Magento (also known as Adobe Commerce) is a flexible and customizable platform that brands like Nike, Land Rover, and thousands more trust. As more businesses move to it, marketers and store owners need to know how to optimize for Magento SEO.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through the foundation of SEO for Magento. You’ll learn how to configure its built-in features and find out which extensions can improve your pages’ visibility, search engine rankings, and sales.
- Magento 2 lets you set page titles, meta descriptions, and headings for every product, category, and CMS page directly from the backend.
- If you don’t configure canonical tags and manage URL parameters, your site can end up with duplicate pages that compete with each other.
- Filters and sort options can generate unnecessary URLs that slow down indexing if not set up correctly, which is a common issue in Magento e-commerce SEO.
- Whenever a page link changes, a redirect should be added to ensure the old hyperlink still leads somewhere, rather than sending visitors to 404 pages.
- There’s no built-in blogging feature in Magento 2, so sites that want to draw in more relevant traffic through content need to use a third-party extension.
Magento SEO Foundation
Magento 2 lets store owners handle three major facets of ecommerce SEO — on-page, technical, and mobile. This part of the guide will walk you through how to set them up.
On-Page SEO
Your on-page elements send signals to search engines and help them understand the context of your content. They take that into account when showing your site to relevant search queries. Here’s how to configure them in Magento.
Metadata Setup in Magento
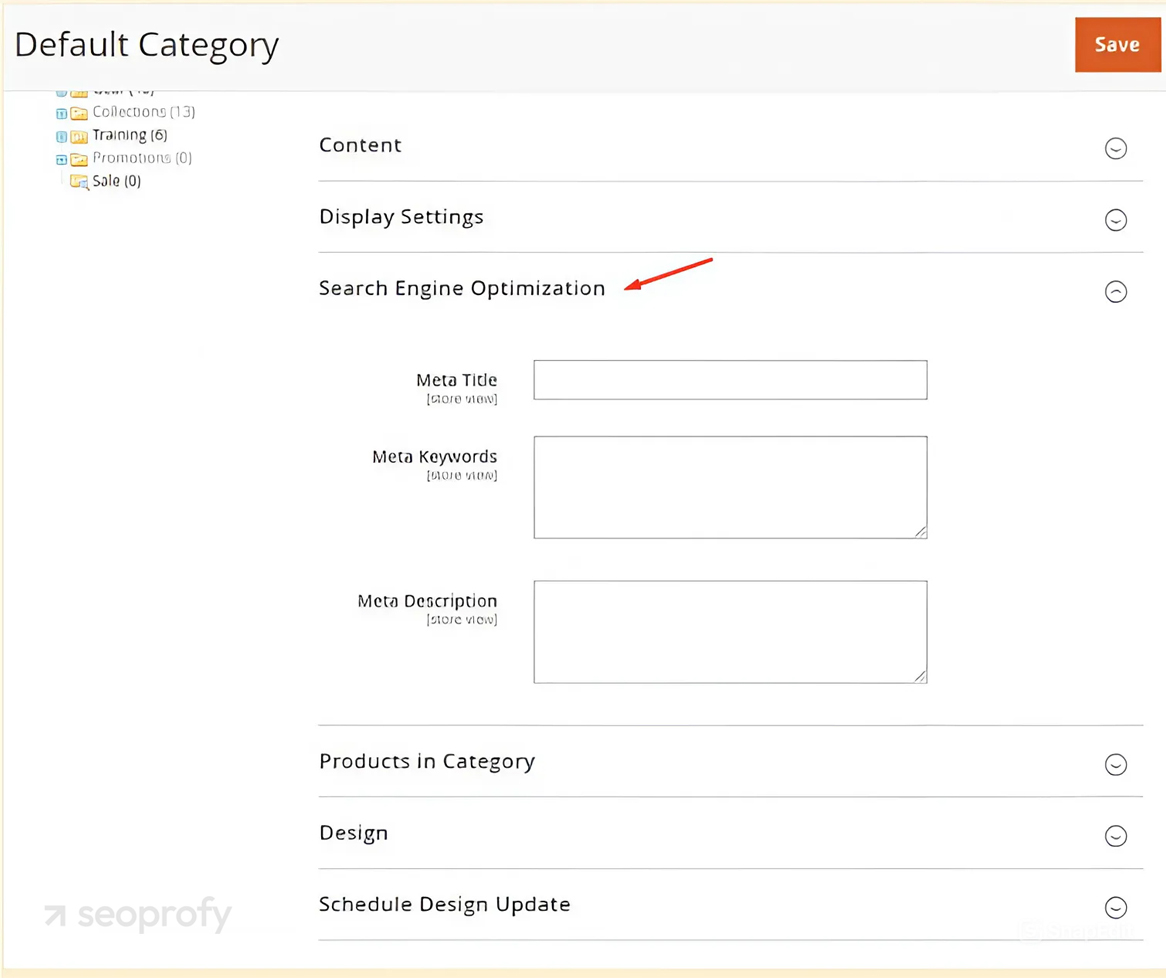
Titles and meta descriptions are shown directly in search results, so they influence both your rankings and click-through rate (CTR). In Magento, your product, category, homepage, and CMS pages each have fields for meta titles and descriptions.
You can find these under the Search Engine Optimization section in the admin panel. For product metadata, you’ll need to go to Catalog → Products, while Content Management System pages are managed through Content → Pages. If you skip them, Magento might reuse generic content or leave them blank altogether, which isn’t ideal for search, so remember to fill these out.
