because of AI.
As more people research products directly in AI interfaces, many are getting instant recommendations via product cards and purchase options. This is especially true through recent ChatGPT shopping features. Consequently, the priority is now to show up in these tools so they recommend your products and drive sales.
So what does this mean for stores, and how can your BigCommerce brand approach it? Here are the key moves:
- Add structured data to your pages: AI systems extract exact details like prices, ratings, materials, and availability to feature your catalog in summaries and shopping answers.
- Optimize for voice and multimodal search: People search conversationally in AI tools, so use natural, long-tail keywords on your pages to help match specific needs.
- Invest in digital PR: The more quality outlets reference your brand or products, the stronger your entity recognition becomes.
The stores that will win in 2026 are the ones that optimize for all the search surfaces. We’ve seen this firsthand with our clients, who are already capturing extra market share by appearing as the top-cited recommendation in AI chat responses. So, if you’re looking for BigCommerce SEO services that deliver both SEO and AEO results for growing stores, get in touch.