For smaller catalogs, you can handle this process manually. But if you’re working with hundreds or even thousands of products, you’ll need a system in place that generates your metadata with the help of placeholders.
Magento’s built-in Product Fields Auto-Generation tool supports a limited set of variables, such as {{name}}, {{description}}, and {{sku}}. To set it up, you’ll need to click on Stores → Configuration → Catalog → Product Fields Auto-Generation. This works for setting basic templates, but there are the following limits:
- Only applies to new products (not retroactive)
- Doesn’t allow targeting specific categories, stores, or languages
- Can’t use extended attributes like size, color, or brand
For more advanced control, a better option is to go with Magento SEO extensions. The best two options that you can use are:
- MageWorx SEO Suite Ultimate: Offers product, category, and filter-based templates, along with description and H1 optimization.
- Amasty SEO Meta Templates: Supports 11 template types, attribute-based rules, preview functions, and cron-based scheduling.
Run a Screaming Frog crawl to flag missing, duplicate, or overly long titles and descriptions.
Product Category Pages and Layered Navigation
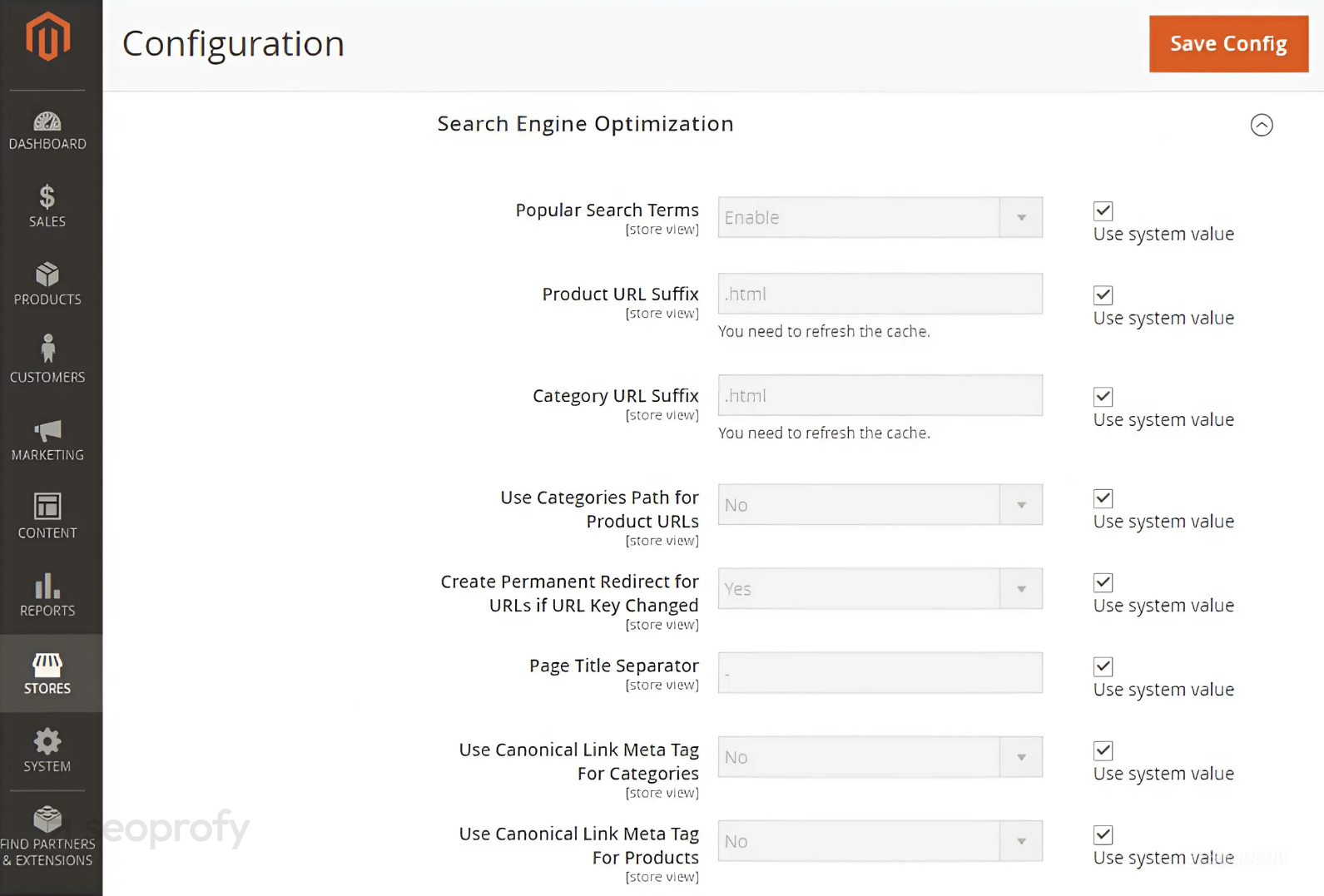
If you need more control over how product and category URLs behave, head to Stores → Configuration → Catalog → Catalog → Search Engine Optimization. This is where you’ll find all the general SEO-related settings.
You can choose whether to use category paths in product URLs, decide on URL suffixes for both products and categories, and enable or disable fields like popular search terms. Canonical tag options are also configured here, and we’ll get into those a bit later.
Headings (H1–H6)
Headings let visitors find information faster and show search engines how the page is structured. Magento is one of those ecommerce SEO platforms, where this structure depends on your theme and how content is formatted.
By default, it uses your page title as the H1. That could be your product name, a category title, or the name of a CMS page.
What happens after that (H2s, H3s, and so on) comes down to how you structure your page content. To get the most value from your headings, here are some Magento SEO best practices:
- Use only one H1 per page. It should describe the page’s main topic, and ideally include the primary keyword you’re targeting.
- Add secondary keywords to H2s and H3s where it makes sense. These can support the primary topic and help search engines better understand the depth of your content.
- Follow a logical hierarchy. Use H2s for main sections, H3s for subpoints, and only add H4 and H5 if your content needs that level of detail.
- Keep headings concise. Around 60 characters is a good general rule for readability.
- Avoid headings on global elements. Don’t use heading tags for your navigation, search bar, or calls to action that appear on every page.
- Don’t wrap images or decorative elements in heading tags. Search engines use text within headings to understand page structure, and images can muddy that signal.
Overall, your headings support your keyword strategy and improve user experience and accessibility, so it’s worth taking the time to optimize them. Once your on-page SEO is taken care of, the next step is to look at the technical aspects. Let’s get into it.
Technical SEO for Magento
In this section, we’ll review ways to optimize the technical side of your store so that it gets indexed, ranks well in Google’s SERPs, and attracts potential customers.
Create SEO-Friendly URLs
An SEO-friendly URL structure helps Google and other search engines understand your content hierarchy. It improves your user experience too, as visitors can better navigate your site.
That said, URL structure isn’t something you want to leave on default. Magento’s system gives you tools to rewrite (configure) the settings and optimize them for better SEO performance. To enable it, go to the admin panel and click on Stores → Configuration → General → Web → Search Engine Optimization.
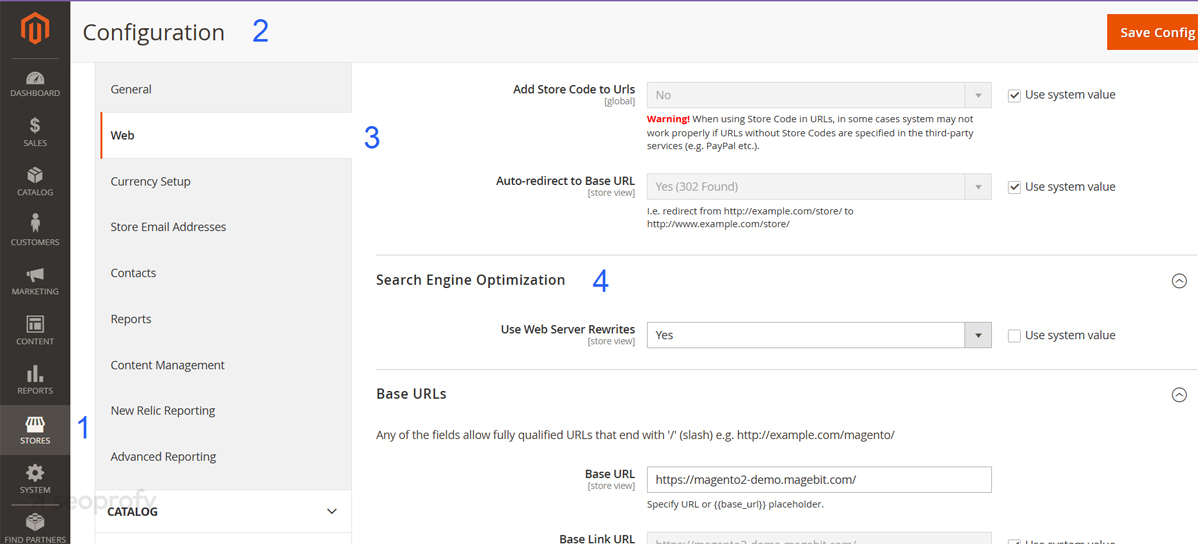
Click Yes to Use Web Server Rewrites and save the settings. You’ll also want to make sure Magento creates redirects when a product name or URL key changes. Otherwise, any update can break your internal links or send users to dead ends. In the same settings section, turn Create Permanent Redirect for URLs if the URL Key is changed to Yes.
Overall, keep your URLs concise and descriptive. As for naming, product and category URLs should reflect what visitors will find on the page. Here are some other tips to keep in mind:
- Use lowercase and hyphens (preferred by search engines)
- Add the product name in the URL to improve relevance and CTR
- Keep it readable and don’t add extra numbers
One of the stores that handles URLs well on Magento is Helly Hansen. They create simple, descriptive URLs that follow all the above-mentioned best practices. Here’s an example of their shell jackets page:
hellyhansen.com/en_global/women/jackets/shell-jacket
Lastly, if you’re working with a large catalog or doing bulk changes, it’s a good idea to use a Screaming Frog crawl or similar tool to audit your URLs and flag duplicates, chains, or broken links.
Enable Canonical URLs
Magento lets multiple URLs point to the same content. This means your products can sit in different categories, show up under filtered results, and still exist on their standalone store pages. That might seem fine, but for search engines, it creates duplicate content.
To help solve that, Magento 2 offers canonical URL support. These tags tell search engines which version of a URL should be treated as the main one. You’ll need to enable this manually by going to Stores → Configuration → Catalog → Catalog → Search Engine Optimization. Once here, change the following settings:
- Use Canonical Link Meta Tag for Categories → Yes
- Use Canonical Link Meta Tag for Products → Yes
This doesn’t rewrite or redirect anything; it simply adds a tag in the page’s <head> to point to the preferred URL. If a product appears under several paths, the canonical tag will always point to the “clean” version and will prevent you from having duplicate pages. Moreover, it helps consolidate rankings and improves indexing, as search engines spend less time on the duplicates.
In many cases, Magento 2’s built-in settings are all you need. But there are times when you’ll want more control. Maybe you need to handle canonicals differently across store views or languages. Or, maybe, you want a product’s canonical to lead somewhere entirely different, like a landing page.
For these complex rules, you’ll need to use SEO extensions. The good options are from FME and Ulmod. They offer more advanced features, such as adding canonical URLs to CMS pages, pagination, layered navigation, and cross-domain canonicalization.
Still, canonical URLs have limitations. Although they act as a reference for search engines, they don’t stop them from crawling your pages. This can lead to crawl traps, which direct us to our next section.
Fix Crawl Traps in Filtered Pages
Filters like color, size, or price are great for users. It helps them narrow down their choices. But on the technical side, it opens the door to a flood of URLs, most of which search engines don’t need to see.
In Magento, every time a shopper clicks a filter, the system adds a new parameter to the URL. The platform treats them as separate pages, and so do crawlers. Multiply that across all your categories and filters, and suddenly Google’s spending time on pages that don’t offer anything new. That’s the problem for your crawl budget.
To stop that from happening, you’ll want to change how search engine bots move through your site. One of the simplest ways to do this is through your robots.txt file. In Magento 2, you’ll find it under Content → Design → Configuration → [Your Store View] → Edit → Search Engine Robots.
Scroll down to the Edit Custom Instruction of robots.txt File field. This is where you can add crawl rules directly. To keep search engines out of filtered URLs, you can block parameter patterns like:
- Disallow: /*?color=
- Disallow: /*?size=
- Disallow: /*?price=
Still, not all of your filtered pages need to be blocked from search engine crawlers. Some filtered combinations represent actual user intent, and if they’re relevant and search-worthy, you’ll need to create subcategories. This way, search engines can still index these pages, and you get to capture long-tail search traffic.
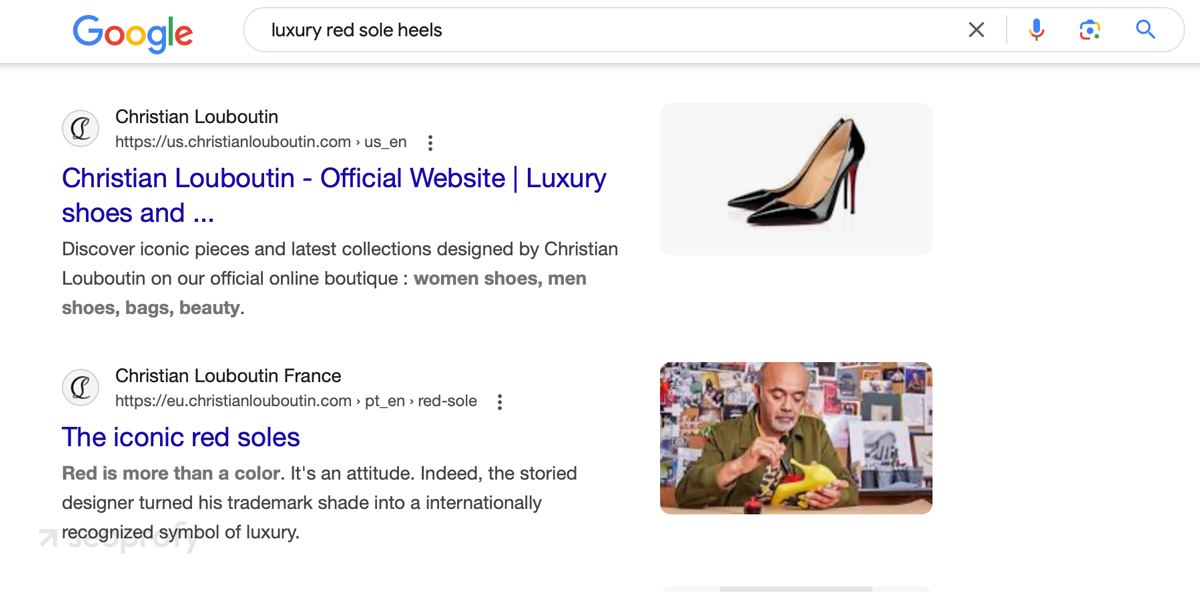
If we look at Christian Louboutin, their store uses this strategy well. They’ve built various product categories and subsets to help visitors browse through different types of shoes. So, when a user is searching for “luxury red sole heels,” as in the screenshot below, Christian Louboutin’s site ranks well for this keyword thanks to the categorization and optimization of product subsets.
Minimize Duplicate or Thin Pages Caused by Sorting
Another thing to block in your robots.txt is sorting parameters. Similar to filtering, Magento creates a new URL for every sort option, even though the content on the page doesn’t change. Over time, this leads to a buildup of thin or duplicate content.
And unlike some filtered pages that might capture long-tail traffic, sorted pages don’t have any search intent. Nobody’s searching for a product list sorted by name or price. Therefore, there’s no SEO value in keeping them indexed or shown in search engine results.
Add Structured Data for Products and Reviews
After dealing with crawl waste and duplicate pages, the next step is to give your products some extra visibility in search engine results pages. To do that, you can use structured data.
It lets you label product information in a way that Google can understand. When that’s in place, engines can show additional details of your listings in search results. In most cases, Magento stores benefit from using two types of schema:
- Product: Marks up individual product details like price, availability, and ratings.
- BreadcrumbList: Helps Google understand the structure of your site and display breadcrumb paths in search results.
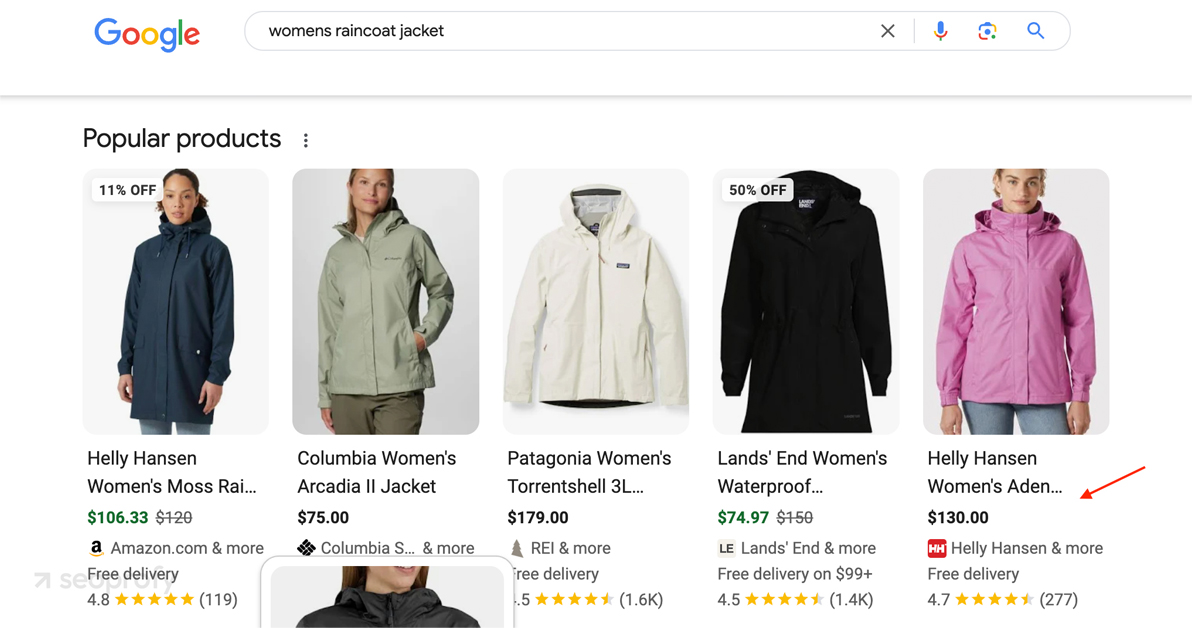
Helly Hansen is a good example of a Magento website that uses product markup. When you search for one of their items, you’ll often see the price, brand, and review score directly in the search results, just like in the screenshot below.
You can add structured data manually with the help of JSON-LD. Additionally, Magento extensions, such as Meetanshi, support schema markup for products.
Once you implement structured data, run it through Google’s Rich Results Test to see how it looks and if all information is displayed accurately.
Set Up an XML Sitemap
Now that we’ve gone through structured data, the next step is to help search engines understand which pages they should crawl. For this, you’ll need an XML sitemap.
An XML sitemap is a file that lists the pages you want search engines to find and index. That means pages that are meant to rank and hold value for search. You then submit this file in your GSC account to help bots index and, for that matter, rank your pages.
Magento 2 gives you native support to enable XML sitemaps. You can set them up under Stores → Configuration → Catalog → XML Sitemap.
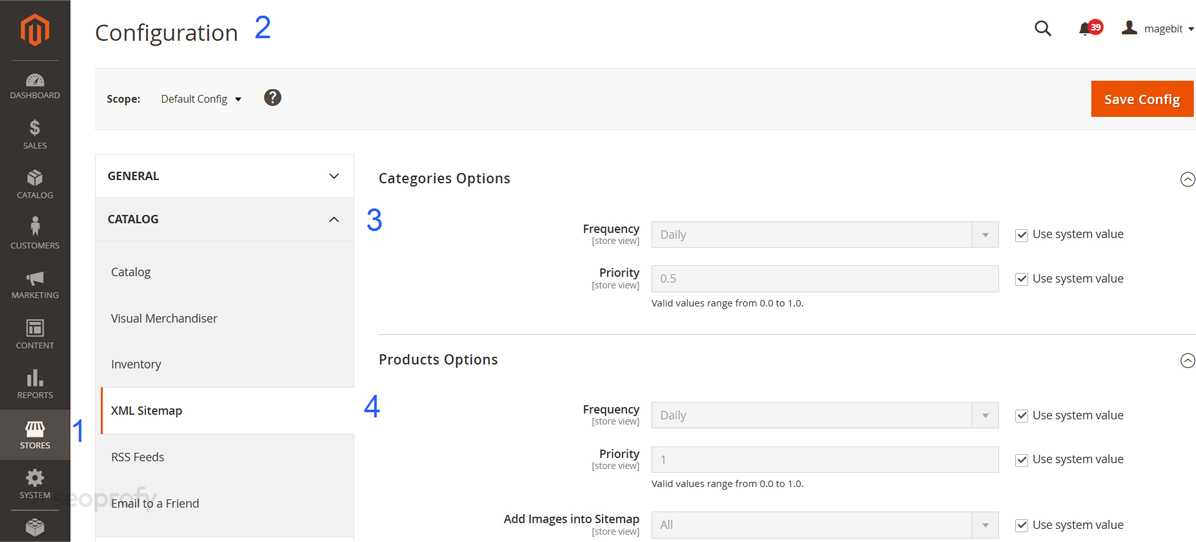
Here, you can decide whether to include product pages, categories, and CMS content. These are usually switched on by default. You’ll also see frequency and priority fields that define how often you’d like robots to crawl your pages.
Please note that Magento won’t filter out URLs set to noindex, blocked in robots.txt, or canonicalized elsewhere. If your store generates a lot of dynamic or filtered pages, it’s worth reviewing what’s being submitted.
To schedule automatic updates, scroll to Generation Settings and turn Enabled to Yes. You can choose daily or weekly updates depending on how often your content changes. Below that, in the Search Engine Submission Settings, set Enable Submission to Robots.txt to Yes. This automatically includes your sitemap URL in the robots.txt file.
Then go to Marketing → SEO & Search → Site Map. Click Add Sitemap, name the file (e.g., sitemap.xml), and enter the path. After saving, go ahead and generate the file. It should be accessible in your browser, so double-check that the URL loads without errors.
When everything looks good, submit the sitemap in Google Search Console. This lets you monitor how Google is crawling your site, which pages are being picked up, and if anything’s being missed or flagged.
Add an HTML Sitemap (Optional but Useful)
In contrast to XML sitemaps, which are made for search engines, HTML sitemaps are built for users. They offer a simple and clickable overview of your site’s structure, listing your main categories, subcategories, and sometimes product pages.
Magento 2 doesn’t include built-in HTML sitemap functionality. So, you’ll need to create it manually or use an extension. SEO plugins like Amasty’s SEO Toolkit offer this feature.
You don’t need to add every product to your sitemap. Only include your main categories or most visited pages, whatever helps people (and bots) find their way through your store.
Overall, sitemap is not a ranking factor, but it does support the crawlability of your page and user experience. For stores with hundreds or thousands of products, it’s worth having it.
An HTML sitemap helps outline your store. But it’s the internal links that hold it together. They show search engines how pages are connected and help shoppers find their way from one part of the site to another.
Create a Strategic Internal Linking Structure
Magento stores often grow fast. You add products, launch collections, change your navigation, and without internal links, your important pages can get lost. A product that isn’t linked anywhere won’t get crawled. And if no other pages — including internal search results pages — point to it, it’s almost invisible to Google. There are also other reasons why you need to interconnect your pages:
- It improves navigation for your customers
- It helps search, crawl, and index your site more effectively
- It distributes authority from high-performing pages to others
In Magento, you can use built-in tools like related products or cross-sells. Use these to create automatic links between products that complement each other.
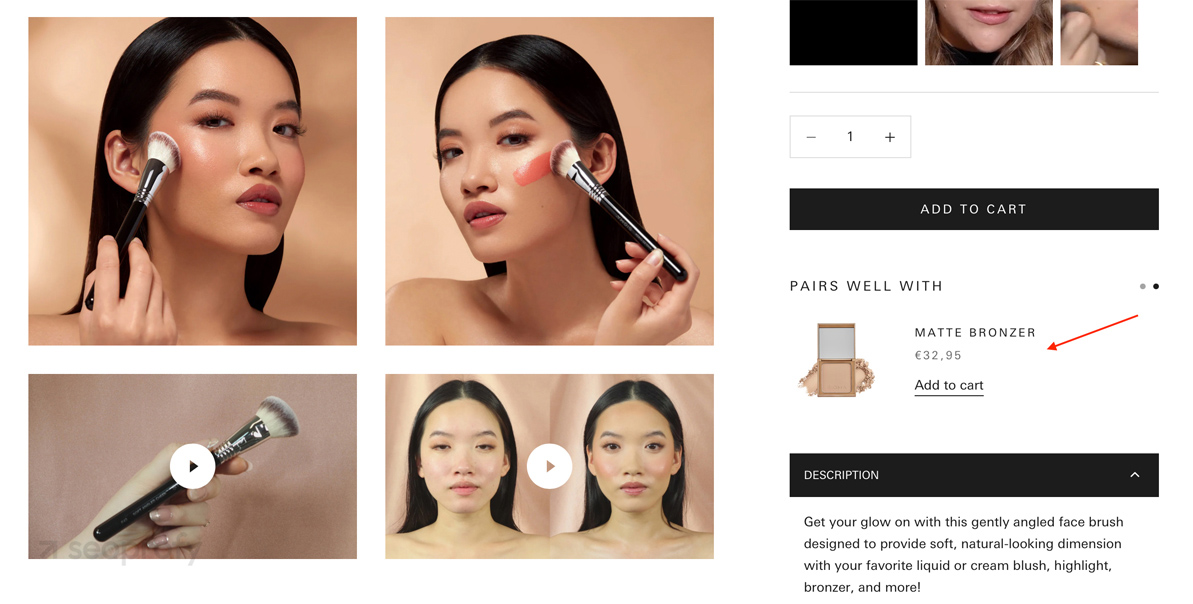
A great example of this in action is Sigma Beauty. On each product page, they include a “Pairs well with” section that links directly to a related item. It’s placed strategically next to the CTA button, so it not only helps with SEO but also gently nudges users to explore more (and buy more).
Additionally, Magento 2 offers multiple extensions, such as FME Cross Linking or the one from Amasty. These tools automate the internal linking for you. Say you have a product page for “Women’s Dresses” and a category called “Dresses.” The tool finds that keyword on the page and turns it into a link to the category — no manual edits needed.
Focus your internal linking on high-priority pages — top categories, bestsellers, or pages that drive conversions. And don’t forget to audit those links from time to time. If a product gets removed or a URL changes, you don’t want users or Google running into 404s (more on that in the next section).
Use 301 Redirects for Changed URLs
When you update a product name or category in Magento, the system changes the page link. It helps keep your URLs clean, but it also breaks the old ones.
If someone clicks that old page link, be it from Google, an email, or another site, they land on a 404. That’s not just a bad experience for your visitors. It also means fewer visits and fewer sales for your store.
Magento has a built-in setting to prevent this. When editing a product or category, turn on Create Permanent Redirect for old URL. It automatically adds a 301 redirect from the old page to the new one. You can also enable it globally under Stores → Configuration → Catalog → Search Engine Optimization.
If you’re working with a big catalog or making regular updates, this setting helps avoid broken links and saves you from doing redirects manually.
In case you need even more control, you can use Amasty SEO Toolkit. It lets you handle redirects in bulk, track errors, and also set your own rules for how URL changes are managed.
Performance and Mobile Optimization
To provide an even better user experience for your visitors, your pages need to load fast on both desktop and mobile. Since Google uses mobile-first indexing, and smartphones account for around 78% of global retail traffic, mobile should be your priority. Let’s look at how you could do that.
Improve your Core Web Vitals
Google uses Core Web Vitals to measure how fast your site loads, how stable it is, and how smooth it feels for users. These are ranking factors too, so it’s not just about UX; it also affects your SEO performance. As for Magento stores, here’s what to pay attention to:
- LCP (Largest Contentful Paint): How quickly the largest content element in the viewport loads
- CLS (Cumulative Layout Shift): How much the layout jumps around while loading
- INP (Interaction to Next Paint): How long it takes your store to respond after someone taps, clicks, or types
Big banners, uncompressed images, and third-party scripts tend to be the usual suspects here. They slow things down and push content around, especially on mobile.
To see how your store is doing, run it through PageSpeed Insights. You’ll get a performance score along with suggestions on what to improve. In addition, here are some Magento SEO tips you can follow:
- Set up full-page caching with Varnish or Redis. Go to Stores → Configuration → Advanced → System → Full Page Cache. Choose Varnish or Redis to reduce server processing and improve page delivery time.
- Enable lazy loading across your store. Magento supports it, but it may not apply to all image blocks depending on your theme. If it’s missing in your category, product, and CMS pages, fix it with the Amasty Lazy Load extension.
- Compress and resize images. Use tools like TinyPNG or convert them to WebP. Avoid oversized files and don’t rely on CSS to shrink them.
- Use a lightweight theme built for speed. Hyvä is optimized out of the box. In case you’re still using Luma, be ready to tweak the front end to reach decent performance scores.
- Remove third-party scripts you don’t use. Too many extensions or marketing tools can slow down load times. Disable what you don’t need and defer non-critical JavaScript where possible.
- Set fixed dimensions for all images and banners. Add width and height directly in the code. This keeps the layout stable while the page loads and helps avoid layout shifts.
After you’ve made changes to your site, test it with Google’s Lighthouse or GTmetrix to see if there’s a score improvement.
Why Do Most Magento Sites Struggle with SEO?
Magento 2 has a decent set of SEO tools, but that doesn’t mean it’s ready to perform in search results with the default settings. Many stores built on the platform end up with visibility issues — not because the platform lacks functionality, but because the site isn’t configured with SEO best practices in mind from the start. Below are some of the most common problems that affect Magento stores:
Duplicate Product Content
It’s common for merchants to use the default product descriptions provided by suppliers. Even though it’s efficient, this leads to thousands of pages across the web that say exactly the same thing. When search engines see that level of repetition, there’s no reason for them to rank one product page over another, so your store can get buried in search results.
Write unique product descriptions or use dynamic content fields to differentiate your pages.
Crawlability Issues Caused by Layered Navigation and Pagination
Magento’s filtering system (size, color, brand, etc.) generates a large number of URLs that display very similar content. If unmanaged, search engines waste a crawl budget going through countless versions of the same category, which adds no SEO value.
Use canonical tags, adjust robots.txt to block low-value filters, and configure noindex where appropriate.
Overuse of Parameterized URLs
URLs with parameters are everywhere in Magento setups. These versions often get indexed, even when they show nearly the same content. Over time, this bloats your index and weakens how search engines interpret the structure of your site.
Limit which parameters are crawlable, and use canonicals to point back to the main category page.
Missing Technical Configurations
Many stores launch with missing canonical URLs, no structured data, and robots.txt files that allow access to pages that shouldn’t be indexed. This lack of direction confuses crawlers and often leads to duplicate content problems or key pages being ignored.
Set up canonical URLs, add product schema, and properly configure indexing rules in your Magento admin.
Magento SEO Checklist: Tools & Extensions
We’ve already mentioned several helpful Magento SEO extensions throughout this guide. So now, we’ll summarize them and also add some extra ones that can come in handy for e-commerce sites:
- Mirasvit SEO Extension: This tool handles metadata across your store. You can set up rules to auto-generate titles and descriptions based on product info, so you don’t have to update every page by hand. It also helps with canonicals, redirects, and sitemap generation.
- BSS Commerce SEO: Similar to what the previous one does, this extension has tools for structured data, meta tag templates, and better control over layered navigation URLs.
- Amasty’s Google Rich Snippets: With this extension, you can add structured data and enable breadcrumbs, so that Google and other search engines can show more details about your products in the search results.
- HTML Sitemap: Magento has in-built functionality for XML sitemaps, but this tool also builds an HTML version that users can browse. It links out to categories and products to help your visitors and crawlers find important content.
- Lazy Load: Long pages with lots of images tend to load slowly. This extension makes images load only when they’re needed, which cuts down on the initial load time.
Content Strategy for Magento Stores
Not every e-commerce site needs a blog. For many stores, most of the search traffic lands on product or category pages, and that’s enough. You’ve probably seen dozens of stores without a single article on the site, and they do just fine.
But if you want to reach customers earlier in their decision-making process, a content strategy for ecommerce gives you a way to show up in those searches. It helps you target keywords that don’t belong on product listings and point visitors toward the right goods.
Say you’re selling makeup brushes. You might notice people searching for how to clean a foundation brush. This is a relevant query that doesn’t go on a product or category page. Instead, a short article can answer those questions and naturally link to the right items in your catalog.
That’s exactly what CeraVe does. They write helpful skincare tips for their target audience and use internal links to direct readers to relevant products that they sell.
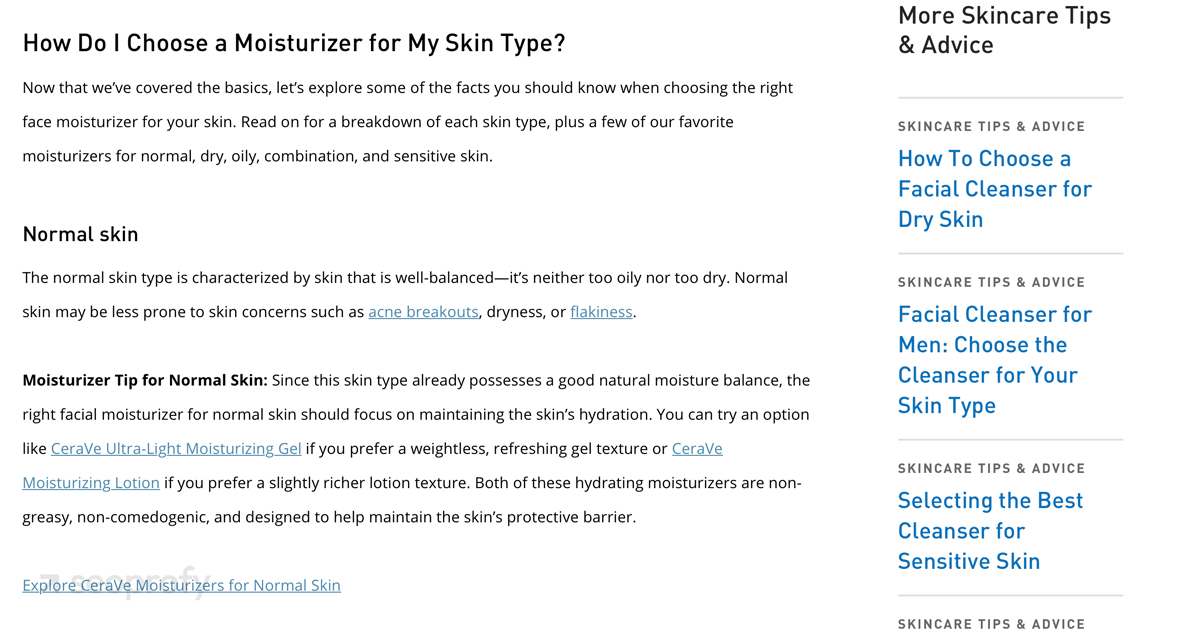
Even though Magento doesn’t include a blog feature by default, extensions like Magefan Blog, Amasty Blog Pro, and Aheadworks Blog let you manage posts directly in your Magento admin. You can set custom URLs, edit metadata, schedule articles, and link products into the content.
A blog won’t fix every SEO gap. But if your product and category pages aren’t covering all the search intents you care about, this gives you a way to expand your reach, without sending people off-site or relying on third-party publishers.
Measure Your Magento SEO Performance
After all the work you’ve put into optimizing your site and configuring all the elements, it’s important to keep track of how it’s performing in search. Not just once, but regularly.
Google Search Console is a good place to start. It’s free and shows how your site appears in search results. In its reports, you can find the following details:
- Which pages are being indexed
- What keywords are triggering impressions and clicks
- Click-through rates for main product pages
- Indexing errors or pages that dropped out of the search
- Sitemap and coverage reports to catch crawling issues
Additionally, use GA4 to track the way people are moving around your store. You can turn on event tracking for items like product views, add-to-cart, checkout starts, and purchases.
To complete the picture, take a look at Magento’s built-in reports. They won’t replace GSC or GA4, but they show product views, sales numbers, and how customers move across your catalog. It’s useful when you want to tie organic traffic to orders in your SEO strategy.
All in all, don’t wait for problems to show up in your traffic. Schedule time once a month to run a health site check and look for broken links, redirect chains, mobile issues, and slow-loading pages. Screaming Frog and PageSpeed Insights can help you catch these quickly before they impact rankings or user experience.
Future-Proof Your Magento SEO
Magento 2 SEO doesn’t end when the setup is done. Even once you’ve configured your on-page and technical SEO, it still takes time for search engines to register those changes.
You’ll likely wait a few weeks to see signs of progress. In some cases, it may take longer. That’s just how organic search works. But that doesn’t mean the work is wasted. Every improvement you make strengthens your foundation. You’re building a store that’s faster to crawl, easier to understand, and better equipped to show up for the right searches.
And if you don’t have the time or team to manage it all in-house, we’ve worked with plenty of online stores across different platforms, extensions, and custom setups. We offer SEO services for Magento and know how to build a strategy that fits your store, goals, and resources. If you ever need a hand, we’d be happy to help.